|
Dispersion Forces
London dispersion forces (LDF, also known as dispersion forces, London forces, instantaneous dipole–induced dipole forces, fluctuating induced dipole bonds or loosely as van der Waals forces) are a type of intermolecular force acting between atoms and molecules that are normally electrically symmetric; that is, the electrons are symmetrically distributed with respect to the nucleus. They are part of the van der Waals forces. The LDF is named after the German physicist Fritz London. They are the weakest intermolecular force. Introduction The electron distribution around an atom or molecule undergoes fluctuations in time. These fluctuations create instantaneous electric fields which are felt by other nearby atoms and molecules, which in turn adjust the spatial distribution of their own electrons. The net effect is that the fluctuations in electron positions in one atom induce a corresponding redistribution of electrons in other atoms, such that the electron motions become corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
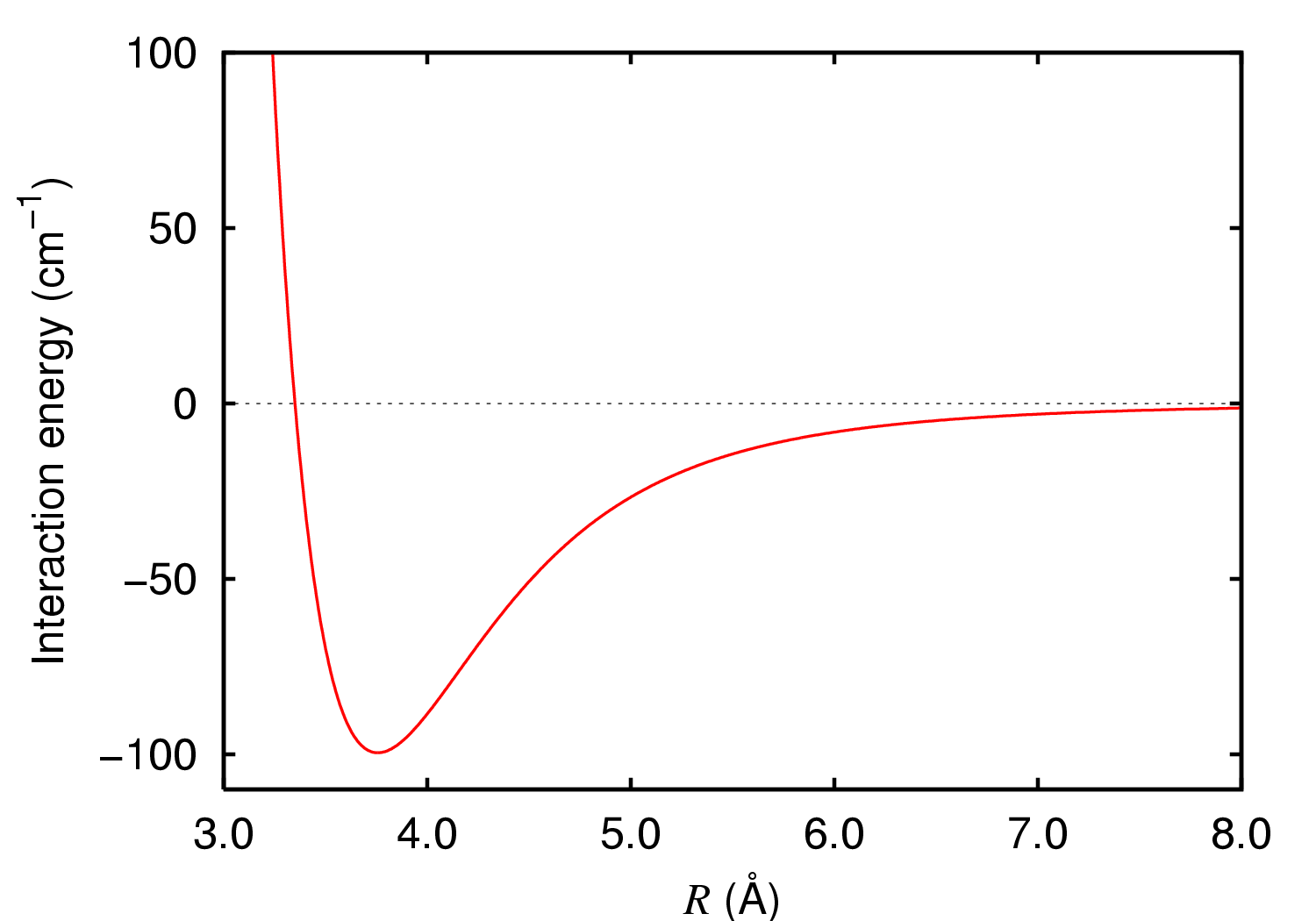
Argon Dimer Potential
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abundant as water vapor (which averages about 4000 ppmv, but varies greatly), 23 times as abundant as carbon dioxide (400 ppmv), and more than 500 times as abundant as neon (18 ppmv). Argon is the most abundant noble gas in Earth's crust, comprising 0.00015% of the crust. Nearly all of the argon in Earth's atmosphere is radiogenic argon-40, derived from the decay of potassium-40 in Earth's crust. In the universe, argon-36 is by far the most common argon isotope, as it is the most easily produced by stellar nucleosynthesis in supernovas. The name "argon" is derived from the Greek word , neuter singular form of meaning 'lazy' or 'inactive', as a reference to the fact that the element undergoes almost no chemical reactions. The complete o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |