|
Denys Finch Hatton
The Honourable Denys George Finch Hatton MC (24 April 1887 – 14 May 1931) was an English aristocratic big-game hunter and the lover of Baroness Karen Blixen (also known by her pen name, Isak Dinesen), a Danish noblewoman who wrote about him in her autobiographical book ''Out of Africa'', first published in 1937. In the book, his name is hyphenated: "Finch-Hatton". Early life Born in Kensington, Finch Hatton was the second son and third child of Henry Finch-Hatton, 13th Earl of Winchilsea, by his wife, the former Anne "Nan" Codrington, daughter of Admiral of the Fleet Sir Henry Codrington. He was educated at Eton and Brasenose College, Oxford. At Eton, he was Captain of the cricket Eleven, Keeper of the Field and the Wall (two major sports played at Eton), President of the Prefects Society called "Pop", and Secretary of the Music Society. Africa In 1910, after a trip to South Africa, he travelled to British East Africa and bought some land on the western side of the Great R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Honourable
''The Honourable'' (British English) or ''The Honorable'' (American English; see spelling differences) (abbreviation: ''Hon.'', ''Hon'ble'', or variations) is an honorific style that is used as a prefix before the names or titles of certain people, usually with official governmental or diplomatic positions. Use by governments International diplomacy In international diplomatic relations, representatives of foreign states are often styled as ''The Honourable''. Deputy chiefs of mission, , consuls-general and consuls are always given the style. All heads of consular posts, whether they are honorary or career postholders, are accorded the style according to the State Department of the United States. However, the style ''Excellency'' instead of ''The Honourable'' is used for ambassadors and high commissioners. Africa The Congo In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the prefix 'Honourable' or 'Hon.' is used for members of both chambers of the Parliament of the Democratic Repu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out Of Africa
''Out of Africa'' is a memoir by the Danish people, Danish author Karen Blixen. The book, first published in 1937, recounts events of the seventeen years when Blixen made her home in Kenya, then called East Africa Protectorate, British East Africa. The book is a lyrical meditation on Blixen's life on her coffee plantation, as well as a tribute to some of the people who touched her life there. It provides a vivid snapshot of African colonial life in the last decades of the British Empire. Blixen wrote the book in English language, English and then rewrote it in Danish language, Danish. The book has sometimes been published under the author's pen name, Isak Dinesen. Background Karen Blixen moved to East Africa Protectorate, British East Africa in late 1913, at the age of 28, to marry her second cousin, the Swedish people, Swedish Swedish nobility, Baron Bror von Blixen-Finecke, and make a life in the British colony known today as Kenya. The young Baron and Baroness bought farmlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); the remaining three are in the Republic of Ireland. It is the second-largest (after Munster) and second-most populous (after Leinster) of Ireland's four traditional provinces, with Belfast being its biggest city. Unlike the other provinces, Ulster has a high percentage of Protestants, making up almost half of its population. English is the main language and Ulster English the main dialect. A minority also speak Irish, and there are Gaeltachtaí (Irish-speaking regions) in southern County Londonderry, the Gaeltacht Quarter, Belfast, and in County Donegal; collectively, these three regions are home to a quarter of the total Gaeltacht population of Ireland. Ulster-Scots is also spoken. Lough Neagh, in the east, is the largest lake i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo–Irish
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the established church of Ireland until 1871, or to a lesser extent one of the English dissenting churches, such as the Methodist church, though some were Roman Catholics. They often defined themselves as simply "British", and less frequently "Anglo-Irish", "Irish" or "English". Many became eminent as administrators in the British Empire and as senior army and naval officers since Kingdom of England and Great Britain were in a real union with the Kingdom of Ireland until 1800, before politically uniting into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland) for over a century. The term is not usually applied to Presbyterians in the province of Ulster, whose ancestry is mostly Lowland Scottish, rather than English or Irish, and who are sometimes identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reginald Berkeley Cole
Captain Reginald Berkeley Cole (26 November 1882 - 27 April 1925) was a prominent Anglo-Irish aristocrat, soldier, and white settler in Kenya. He is notable as the founder of the Muthaiga Club in Nairobi. Biography Cole was born in Northwich, England, the youngest child of Viscount Cole and his wife Charlotte Baird. He was commissioned into the Royal Sussex Regiment as a second lieutenant on 23 February 1901, during the Second Boer War, and transferred to the 9th Lancers on 19 October. After the war, along with his brother Galbraith, he settled in Kenya. Their sister Florence had in 1899 married Lord Delamere, the pioneer of European settlement in Kenya. On 18th September 1914, he was promoted to the temporary rank of captain while serving in the East African Campaign of the First World War. He led an irregular unit known as Cole's Scouts, formed of Somali soldiers and soldiers from the 2nd Battalion Loyal Regiment (North Lancashire). The unit was plagued by ill-discipline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
) , national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"() , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Nairobi , coordinates = , largest_city = Nairobi , official_languages = Constitution (2009) Art. 7 ational, official and other languages"(1) The national language of the Republic is Swahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are Swahili and English. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities." , languages_type = National language , languages = Swahili , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2019 census , religion = , religion_year = 2019 census , demonym = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eldoret
Eldoret is a principal town in the Rift Valley region of Kenya and serves as the capital of Uasin Gishu County. The town was referred to by white settlers as Farm 64, 64 and colloquially by locals as 'Sisibo'. As per the 2019 Kenya Population and Housing Census, Eldoret is the fifth most populated urban area in the country after Kenya's 4 cities of Nairobi, Mombasa, Kisumu and Nakuru. Lying south of the Cherangani Hills, the local elevation varies from about at the airport to more than in nearby areas. The population was 289,380 in the 2009 Census, and it is currently the fastest growing town in Kenya with 475,716 people according to 2019 National Census. Eldoret was on course to be named Kenya's fourth city, but was edged out by Nakuru in 2021. Etymology The name "Eldoret" is based on the Maasai word "eldore" meaning "stony river"; a reference to the bed of the Sosiani River (a tributary of the Nile), that runs through the city. History Eldoret and the plateau around it h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
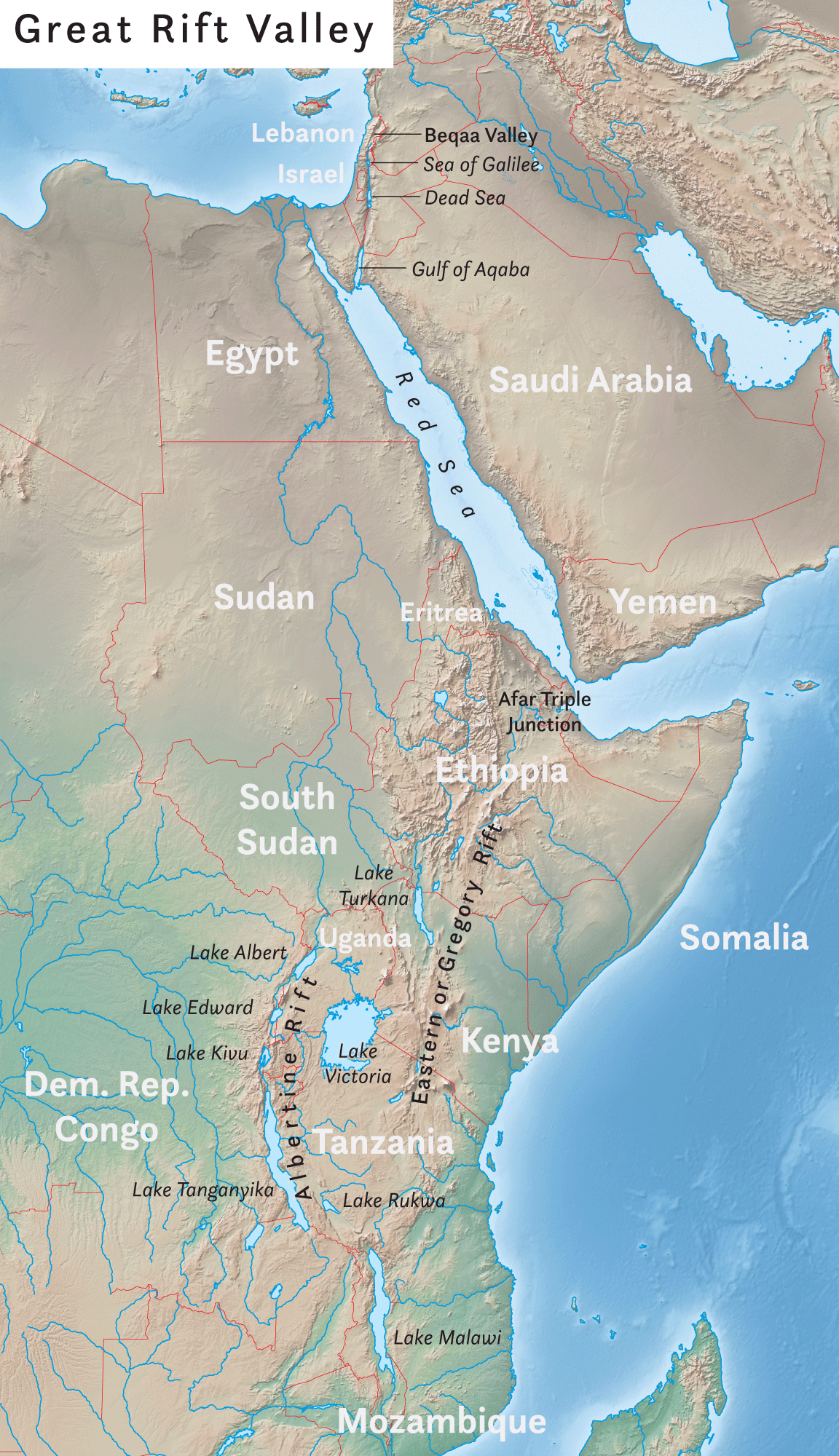
Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it is considered an imprecise merging of separate though related rift and fault systems. This valley extends northward for 5,950 km through the eastern part of Africa, through the Red Sea, and into Western Asia. Several deep, elongated lakes, called ribbon lakes, exist on the floor of this rift valley: Lakes Malawi, Rudolf and Tanganyika are examples of such lakes. The region has a unique ecosystem and contains a number of Africa's wildlife parks. The term Great Rift Valley is most often used to refer to the valley of the East African Rift, the divergent plate boundary which extends from the Afar Triple Junction southward through eastern Africa, and is in the process of splitting the African Plate into two new and separate plates. Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British East Africa
East Africa Protectorate (also known as British East Africa) was an area in the African Great Lakes occupying roughly the same terrain as present-day Kenya from the Indian Ocean inland to the border with Uganda in the west. Controlled by Britain in the late 19th century, it grew out of British commercial interests in the area in the 1880s and remained a protectorate until 1920 when it became the Colony of Kenya, save for an independent coastal strip that became the Kenya Protectorate.Kenya Protectorate Order in Council, 1920 S.R.O. 1920 No. 2343, S.R.O. & S.I. Rev. VIII, 258, State Pp., Vol. 87 p. 968 Administration European missionaries began settling in the area from Mombasa to Mount Kilimanjaro in the 1840s, nominally under the protection of the Sultanate of Zanzibar. In 1886, the British government encouraged William Mackinnon, who already had an agreement with the Sultan and whose shipping company traded extensively in the African Great Lakes, to establish British inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris - Bonhams 2013 - De Havilland DH
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelligenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nairobi KarenBlixenMuseum 2
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper had a population of 4,397,073 in the 2019 census, while the metropolitan area has a projected population in 2022 of 10.8 million. The city is commonly referred to as the Green City in the Sun. Nairobi was founded in 1899 by colonial authorities in British East Africa, as a rail depot on the Uganda - Kenya Railway.Roger S. Greenway, Timothy M. Monsma, ''Cities: missions' new frontier'', (Baker Book House: 1989), p.163. The town quickly grew to replace Mombasa as the capital of Kenya in 1907. After independence in 1963, Nairobi became the capital of the Republic of Kenya. During Kenya's colonial period, the city became a centre for the colony's coffee, tea and sisal industry. The city lies in the south central part of Kenya, at an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eton Wall Game
The Eton wall game is a game that originated at and is still played at Eton College. It is played on a strip of ground 5 metres wide and 110 metres long ("The Furrow") next to a slightly curved brick wall ("The Wall") erected in 1717. It is one of two codes of football played at Eton, the other being the Eton field game. The traditional and most important match of the year is played on Saint Andrew's Day, as the Collegers (King's Scholars) take on the Oppidans (the rest of the school). Although College has only 70 boys to pick from, compared to the 1250 or so Oppidans, the Collegers have one distinct advantage: access to the field on which the wall game is played is controlled by a Colleger. Despite this, it is usual for them to allow the Oppidans to use it whenever they wish. At the annual St Andrew's Day match, the Oppidans climb over the wall, after throwing their caps over in defiance of the Scholars, while the Collegers march down from the far end of College Field, arm-in- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |