|
Dunkleosteus
''Dunkleosteus'' is an extinct genus of large armored, jawed fishes that existed during the Late Devonian period, about 382–358 million years ago. It consists of ten species, some of which are among the largest placoderms to have ever lived: ''D. terrelli'', ''D. belgicus'', ''D. denisoni'', ''D. marsaisi'', ''D. magnificus'', ''D. missouriensis'', ''D. newberryi'', ''D. amblyodoratus'', and ''D. raveri''. The largest and most well known species is ''D. terrelli'', which grew up to long and in weight. ''Dunkleosteus'' could quickly open and close its jaw, like modern-day suction feeders, and had a bite force of at the tip and at the blade edge. Numerous fossils of the various species have been found in North America, Poland, Belgium, and Morocco. Etymology ''Dunkleosteus'' was named in 1956 to honour David Dunkle (1911–1982), former curator of vertebrate paleontology at the Cleveland Museum of Natural History. The genus name ''Dunkleosteus'' combines David Dunkle's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkleosteidae
Dunkleosteidae is an extinct family of arthrodire placoderms that lived during the Devonian period. The gigantic apex predator ''Dunkleosteus terrelli'' is the best known member of this group. Phylogeny While members of Dunkleosteidae were previously thought to be close relatives of the genus '' Dinichthys'' (when they were not synonymized as each other) and grouped together in the family Dinichthyidae, more recent phylogenetic studies have shown that the two taxa represent two very distinct clades within Arthrodira. Dunkleosteidae was then established as the sister taxon to the family Panxiosteidae, which together comprised the superfamily Dunkleosteoidea (one of the three major clades of Eubrachythoraci). Dunkleosteidae was thus cladistically defined as including the type genus ''Dunkleosteus'' and all other genera in Dunkleosteoidea more closely related to ''Dunkleosteus'' than to '' Panxiosteus''. The phylogeny of Dunkleosteidae from the 2013 Zhu & Zhu study is shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinichthyidae
''Dinichthys'' (from el, δεινός , 'terrible' and el, ἰχθύς 'fish') is an extinct monospecific genus of giant, marine arthrodire placoderm from the Late Devonian ( Famennian stage), comparable in size, shape, and ecological role to the better-known '' Dunkleosteus''. Fossils were recovered from the Ohio Shale Formation along the Olentangy River in Delaware County, Ohio. Classification History ''Dinichthys'' was originally described in 1868 by John Newberry on the basis of an incomplete skull roof and mandibles ( holotype AMNH 81). Subsequently, many unrelated large arthrodires were originally classified together within this genus, including species now assigned to '' Dunkleosteus'', '' Eastmanosteus'', and '' Titanichthys''. Notably, the type species of ''Dunkleosteus'' was originally described as ''Dinichthys terrelli'' by Newberry in 1873, and was later separated into ''Dunkleosteus'' by Jean-Pierre Lehman in 1956. ''Dunkleosteus'' was still thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinichthys
''Dinichthys'' (from el, δεινός , 'terrible' and el, ἰχθύς 'fish') is an extinct monospecific genus of giant, marine arthrodire placoderm from the Late Devonian ( Famennian stage), comparable in size, shape, and ecological role to the better-known '' Dunkleosteus''. Fossils were recovered from the Ohio Shale Formation along the Olentangy River in Delaware County, Ohio. Classification History ''Dinichthys'' was originally described in 1868 by John Newberry on the basis of an incomplete skull roof and mandibles ( holotype AMNH 81). Subsequently, many unrelated large arthrodires were originally classified together within this genus, including species now assigned to '' Dunkleosteus'', '' Eastmanosteus'', and '' Titanichthys''. Notably, the type species of ''Dunkleosteus'' was originally described as ''Dinichthys terrelli'' by Newberry in 1873, and was later separated into ''Dunkleosteus'' by Jean-Pierre Lehman in 1956. ''Dunkleosteus'' was still thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastmanosteus
''Eastmanosteus'' ("Eastman's bone") is a fossil genus of dunkleosteid placoderms. It was closely related to the giant '' Dunkleosteus'', but differed from that genus in size, in possessing a distinctive tuberculated bone ornament, a differently shaped nuchal plate and a more zig-zagging course of the sutures of the skull roof.http://www.ivpp.cas.cn/cbw/gjzdwxb/xbwzxz/200812/W020090813371138329343.pdf Species of ''Eastmanosteus'' had powerful jaws with sharp cutting edges and were likely active predators. Fossils have been found in many parts of the world in marine sediments dating from the Middle to Late Devonian. They were medium-to-large fish, with specimens ''E. pustulosus'' and ''E. licharevi'' approaching a total length of 3 metres. Complete exoskeletons with soft-tissue traces of ''E. calliaspis'' from Australia make this one of the best known dunkleosteids. Phylogeny ''Eastmanosteus'' and its relative '' Dunkleosteus'' belong to the family Dunkleosteidae. The phylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Dunkle
David Hosbrook Dunkle (September 9, 1911 – January 3, 1984) was an American paleontologist. Dunkle was curator of vertebrate paleontology for the Cleveland Museum of Natural History and later associate curator for the Smithsonian Museum of Natural History. Dunkle's research and published works focused mainly on fish fossils. The genus '' Dunkleosteus'' is named in his honor. Biography Dunkle was born in Winnipeg, Manitoba, and grew up in Indiana, United States. He attended the University of Kansas and Harvard University. At Harvard, he studied under Alfred Romer and earned a PhD in 1939. Afterwards, he worked at the Cleveland Museum of Natural History (CMNH) as a curator of vertebrate paleontology. There, he studied and published papers about arthrodires from the Cleveland area. In the 1940s, he led two trips to the west to bolster the museum's collection of fossils. A notable object he collected for the museum was CMNH 7541, a dinosaur skull upon which the controv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspinothoracidi
Aspinothoracidi is a clade of placoderms, extinct armored fish most diverse during the Devonian. The gigantic apex predator '' Dinichthys'', is the best-known member of this group. Many other genera, such as the infamous '' Dunkleosteus'', were previously thought to be close relatives of ''Dinichthys'' and were grouped together in the family Dinichthyidae, though more recent studies have restricted that family to only its type species. Phylogeny Eubrachythoraci is divided into the clades Coccosteomorphi and Pachyosteomorphi, the latter of which can be further sub-divided into Aspinothoracidi and Dunkleosteoidea, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... below: References Arthrodires {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
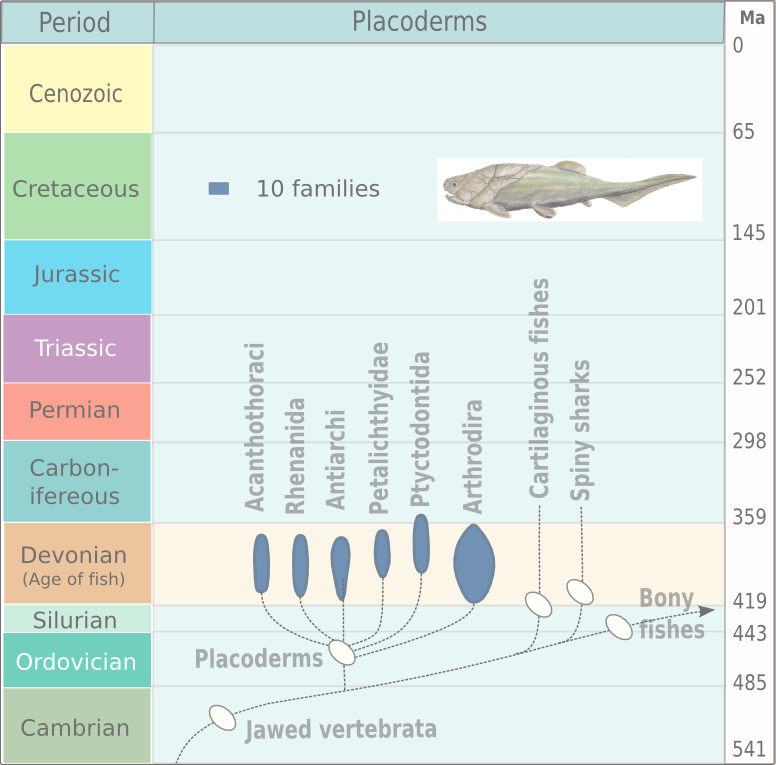
Arthrodira
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus '' Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, '' Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed '' Rolfosteus'' measured j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland Museum Of Natural History
The Cleveland Museum of Natural History is a natural history museum located approximately five miles (8 km) east of downtown Cleveland, Ohio in University Circle, a 550-acre (220 ha) concentration of educational, cultural and medical institutions. The museum was established in 1920 by Cyrus S. Eaton to perform research, education and development of collections in the fields of anthropology, archaeology, astronomy, botany, geology, paleontology, wildlife biology, and zoology. The museum traces its roots to the Ark, formed in 1836 on Cleveland's Public Square by William Case, the Academy of Natural Science formed by William Case and Jared Potter Kirtland, and the Kirtland Society of Natural History, founded in 1869 and reinvigorated in 1922 by the trustees of the Cleveland Museum of Natural History. Donald Johanson was the curator of the museum when he discovered " Lucy," the skeletal remains of the ancient hominid ''Australopithecus afarensis''. The current Curator and Head o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Strong Newberry
John Strong Newberry (December 22, 1822 – December 7, 1892) was an American physician, geologist and paleontologist. He participated as a naturalist and surgeon on three expeditions to explore and survey the western United States. During the Civil War he served in the US Sanitary Commission and was appointed secretary of the western department of the commission. After the war he became professor of geology and paleontology at Columbia University School of Mines. Biography John Strong Newberry was born in Windsor, Connecticut to Henry and Elizabeth Strong. At the age of two he moved with his family to northeastern Ohio where his father opened a coal mining business. The fossils found in the coal deposits stimulated his interest in science and a visit in 1841 with James Hall, an eminent geologist and paleontologist, furthered his interests. He graduated from Western Reserve College in 1846 and from Cleveland Medical School in 1848. That same year he married Sarah Gaylord an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |