|
Diopecephalus
''Diopecephalus'' is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Lower Tithonian (Upper Jurassic) of the Lithographic Limestone, Bavaria, Germany. The type and only species is ''D. kochi'', although the name has been applied to ''Pterodactylus longicollum'', with ''longicollum'' erroneously listed as the type species. Assigned species Like many pterosaurs, it has had a confusing taxonomic history, being given names by various authorities which identify it with four other genera: *''Pterodactylus longicollum'' (von Meyer 1854) *''Pterodactylus vulturinus'' (Wagner 1857) *''Pterodactylus longicollis'' (Wagner 1858) *''Pterodactylus suevicus'' (Fraas 1878) *''Cycnorhamphus fraasii'' (Seeley 1891) *''Pterodactylus frassi'' (Seeley 1901) *''Gallodactylus longicollum'' (Fabre 1974) *''Ornithocephalus longipes'' (Olshevsky 1978) (''Ornithocephalus'' is an obsolete name for ''Pterodactylus'') *''Ornithocephalus vulturinus'' (Olshevsky 1978) In 2017, Steven U. Vidovic and David M. Mart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactylus Antiquus
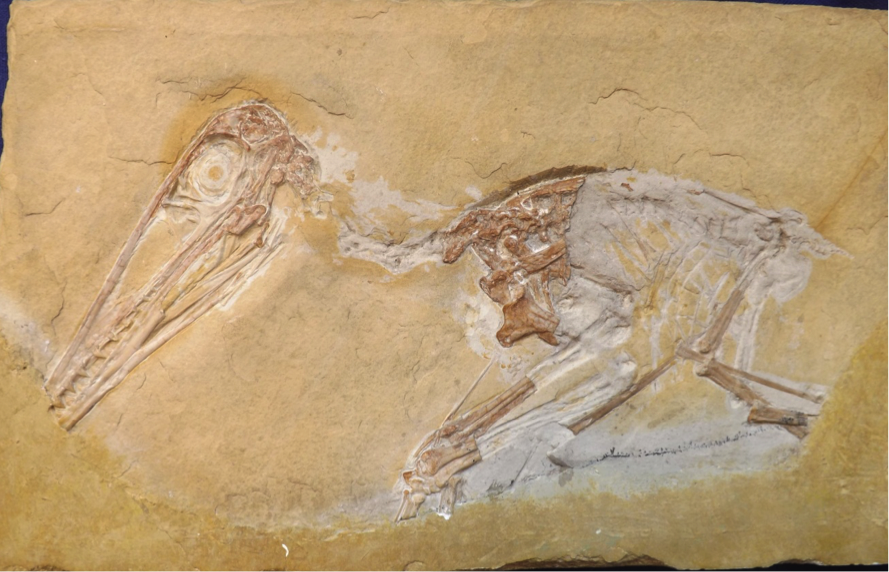
''Pterodactylus'' (from Greek () meaning 'winged finger') is an extinct genus of pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (early Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pterosaur compared to other famou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
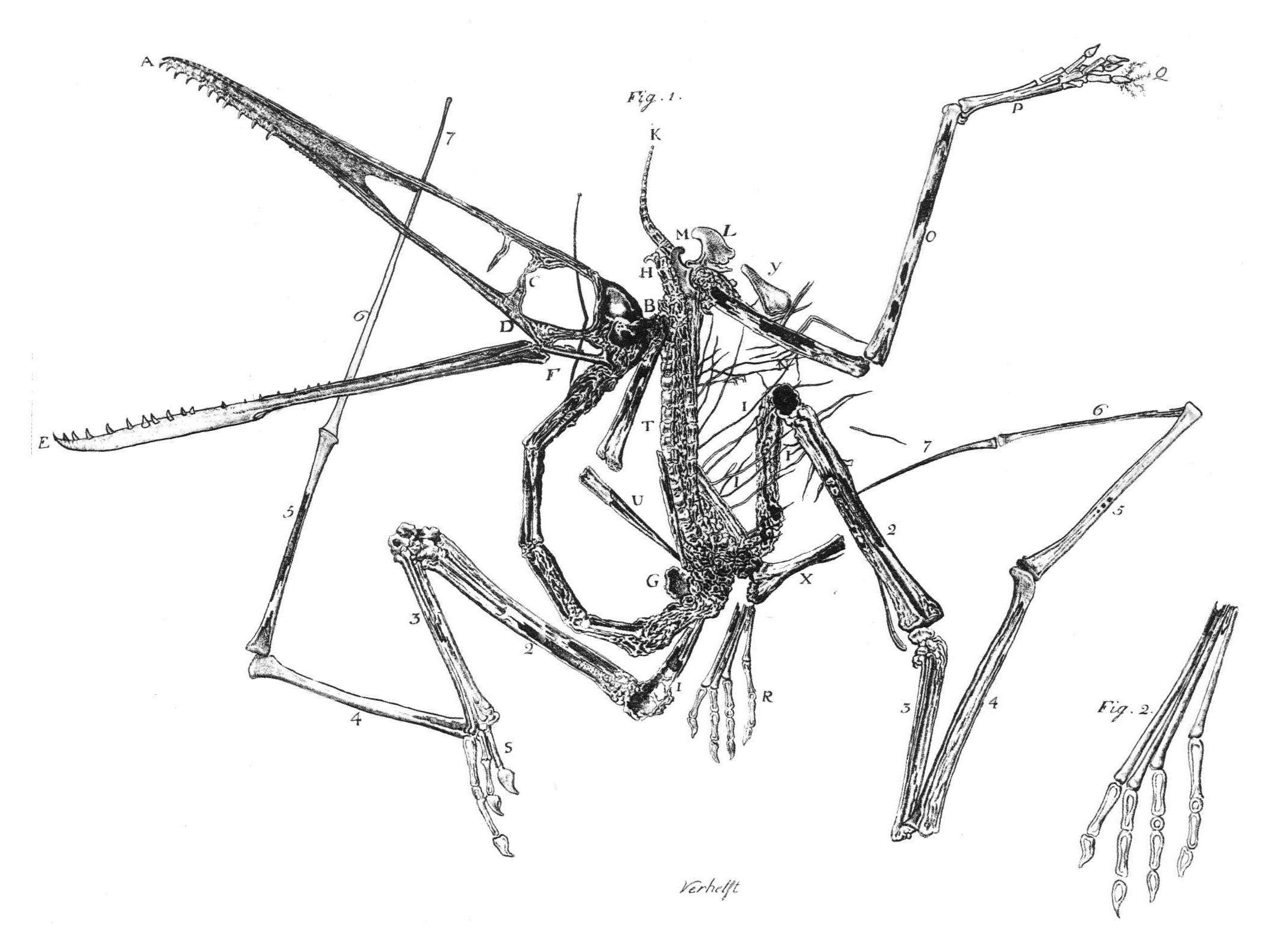
Pterodactylus
''Pterodactylus'' (from Greek () meaning 'winged finger') is an extinct genus of pterosaurs. It is thought to contain only a single species, ''Pterodactylus antiquus'', which was the first pterosaur to be named and identified as a flying reptile. Fossil remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have primarily been found in the Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, Germany, which dates from the Late Jurassic period (early Tithonian stage), about 150.8 to 148.5 million years ago. More fragmentary remains of ''Pterodactylus'' have tentatively been identified from elsewhere in Europe and in Africa. ''Pterodactylus'' was a generalist carnivore that probably fed on a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. Like all pterosaurs, ''Pterodactylus'' had wings formed by a skin and muscle membrane stretching from its elongated fourth finger to its hind limbs. It was supported internally by collagen fibres and externally by keratinous ridges. ''Pterodactylus'' was a small pterosaur compared to other famo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euctenochasmatia
Euctenochasmatia is an extinct group of pterodactyloid pterosaurs. It was named by David Unwin in 2003 as the group that contains the most recent common ancestor of ''Pterodactylus'' and ''Ctenochasma'', and all their descendants. Euctenochasmatians were specialized pterosaurs that had elongated necks as well as specialized teeth. A peculiar family within this group is the Ctenochasmatidae, which most of the members had very distinguishing teeth that were lined within their