|
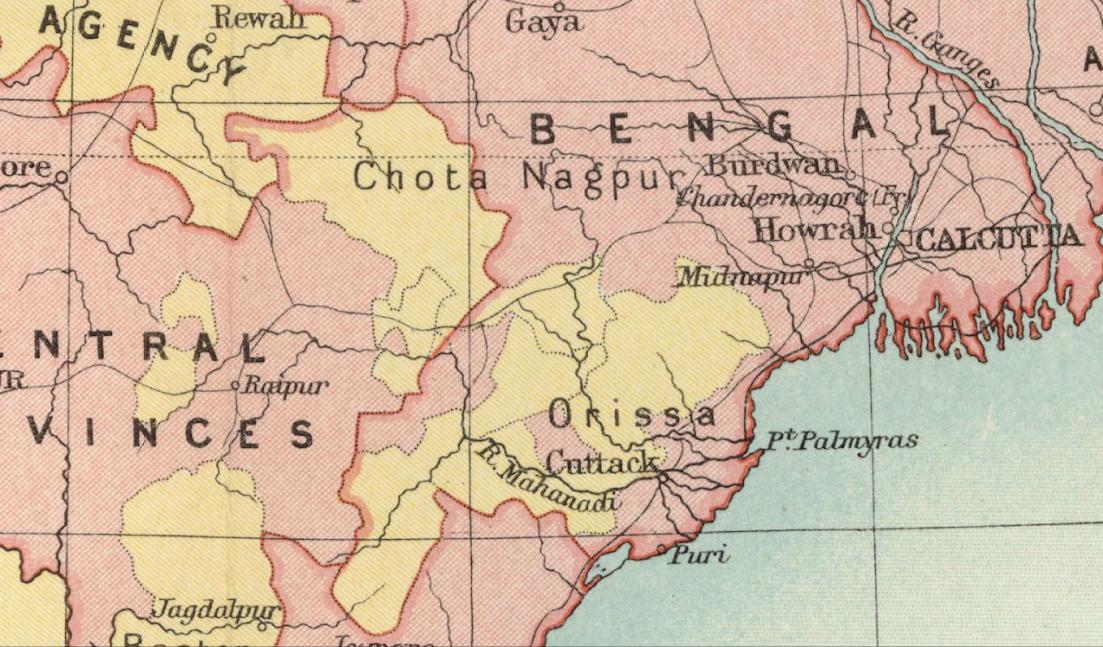
Dhenkanal (State)
Dhenkanal State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. The state is now referred to as Dhenkanal district, Odisha, with Dhenkanal town as its district headquarters. History Foundation of Dhenkanal District In 1530 CE, Dhenkanal is reported to have been a local tribal kingdom under the rule of Sabara. A campaign launched by the Harisingh Vidyadhara, commander and minister of the Gajapati Maharaja, Prataparudra Deva to bring it under the umbrage of the larger kingdom. Harisingh Vidyadhar belonged to the Bhoi dynasty, whose brother Govinda Vidyadhara would later overthrow Prataparudra Deva's successors to become the Gajapati ruler of Odisha. Dhenkanal, situated 150 km north of Puri, was conquered by the Vidyadhar using a force of cavalry and foot soldiers in a battle between the Gajapati's army and the ruling chief. Vidyadhar was then appointed by Gajapati Maharaja as the Raja of Dhenkanal and the Raja became the hereditary ruler of D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757 the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), factories (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century, three ''presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India (1757–1858), the company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested from the Rigveda, where a ' is a ruler, see for example the ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the Indian salute states (those granted a gun salute by the British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the Raja of Pindrawal * the Raja of Morni * the Raja of Rajouri * the Raja of Ali Rajpur * the Raja of Bilaspur * the Raja of Chamba * the Raja of Faridkot * the Raja of Jhabua * the Raja of Mandi * the Raja of Manipur * the Raja of Narsinghgarh * the Raja of Pudukkottai * the Raja of Rajgarh * the Raja of Sangli * the Raja of Sailana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern States Agency
The Eastern States Agency was an agency or grouping of princely states in eastern India, during the latter years of the Indian Empire. It was created in 1933, by the unification of the former Chhattisgarh States Agency and the Orissa States Agency; the agencies remained intact within the grouping. In 1936, the Bengal States Agency was added. History Since the 19th century the princely states and the tributary states of Orissa and Chhota Nagpur were not part of Bengal, but British relations with them were managed by its government through the Bengal Presidency. The Eastern States Agency was created on 1 April 1933. This agency dealt with forty-two princely states in eastern India, located in the present-day Indian states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal and Tripura. Before the creation of the Eastern States Agency in 1933, twenty-three native states of the former Orissa Tributary States and Chhota Nagpur States were under the suzerainty of the British provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamakhya Prasad Singh Deo
Brigadier Kamakhya Prasad Singh Deo AVSM (born 6 August 1941), the scion of Dhenkanal is a former Member of Parliament and a retired Indian Territorial Army officer. He was a member of the 4th, 7th, 8th, 10th, 11th and 13th Lok Sabha. He was first elected to Lok Sabha in 1967 representing Swatantra Party. Details Political career K.P. Singh Dev is the son of the late Shankar Pratap Singh Dev, the last Raja of Dhenkanal. In the 1967 Lok Sabha elections, he stood as a candidate for the Swatantra Party and was elected from the Dhenkanal constituency of Odisha. Aged 25, he was among the youngest MPs elected that year. From 1967 until 1970, he served as chief whip for the party in the Lok Sabha. By 1980, he had transferred his allegiance to the Indian National Congress. He was the president of the Orissa Pradesh Congress Committee. Military career Singh Dev was commissioned a Territorial Army second lieutenant in the Regiment of Artillery on 1 June 1971. He was awarded Ati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Empire in Asia and Africa. From the late 19th century, and especially after 1920, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, the Congress became the principal leader of the Indian independence movement. The Congress led India to independence from the United Kingdom, and significantly influenced other anti-colonial nationalist movements in the British Empire. Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, along with its main rival the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is a "big tent" party whose platform is generally considered to lie in the centre to of Indian politics. After Indian independence in 1947, Congress emerged as a catch-all and secular party, dominating Indian politics for the next 20 years. The party's first prime min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baji Rout
Baji Rout (5 October 1926 11 October 1938) ( Odia: ସହିଦ୍ ବାଜି ରାଉତ)was young Indian freedom fighter and martyr in 20th century, having been killed at the age of twelve. He was born on 5 October 1926. Rout, who was a boat boy, was shot by British police when he refused to ferry them across the Brahmani River on the night of 11 October 1938 at Nilakanthapur Ghat, Bhuban, Dhenkanal district. Baji Rout was the youngest son of a boatman on the Brahmani river. As an active member of the Banar Sena of Prajamandal (Party of People), he had volunteered to keep watch by the river at night. The British Police force ordered him to cross the river by his boat which he denied. The police force then fired upon Baji Rout along with Laxman Malik, Fagu Sahoo, Hrushi Pradhan and Nata Malik. He was born on 5 October 1926 as the youngest son of Hari Rout and Rania Devi in the village Nilakanthapur in the then state of Dhenkanal. He lost his father in his childhood. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king". A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, and Chandragupta Maurya. 'Title inflation' soon led to most being rather mediocre or even petty in real power, which led to compound titles (among other efforts) being used in an attempt to distinguish some among their ranks. The female equivalent, Maharani (or Maharanee, Mahārājñī, Maharajin), denotes either the wife of a Maharaja (or Maharana etc.) or also, in states where it was customary, a woman ruling without a husband. The widow of a Maharaja is known as a Rajmata, "queen mother". Maharajakumar generally denotes a son of a Maharaja, but more specific titulatures are often used at each court, including Yuvaraja for the heir (the crown prince). The form "Maharaj" (without "-a") indicates a separation of noble and religious o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praja Mandal
The All India States Peoples' Conference (AISPC) was a conglomeration of political movements in the princely states of the British Raj, which were variously called ''Praja Mandals'' or ''Lok Parishads''.; The first session of the organisation was held in Bombay in December 1927. The Conference looked to the Indian National Congress for support, but Congress was reluctant to provide it until 1939, when Jawaharlal Nehru became its president, serving in this position till 1946. After the Indian Independence, however, the Congress distanced itself from the movement, allying itself with the princely rulers via its national government's accession relationships. The States Peoples' Conference dissolved itself on 25 April 1948 and all its constituent units merged into the Congress, with one exception, viz., the Jammu & Kashmir National Conference. This body, under the leadership of Sheikh Abdullah remained independent, while one section of it merged with the Congress in 1965. Organisati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewan Damodar Patnaik
''Dewan'' (also known as ''diwan'', sometimes spelled ''devan'' or ''divan'') designated a powerful government official, minister, or ruler. A ''dewan'' was the head of a state institution of the same name (see Divan). Diwans belonged to the elite families in the history of Mughal and post-Mughal India and held high posts within the government. Etymology The word is Persian in origin and was loaned into Arabic. The original meaning was "bundle (of written sheets)", hence "book", especially "book of accounts," and hence "office of accounts," "custom house," "council chamber". The meaning of the word, ''divan'' "long, cushioned seat" is due to such seats having been found along the walls in Middle Eastern council chambers. It is a common surname among Sikhs in Punjab. Council The word first appears under the Caliphate of Omar I (A.D. 634–644). As the Caliphate state became more complicated, the term was extended over all the government bureaus. The ''divan of the Sublime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortured
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. Some definitions are restricted to acts carried out by the state, but others include non-state organizations. Torture has been carried out since ancient times. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, Western countries abolished the official use of torture in the judicial system, but torture continued to be used throughout the world. A variety of methods of torture are used, often in combination; the most common form of physical torture is beatings. Since the twentieth century, many torturers have preferred non-scarring or psychological methods to provide deniability. Torturers are enabled by organizations that facilitate and encourage their behavior. Most victims of torture are poor and marginalized people suspected of crimes, although torture against political prisoners or duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of extreme hardship to either themselves or members of their families. Unfree labour includes all forms of slavery, penal labour and the corresponding institutions, such as debt slavery, serfdom, corvée and labour camps. Definition Many forms of unfree labour are also covered by the term forced labour, which is defined by the International Labour Organization (ILO) as all involuntary work or service exacted under the menace of a penalty. However, under the ILO Forced Labour Convention of 1930, the term forced or compulsory labour does not include: *"any work or service exacted in virtue of compulsory military service laws for work of a purely military character;" *"any work or service which forms part of the normal civic obligations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |