|
Death's-head Hawkmoth
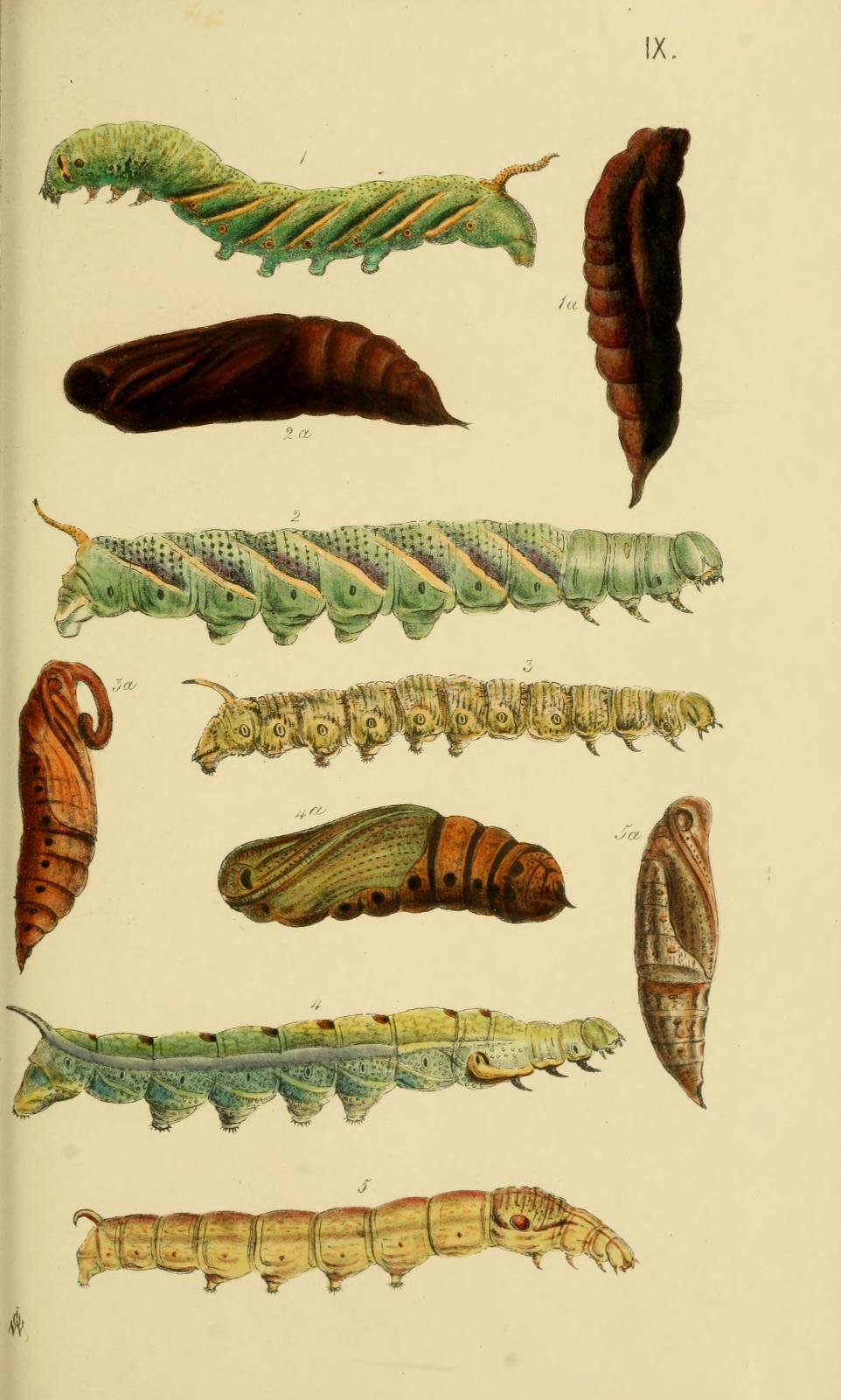
The name death's-head hawkmoth refers to any of three moth species of the genus ''Acherontia'' (''Acherontia atropos'', ''Acherontia styx'' and ''Acherontia lachesis''). The former species is found in Europe and throughout Africa, the latter two are Asian; most uses of the common name refer to the European species. These moths are easily distinguishable by the vaguely human skull-shaped pattern of markings on the thorax. They are large nocturnal moths with brown and yellow or orange coloring, and all three species are fairly similar in size, coloration and life cycle. Description The African death's-head hawkmoth (''Acherontia atropos'') is the largest moth in the British Isles, with a wingspan of ; it is a powerful flier, having sometimes been found on ships far from land. The forewings are a mottled dark brown and pale brown, and the hind wings are orangey-buff with two narrow dark bands parallel with the hind margin. The abdomen is a similar orangey-brown, with a broad, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acherontia Lachesis
''Acherontia lachesis'', the greater death's head hawkmoth or bee robber, is a large (up to 13 cm wingspan) Sphingidae, sphingid moth found in India, Sri Lanka and much of the Oriental region. It is one of the three species of death's-head hawkmoth genus, ''Acherontia''. The species was Species description, first described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1798. It is nocturnal and very fond of honey; they can mimic the scent of honey bees so that they can enter a hive unharmed to get honey. Their tongue, which is stout and very strong, enables them to pierce the wax cells and suck the honey out. This species occurs throughout almost the entire Oriental region, from India, Pakistan and Nepal to the Philippines, and from southern Japan and the southern Russian Far East to Indonesia, where it attacks colonies of several different honey bee species. It has recently become established on the Hawaiian Islands. Description ''A. lachesis'' is much larger than ''Acherontia styx''. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
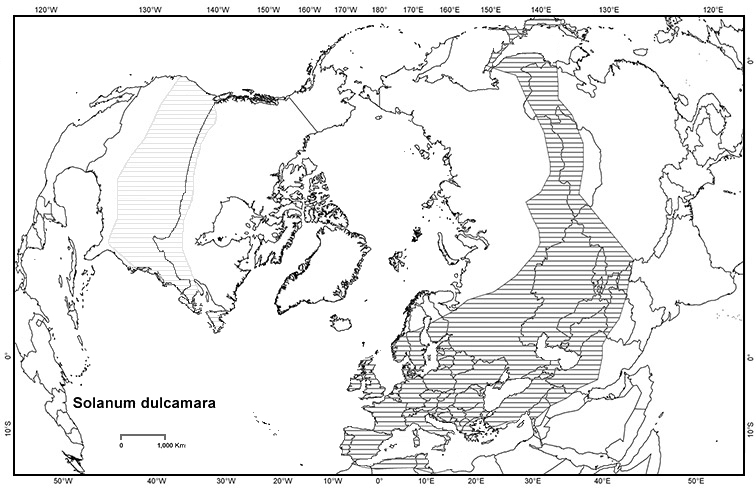
Solanum Dulcamara
''Solanum dulcamara'' is a species of vine in the genus '' Solanum'' (which also includes the potato and the tomato) of the family Solanaceae. Common names include bittersweet, bittersweet nightshade, bitter nightshade, blue bindweed, Amara Dulcis, climbing nightshade, felonwort, fellenwort, felonwood, poisonberry, poisonflower, scarlet berry, snakeberry, trailing bittersweet, trailing nightshade, violet bloom, and woody nightshade. It is native to Europe and Asia, and widely naturalised elsewhere, including North America. Overview It occurs in a very wide range of habitats, from woodlands to scrubland, hedges and marshes. ''Solanum dulcamara'' is a very woody herbaceous perennial vine, which scrambles over other plants, capable of reaching a height of 4 m where suitable support is available, but more often 1–2 m high. The leaves are 4–12 cm long, roughly arrowhead-shaped, and often lobed at the base. The flowers are in loose clusters of 3–20, 1–1.5 cm acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver (such as a predator) perceives the similarity between a mimic (the organism that has a resemblance) and a model (the organism it resembles) and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Honey Bee
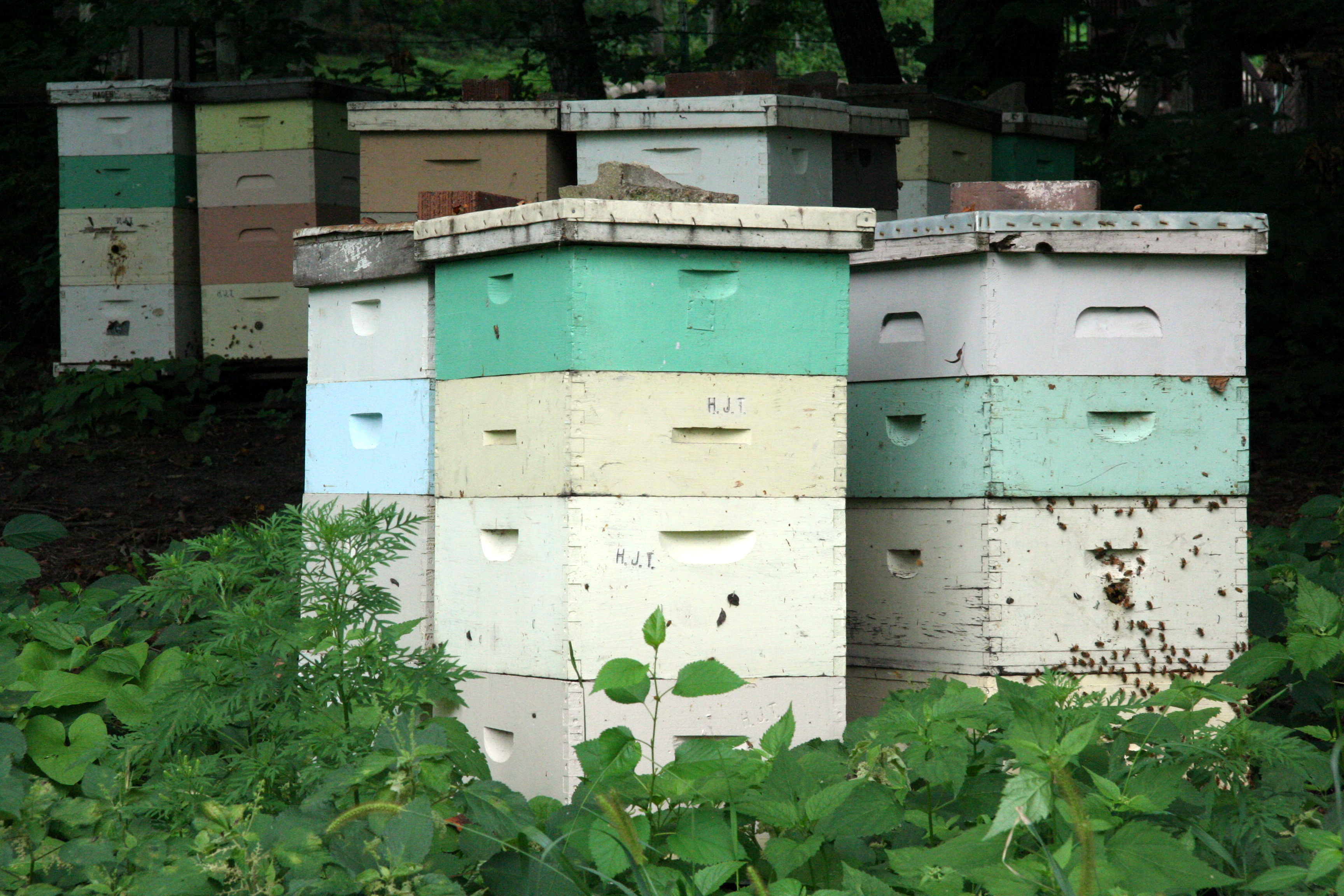
The western honey bee or European honey bee (''Apis mellifera'') is the most common of the 7–12 species of honey bees worldwide. The genus name ''Apis'' is Latin for "bee", and ''mellifera'' is the Latin for "honey-bearing" or "honey carrying", referring to the species' production of honey. Like all honey bee species, the western honey bee is eusocial, creating colonies with a single fertile female (or "queen"), many normally non-reproductive females or "workers", and a small proportion of fertile males or " drones". Individual colonies can house tens of thousands of bees. Colony activities are organized by complex communication between individuals, through both pheromones and the dance language. The western honey bee was one of the first domesticated insects, and it is the primary species maintained by beekeepers to this day for both its honey production and pollination activities. With human assistance, the western honey bee now occupies every continent except Antarctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honey Bee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America (early 16th century), North America (early 17th century), and Australia (early 19th century). Honey bees are known for their construction of perennial colonial nests from wax, the large size of their colonies, and surplus production and storage of honey, distinguishing their hives as a prized foraging target of many animals, including honey badgers, bears and human hunter-gatherers. Only eight surviving species of honey bee are recognized, with a total of 43 subspecies, though historically 7 to 11 species are recognized. Honey bees represent only a small fraction of the roughly 20,000 known species of bees. The best known honey bee is the western h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beehive
A beehive is an enclosed structure in which some honey bee species of the subgenus '' Apis'' live and raise their young. Though the word ''beehive'' is commonly used to describe the nest of any bee colony, scientific and professional literature distinguishes ''nest'' from ''hive''. ''Nest'' is used to discuss colonies that house themselves in natural or artificial cavities or are hanging and exposed. ''Hive'' is used to describe an artificial/man-made structure to house a honey bee nest. Several species of ''Apis'' live in colonies, but for honey production the western honey bee (''Apis mellifera'') and the eastern honey bee (''Apis cerana'') are the main species kept in hives. The nest's internal structure is a densely packed group of hexagonal prismatic cells made of beeswax, called a honeycomb. The bees use the cells to store food (honey and pollen) and to house the brood (eggs, larvae, and pupae). Beehives serve several purposes: production of honey, pollination of nearb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely read magazines of all time. The magazine was founded in 1888 as a scholarly journal, nine months after the establishment of the society, but is now a popular magazine. In 1905, it began including pictures, a style for which it became well-known. Its first color photos appeared in the 1910s. During the Cold War, the magazine committed itself to present a balanced view of the physical and human geography of countries beyond the Iron Curtain. Later, the magazine became outspoken on environmental issues. Since 2019, controlling interest has been held by The Walt Disney Company. Topics of features generally concern geography, history, nature, science, and world culture. The magazine is well known for its distinctive appearance: a thick s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accordion
Accordions (from 19th-century German ''Akkordeon'', from ''Akkord''—"musical chord, concord of sounds") are a family of box-shaped musical instruments of the bellows-driven free-reed aerophone type (producing sound as air flows past a reed in a frame), colloquially referred to as a squeezebox. A person who plays the accordion is called an accordionist. The concertina , harmoneon and bandoneón are related. The harmonium and American reed organ are in the same family, but are typically larger than an accordion and sit on a surface or the floor. The accordion is played by compressing or expanding the bellows while pressing buttons or keys, causing ''pallets'' to open, which allow air to flow across strips of brass or steel, called '' reeds''. These vibrate to produce sound inside the body. Valves on opposing reeds of each note are used to make the instrument's reeds sound louder without air leaking from each reed block.For the accordion's place among the families of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epipharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food and air to the esophagus and larynx respectively. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is also important in vocalization. In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bignoniaceae
Bignoniaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Lamiales commonly known as the bignonias or trumpetvines.Vernon H. Heywood, Richard K. Brummitt, Ole Seberg, and Alastair Culham. ''Flowering Plant Families of the World''. Firefly Books: Ontario, Canada. (2007). . It is not known to which of the other families in the order it is most closely related.Peter F. Stevens (2001 onwards). "Bignoniaceae" At: Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. At: Botanical Databases At: Missouri Botanical Garden Website. (see ''External links'' below) Nearly all of the Bignoniaceae are woody plants, but a few are subwoody, either as vines or subshrubs. A few more are herbaceous plants of high- elevation montane habitats, in three exclusively herbaceous genera: ''Tourrettia'', ''Argylia'', and '' Incarvillea''. The family includes many lianas, climbing by tendrils, by twining, or rarely, by aerial roots. The largest tribe in the family, called Bignonieae, consists mostly of lianas and is note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleaceae
Oleaceae, also known as the olive family, is a taxonomic family of flowering shrubs, trees, and a few lianas in the order Lamiales, It presently comprises 28 genera, one of which is recently extinct.Peter S. Green. 2004. "Oleaceae". pages 296-306. In: Klaus Kubitzki (editor) and Joachim W. Kadereit (volume editor). ''The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants'' volume VII. Springer-Verlag: Berlin; Heidelberg, Germany. The extant genera include ''Cartrema'', which was resurrected in 2012. The number of species in the Oleaceae is variously estimated in a wide range around 700. The flowers are often numerous and highly odoriferous.Vernon H. Heywood, Richard K. Brummitt, Ole Seberg, and Alastair Culham. ''Flowering Plant Families of the World''. Firefly Books: Ontario, Canada. . The family has a sub cosmopolitan distribution, ranging from the subarctic to the southernmost parts of Africa, Australia, and South America. Notable members include olive, ash, jasmine, and several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verbenaceae
The Verbenaceae ( ), the verbena family or vervain family, is a family of mainly tropical flowering plants. It contains trees, shrubs, and herbs notable for heads, spikes, or clusters of small flowers, many of which have an aromatic smell. The family Verbenaceae includes 32 genera and 800 species. Phylogenetic studies have shown that numerous genera traditionally classified in Verbenaceae belong instead in Lamiaceae. The mangrove genus '' Avicennia'', sometimes placed in the Verbenaceae or in its own family, Avicenniaceae, has been placed in the Acanthaceae. Economically important Verbenaceae include: * Lemon verbena (''Aloysia triphylla''), grown for aroma or flavoring * Verbenas or vervains (''Verbena''), some used in herbalism, others grown in gardens Taxonomy Tribes and genera in the family and their estimated species numbers: Casselieae (Schauer) Tronc. * ''Casselia'' Nees & Mart. - 6 species * ''Parodianthus'' Tronc. - 2 species * ''Tamonea'' Aubl. - 6 species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








_W_IMG_9162.jpg)