elongated snouts. A genus called ''Pterofiltrus'' only had 112 teeth, but these teeth cover about 55.8% of the total skull, and the skull itself measured about in length. Description Euctenochasmatians had very distinctive features in comparison to other pterosaurs, including the shape of their jaws, as well as their highly specialized teeth. These teeth are thought to have been used for filter-feeding, the genus ''Pterodaustro'' for example, had a long snout and its lower jaws curve strongly upwards, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenochasmatoidea
Ctenochasmatoidea is a group of early pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Their remains are usually found in what were once coastal or lake environments. They generally had long wings, long necks, and highly specialized teeth. Evolutionary history The earliest known ctenochasmatoid remains date to the Late Jurassic Kimmeridgian age. Previously, a fossil jaw recovered from the Middle Jurassic Stonesfield Slate formation in the United Kingdom, was considered the oldest known. This specimen supposedly represented a member of the family Ctenochasmatidae,Buffetaut, E. and Jeffrey, P. (2012). "A ctenochasmatid pterosaur from the Stonesfield Slate (Bathonian, Middle Jurassic) of Oxfordshire, England." ''Geological Magazine'', (advance online publication) though further examination suggested it belonged to a teleosaurid stem-crocodilian instead of a pterosaur. Ecology Most ctenochasmatoids were aquatic or semi-aquatic pterosaurs, possessing large webbed hindfeet and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardeadactylus Longicollum
''Ardeadactylus'' (from ''Ardea'' – meaning " heron", and also a name of a genus of herons – and ''dactylus'', meaning "finger") is an extinct genus of ctenochasmatoid pterosaur known from the Late Jurassic Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, southern Germany. It contains a single species, ''Ardeadactylus longicollum'', which was originally thought to be a species of ''Pterodactylus'', as ''P. longicollum''. History Only two specimens of ''Ardeadactylus'' are known to exist currently: SMNS 56603 (earlier SMNS 5802) found in 1874, a specimen from Nusplingen initially thought to belong to the species '' Pterodactylus suevicus'' (currently ''Cycnorhamphus''), and the neotype of the species, JME-SOS 2428, a specimen held at Jura Museum in Eichstätt. Other known specimens, including the holotype designated by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer when he named the type species ''Pterodactylus longicollum'' in 1854,Meyer, C.E.H. von, 1854, "Mittheilungen an Professor Bronn: Anthracot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanodactylus Cristatus
''Germanodactylus'' ("German finger") is a genus of germanodactylid pterodactyloid pterosaur from Upper Jurassic-age rocks of Germany, including the Solnhofen Limestone. Its specimens were long thought to pertain to ''Pterodactylus''. The head crest of ''Germanodactylus'' is a distinctive feature. History ''G. cristatus'' is based on specimen BSP 1892.IV.1, from the Solnhofen limestone of Eichstätt, Germany. It was originally described by Plieninger in 1901 as a specimen of ''Pterodactylus kochi'', and was given its current specific name by Carl Wiman in 1925, meaning "crested" in Latin. Yang Zhongjian determined that it deserved its own genus in 1964. A second species called ''G. ramphastinus'' (in 1858 accidentally revised to ''rhamphastinus'' by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer) was named as a distinct species long before ''G. cristatus'', described by Johann Andreas Wagner in 1851 as a species of the now deprecated genus '' Ornithocephalus''. The specific name refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeopterodactyloidea
Archaeopterodactyloidea (meaning "ancient Pterodactyloidea") is an extinct clade of pterodactyloid pterosaurs that lived from the middle Late Jurassic to the latest Early Cretaceous periods (Kimmeridgian to Albian stages) of Africa, Asia, Europe and North America. It was named by Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner in 1996 as the group that contains ''Germanodactylus'', ''Pterodactylus'', the Ctenochasmatidae and the Gallodactylidae. In 2003, Kellner defined the clade as a node-based taxon consisting of the last common ancestor of ''Pterodactylus'', ''Ctenochasma'' and ''Gallodactylus'' and all its descendants. Although phylogenetic analyses that based on David Unwin's 2003 analysis do not recover monophyletic Archaeopterodactyloidea, phylogenetic analyses that based on Kellner's analyses, or the analyses of Brian Andres (2008, 2010, 2018) recover monophyletic Archaeopterodactyloidea at the base of the Pterodactyloidea. The Antarctic Campanian specimen MN 7801-V was referred to Archa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactylus Longicollum
''Ardeadactylus'' (from ''Ardea'' – meaning " heron", and also a name of a genus of herons – and ''dactylus'', meaning "finger") is an extinct genus of ctenochasmatoid pterosaur known from the Late Jurassic Solnhofen limestone of Bavaria, southern Germany. It contains a single species, ''Ardeadactylus longicollum'', which was originally thought to be a species of ''Pterodactylus'', as ''P. longicollum''. History Only two specimens of ''Ardeadactylus'' are known to exist currently: SMNS 56603 (earlier SMNS 5802) found in 1874, a specimen from Nusplingen initially thought to belong to the species '' Pterodactylus suevicus'' (currently ''Cycnorhamphus''), and the neotype of the species, JME-SOS 2428, a specimen held at Jura Museum in Eichstätt. Other known specimens, including the holotype designated by Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer when he named the type species ''Pterodactylus longicollum'' in 1854,Meyer, C.E.H. von, 1854, "Mittheilungen an Professor Bronn: Anthracot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterodactyloidea
Pterodactyloidea (derived from the Greek words ''πτερόν'' (''pterón'', for usual ''ptéryx'') "wing", and ''δάκτυλος'' (''dáktylos'') "finger" meaning "winged finger", "wing-finger" or "finger-wing") is one of the two traditional suborders of pterosaurs ("wing lizards"), and contains the most derived members of this group of flying reptiles. They appeared during the middle Jurassic Period, and differ from the basal (though paraphyletic) rhamphorhynchoids by their short tails and long wing metacarpals (hand bones). The most advanced forms also lack teeth, and by the late Cretaceous, all known pterodactyloids were toothless. Many species had well-developed crests on the skull, a form of display taken to extremes in giant-crested forms like ''Nyctosaurus'' and ''Tupandactylus''. Pterodactyloids were the last surviving pterosaurs when the order became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous Period, together with the non-avian dinosaurs and most marine reptiles. "Pteroda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanodactylus Rhamphastinus
''Altmuehlopterus'' (meaning "Altmühl River wing") is a genus of pterosaur belonging to the Pterodactyloidea. It lived in the Late Jurassic of what is now Germany. It was formerly known as "Daitingopterus" (meaning " Daiting Wing"), a '' nomen nudum'', informally coined in 2004. Discovery and naming In 1851, Johann Andreas Wagner named a new species of ''Ornithocephalus'' (a now-obsolete name for the genus ''Pterodactylus''), ''Ornithocephalus ramphastinus''. The specific name referred to the toucan genus ''Ramphastos'', in view of the large beak-like snout of the pterosaur. In 1859/1860, Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer corrected the specific name to ''rhamphastinus''. Although this was incorrect by modern standards, the new spelling has become valid by being accepted and used by subsequent authors, under article ICZN 33.3.1. The holotype, BSP AS.I.745, was probably found at Mörnsheim near Daiting in a layer of the '' Malm Zeta 3'', dating from the Tithonian. It consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanodactylidae
Germanodactylidae is a controversial group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. It was first named by Yang Zhongjian in 1964, and given a formal phylogenetic definition in 2014 by Brian Andres, James Clark, and Xu Xing. They defined it as the least inclusive clade containing ''Germanodactylus cristatus'' and ''Normannognathus wellnhoferi'', which they considered to be close relatives at the time. However, more recent studies by the same researchers have found that these pterosaurs may be only distantly related. Studies performed in the 2000s suggested this group it contained three genera: ''Germanodactylus'', '' Normannognathus'' and ''Tendaguripterus''. Various studies have since placed these pterosaurs within the larger clades Archaeopterodactyloidea, Eupterodactyloidea, or Dsungaripteroidea, though it has also been recovered within the Ctenochasmatoidea. In several 2010s studies, the supposed "germanodactylid" species were not necessarily found to form a natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |