|
Dinitrophenol
Dinitrophenols are chemical compounds which are nitro derivatives of phenol. There are six isomers of dinitrophenol: * 2,3-Dinitrophenol * 2,4-Dinitrophenol * 2,5-Dinitrophenol * 2,6-Dinitrophenol * 3,4-Dinitrophenol * 3,5-Dinitrophenol Dinitrophenols also form the core structure of some herbicides, which are collectively referred to as dinitrophenol herbicides, including: * Dinofenate * Dinoprop * Dinosam * Dinoseb * Dinoterb Dinoterb is a chemical compound used as an herbicide. It is an uncoupler An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobact ... * DNOC * Etinofen * Medinoterb {{Authority control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,4-Dinitrophenol
2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP or simply DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2. It is a yellow, crystalline solid that has a sweet, musty odor. It sublimates, is volatile with steam, and is soluble in most organic solvents as well as aqueous alkaline solutions. When in a dry form, it is a high explosive and has an instantaneous explosion hazard. It is a precursor to other chemicals and is biochemically active, uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation from the electron transport chain in cells with mitochondria, by allowing protons to pass from the intermembrane space into the mitochondrial matrix. Oxidative phosphorylation is a highly regulated step in aerobic respiration that is inhibited, among other factors, by normal cellular levels of ATP. Uncoupling it results in chemical energy from diet and energy stores such as triglycerides being wasted as heat with minimal regulation, leading to dangerously high body temperatures that may develop into heatstroke. Its use as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
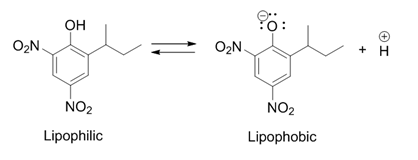
Dinoseb
Dinoseb is a common industry name for 6-sec-butyl-2,4-dinitrophenol, a herbicide in the dinitrophenol family. It is a crystalline orange solid which does not readily dissolve in water. Dinoseb is banned as an herbicide in the European Union (EU) and the United States because of its toxicity. It also finds use as a polymerisation inhibitor, where it is often referred to as DNBP. It is used to prevent the thermally induced polymerisation of styrene and other unsaturated monomers when they are being purified by distillation. History In 1892, dinitro-''ortho''-cresol (2,4-dinitro-6-methylphenol), a chemical compound closely related to dinoseb, was discovered in Germany and first used as an insecticide. It was later also used as an herbicide and also fungicide after those characteristics were discovered. In 1945 the ''ortho''-methyl group was replaced by a ''sec''-butyl group, producing dinoseb. This compound had a superior contact and stomach activity on insects and mites. Dinoseb b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitro-ortho-cresol
Dinitro-''ortho''-cresol (DNOC) is an organic compound with the structural formula CH3C6H2(NO2)2OH. It is a yellow solid that is only slightly soluble in water. DNOC and some related derivatives have been used as herbicides. Preparation This compound is prepared by disulfonation of ''o''-cresol. The resulting disulfonate is then treated with nitric acid to give DNOC. A variety of related derivatives are known including those where the methyl group is replaced by ''sec''-butyl (dinoseb), ''tert''-butyl (dinoterb), and 1-methylheptyl ( dinocap). These are prepared by the direct nitration of the alkyphenols. Applications and safety This toxicant is an uncoupler, which means that it interferes with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production. Symptoms of dinitro-''ortho''-cresol poisoning, due to ingestion or other forms of exposure, include confusion, headache, shortness of breath, and sweat Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoterb
Dinoterb is a chemical compound used as an herbicide. It is an uncoupler An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transp .... References Herbicides Dinitrophenols Tert-butyl compounds Uncoupling agents {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,3-Dinitrophenol
2,3-Dinitrophenol (2,3-DNP) is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H3(NO2)2. 2,3-Dinitrophenol is not planar due to rotation of nitro groups, and is acidic. See also * Dinitrophenol Dinitrophenols are chemical compounds which are nitro derivatives of phenol. There are six isomers of dinitrophenol: * 2,3-Dinitrophenol * 2,4-Dinitrophenol * 2,5-Dinitrophenol * 2,6-Dinitrophenol * 3,4-Dinitrophenol * 3,5-Dinitrophenol Din ... References Dinitrophenols {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitro Compound
In organic chemistry, nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups (). The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores (functional group that makes a compound explosive) used globally. The nitro group is also strongly electron-withdrawing. Because of this property, bonds alpha (adjacent) to the nitro group can be acidic. For similar reasons, the presence of nitro groups in aromatic compounds retards electrophilic aromatic substitution but facilitates nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Nitro groups are rarely found in nature. They are almost invariably produced by nitration reactions starting with nitric acid. Synthesis Preparation of aromatic nitro compounds Aromatic nitro compounds are typically synthesized by nitration. Nitration is achieved using a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, which produce the nitronium ion (), which is the electrophile: + The nitration product produced on the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |