|
Double Ranging Rook
In shogi, Double Ranging Rook (also Double Swinging Rook, Mutual Swinging Rook) (相振り飛車 ''ai-furibisha'') is a class of Ranging Rook openings in which both players choose a Ranging Rook position. The term does not apply when one player (or both) moves their rook to their respective fourth or third files (Right Fourth File Rook, Sleeve Rook) as these are still considered to be Static Rook positions. Double Ranging Rook games were relatively rare compared with Double Static Rook and Static Rook vs Ranging Rook games. However, more recently, they have gained in popularity somewhat as Fairbairn noted in the 1980s. The most often played game among professionals is Black's Opposing Rook vs White's Third File Rook. Opposing Rook vs Third File Rook 1. P-76 P-34. 2. P-66. 2...R-32. Opposing Rook's early eighth pawn advance variation 3. B-77. Opposing Rook's left silver development 3. S-78. Third File Rook's Mino castle with delayed 35 pawn push variation 3. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging Rook
Ranging Rook or Swinging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha'') openings in shogi position the rook to the center or left of the player's board to support an attack there. Ranging Rook strategies used in Ranging Rook vs Static Rook are among the oldest of shogi strategies attested in the historical documents that first describe the rules of shogi around 1600. Description Types of Ranging Rook Traditionally, Ranging Rook has been used as a defensive strategy for White against Static Rook openings played by Black. White's rook can be moved flexibly to counteract Black's attacks. These types of White openings are named simply Ranging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha''). In describing the game positions of both opponents, the term is Static Rook vs Ranging Rook (居飛車対振り飛車 ''ibisha tai furibisha''). In these games, Black has the initiative, and White quickly builds a defense by castling the king and seeks counterattacking opportunities. By default, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
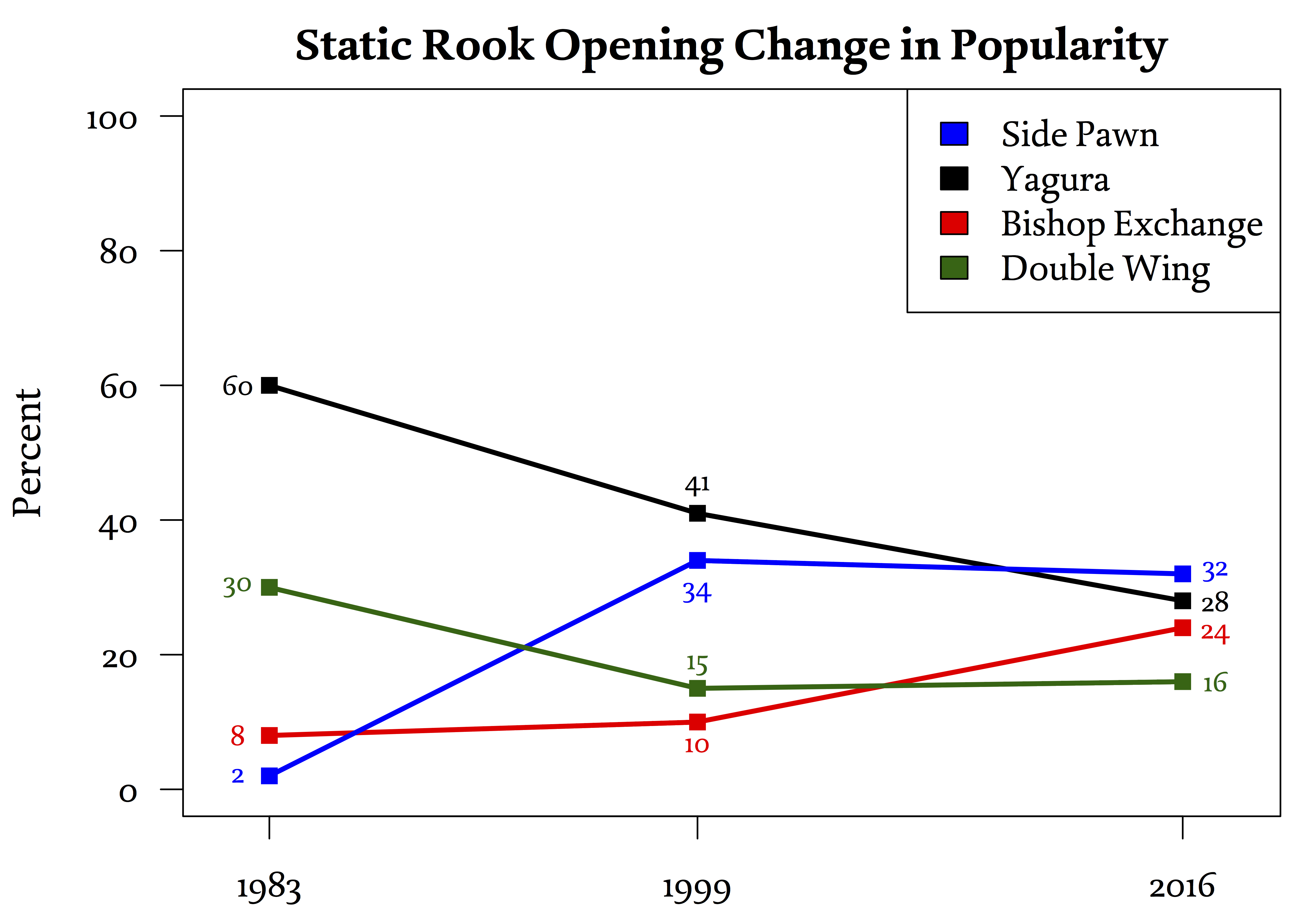
Shogi Opening
A shogi opening ( ) is the sequence of initial moves of a shogi game before the middle game. The more general Japanese term for the beginning of the game is ()''.'' A '' jōseki'' () is the especially recommended sequence of moves for a given opening that was considered balanced play at one point in time for both sides by professional players. (However, some ''s'' have become outdated when they are reevaluated to no longer give balanced play.) ''s'' also typically include commentary about the possible reasons to deviate from the especially regarding blunders. Note that not all openings have ''s''. For example, trap openings like Demon Slayer, while they may have standard moves, are considered to favor one player and are not balanced play. Thus, the Demon Slayer opening is not a jōseki. Introduction The very first opening moves in most games are pawn pushes. In particular, most games start with two types of pawn pushes. A player can move the rook pawn forward (P-26) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Fourth File Rook
In shogi, Right Fourth File Rook (右四間飛車 ''migi shikenbisha'') is a Static Rook opening in which the rook is positioned on the fourth file if played by Black or the sixth file if played by White. Typically, Right Fourth File Rook develops the right silver into a Reclining Silver attacking structure. Fortress vs Right Fourth File Rook Right Fourth File Rook vs Fourth File Rook A Right Fourth File Rook strategy may be played against a Ranging Rook position such as Fourth File Rook. In a Right Fourth File Rook vs Fourth File Rook game, each player's rook will be directly opposing each other on the fourth file supported by attacking silvers. Below shows an example of Black's Right Fourth File Rook against White's Fourth File Rook. 1. P-76 P-34, 2. P-26 P-44, 3. S-48 R-42. The first six moves are standard Static Rook vs Fourth File Rook piece development. (See: Left Silver-57 Rapid Attack vs Fourth File Rook for explication.) 4. P-46. The Right Fourth Fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleeve Rook
In shogi, Sleeve Rook (袖飛車 ''sodebisha,'' also translated as ''Right Third File Rook, Sideways Rook'' or ''Sidestepped Rook'') is a Static Rook opening in which the rook is moved to the third file if played by Black or the seventh file if played by White. Aside from being its own opening, a Sleeve Rook formation is used in some variations of several different openings. For instance, there are Sleeve Rook variations of the Double Fortress and of different Static Rook vs Ranging Rook openings. History The Sleeve Rook opening is one of the oldest shogi openings appearing around the same time as the Black's Static Rook vs White's Traditional Ranging Rook type of openings and the Wrong Diagonal Bishop (thus predating other old openings such as Fortress, etc). The adjacent diagram shows a game from 1614 between Sansa Hon'inbō (Black) and (White), the first Meijin. Hon'inbō is playing a Sleeve Rook position against Ōhashi's Static Rook. See also * Static Rook St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mino Castle
The Mino castle (美濃囲い ''minō gakoi'' or 本美濃囲い ''hon minō gakoi'') is a castle used in shogi. Mino castle is a very commonly used defensive formation that may be used within both Ranging Rook and Static Rook positions against both Ranging Rook and Static Rook opponents. The castle has several variants and may be the initial springboard for other further castle developments (such as the Silver Crown castle variants and the Right Fortress). Due to its popularity, several methods of attacking the Mino castle have been well studied. History The Mino castle was first developed for White in Lance handicap games by , the 10th Lifetime Meijin. The adjacent diagram shows the first recorded example of a Mino castle by Sōkan III in 1765. A major innovation was the adaption of Mino for use in even games by (1795–1839), who was a student of the 9th Lifetime Meijin, , and the second strongest historical player of his time as evaluated by today's standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear-in-the-hole Castle
The Bear-in-the-hole or Anaguma castle (穴熊 ''anaguma'', badger, lit. "hole-bear") is a castle used in shogi. (An anaguma is a Japanese badger.) It is commonly used in professional shogi. History The Bear-in-the-hole was initially a castle used by Ranging Rook players. In modern times, it was at first considered a poor choice for Ranging Rook. Additionally, the renaissance of Ranging Rook strategies that was happening in the first part of the 20th century was in part attributed to the strength of the Mino castle. However, a Static Rook strategy – the King's Head Vanguard Pawn – became a formidable challenge to Ranging Rook positions, as the Mino castle is weak against frontal attacks and the King's Head Vanguard Pawn strategy exploits these weaknesses by attacking the Mino from above. Therefore, a change from a Mino to a Bear-in-the-hole was considered since the Ranging Rook player's king is moved one rank further away from the vanguard pawn offense. The Bear-in- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle (shogi)
In shogi, castles ( ja, 囲い, translit=kakoi) are strong defensive configurations of pieces that protect the king ( ja, 玉). In contrast to the special castling move in western chess, shogi castles are structures that require making multiple individual moves with more than one piece. Introduction Usually the pieces involved in constructing castles are golds ( ja, 金), silvers ( ja, 銀), and pawns ( ja, 歩). Typically, they also require moving the king from its starting position – often to the left or right side of the board. The simplest castle involves two pieces and requires three moves, but it is more common to move at least three different pieces. For example, a simple Mino castle requires moving the king, the rook ( ja, 飛), a silver, and two golds for a total of six moves. Others such as the Static Rook Bear-in-the-hole castle are more complex, which requires moving the king, a pawn, the bishop ( ja, 角), a lance ( ja, 香), a silver, and two golds for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toshiaki Kubo
is a Japanese professional shogi player ranked 9-dan. He is a former Ōshō and Kiō title holder. Early life Kubo was born in Kakogawa, Hyōgo on August 27, 1975. He learned shogi when he was about four years old, and at the encouragement of a friend of his father soon began playing regularly at the Kobe Shogi Center in neighboring Kobe. The center was managed by shogi professional who became Kubo's shogi teacher after the two played a 19-piece "Naked King" handicap game. In 1986, he advanced to the semi-finals of the 11th as fifth-grade elementary school student, but lost to the eventual tournament winner and fellow future shogi professional Daisuke Suzuki. Later that same year, Kubo entered the Japan Shogi Association's apprentice school at the rank of 6-kyū under the guidance of Awaji. He was awarded professional status and the rank of 4-dan on April 1, 1993, at the age of 17. Shogi professional Kubo's first appearance in a major title match came in 2000 when he ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hisashi Namekata
is a Japanese professional shogi player ranked 9-dan. Early life Namekata was born in Hirosaki, Aomori Prefecture on December 30, 1973. As a sixth-grade elementary school student, he finished third in the 10th in 1985. After graduating elementary school in 1986, he entered the Japan Shogi Association's apprentice school at the rank of 6-kyū under the guidance of Yasuharu Ōyama as a twelve year old, and was awarded professional status and the rank of 4-dan on October 1, 1993, at the age of 19. Shogi professional In 2015, Namekata finished tied for first with Akira Watanabe, Toshiaki Kubo and Akihito Hirose in the Class A league for the right to challenge to Habu for the 73rd Meijin title. Each player finished league play with 6 wins and 3 losses, so a playoff was held to determine the challenger. A step-ladder playoff system with the player's league seed determining their playoff seed was held. Namaketa needed to only win one game to become the challenger since he was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meijin
is one of the eight titles in Japanese professional shogi, and is the most prestigious title, along with Ryūō. The word ''meijin'' (名 ''mei'' "excellent, artful", 人 ''jin'' "person") refers to a highly skilled master of a certain field (the various arts found in traditional Japanese culture, such as the Japanese tea ceremony, go, competitive karuta, rakugo, budō). History The Meijin institution started in the 17th century (Edo period), and for around 300 years (1612–1937) was a hereditary title that was passed from the reigning Meijin upon his retirement or death to another selected from three families, as deemed to be worthy. This is known as the Lifetime Meijin system (終生名人制). In 1935, however, the Japan Shogi Association, or JSA, announced that it was abolishing the existing system of succession in favor of something more short-term and reflective of actual playing strength, known as the Real Strength Meijin system (実力名人制). In 1937, the reigni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishi Press
Samuel Howard Sloan (born September 7, 1944) is an American perennial candidate and former broker-dealer. In 1978, he won a case ''pro se'' before the United States Supreme Court, becoming the last non-lawyer to argue a case in front of the court before it prohibited the practice in 2013. In 2006, Sloan served on the executive board of the United States Chess Federation. He has run unsuccessfully or attempted to run for several political offices, including President of the United States. Early life and education Sloan was born in Richmond, Virginia, and graduated from high school in 1962. He studied at the University of California, Berkeley, where he became president of the Sexual Freedom League branch before dropping out. Sloan began studying chess at age 7. In 1959, he was the youngest competitor in the National Capital Open Chess Tournament in Washington, D.C. The United States Chess Federation's database reports that he has played in 152 chess tournaments since 1991 and tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)