|
DAX1
DAX1 (dosage-sensitive sex reversal, adrenal hypoplasia critical region, on chromosome X, gene 1) is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NR0B1'' gene (nuclear receptor subfamily 0, group B, member 1). The ''NR0B1'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of the X chromosome between bands Xp21.3 and Xp21.2, from base pair 30,082,120 to base pair 30,087,136. Function This gene encodes a protein that lacks the normal DNA-binding domain contained in other nuclear receptors. The encoded protein acts as a dominant-negative regulator of transcription of other nuclear receptors including steroidogenic factor 1. This protein also functions as an anti-testis gene by acting antagonistically to SRY. Mutations in this gene result in both X-linked congenital adrenal hypoplasia and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. DAX1 plays an important role in the normal development of several hormone-producing tissues. These tissues include the adrenal glands above each kidney, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-linked Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita
X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita is a genetic disorder that mainly affects males. It involves many endocrine tissues in the body, especially the adrenal glands. Presentation One of the main characteristics of this disorder is adrenal insufficiency, which is a reduction in adrenal gland function resulting from incomplete development of the gland's outer layer (the adrenal cortex). Adrenal insufficiency typically begins in infancy or in childhood and can cause vomiting, difficulty with feeding, dehydration, extremely low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), low sodium levels, and shock. However, adult-onset cases have also been described. See also Addison's disease. Affected males may also lack male sex hormones, which leads to underdeveloped reproductive tissues, undescended testicles (cryptorchidism), delayed puberty, and an inability to father children (infertility). These characteristics are known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Females are rarely affected by this disorder, but a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Hypoplasia Congenita
X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita is a genetic disorder that mainly affects males. It involves many endocrine tissues in the body, especially the adrenal glands. Presentation One of the main characteristics of this disorder is adrenal insufficiency, which is a reduction in adrenal gland function resulting from incomplete development of the gland's outer layer (the adrenal cortex). Adrenal insufficiency typically begins in infancy or in childhood and can cause vomiting, difficulty with feeding, dehydration, extremely low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), low sodium levels, and shock. However, adult-onset cases have also been described. See also Addison's disease. Affected males may also lack male sex hormones, which leads to underdeveloped reproductive tissues, undescended testicles (cryptorchidism), delayed puberty, and an inability to father children (infertility). These characteristics are known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Females are rarely affected by this disorder, but a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Adrenal Hypoplasia
X-linked adrenal hypoplasia congenita is a genetic disorder that mainly affects males. It involves many endocrine tissues in the body, especially the adrenal glands. Presentation One of the main characteristics of this disorder is adrenal insufficiency, which is a reduction in adrenal gland function resulting from incomplete development of the gland's outer layer (the adrenal cortex). Adrenal insufficiency typically begins in infancy or in childhood and can cause vomiting, difficulty with feeding, dehydration, extremely low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), low sodium levels, and shock. However, adult-onset cases have also been described. See also Addison's disease. Affected males may also lack male sex hormones, which leads to underdeveloped reproductive tissues, undescended testicles (cryptorchidism), delayed puberty, and an inability to father children ( infertility). These characteristics are known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Females are rarely affected by this disorder, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Receptor
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroid hormone, steroids, thyroid hormone, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These receptors work with other proteins to regulate the gene expression, expression of specific genes thereby controlling the developmental biology, development, Homeostasis#Overview, homeostasis, and metabolism#Regulation and control, metabolism of the organism. Nuclear receptors bind directly to DNA regulating the expression of adjacent genes; hence these receptors are classified as transcription factors. The regulation of gene expression by nuclear receptors often occurs in the presence of a ligand (biochemistry), ligand—a molecule that affects the receptor's behavior. Ligand binding to a nuclear receptor results in a Conformational isomerism, conformational change activating the receptor. The result is Regulation of gene expression#Up-regulation and down-regulation, up- o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroidogenic Factor 1
The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein is a transcription factor involved in sex determination by controlling activity of genes related to the reproductive glands or gonads and adrenal glands. This protein is encoded by the NR5A1 gene, a member of the nuclear receptor subfamily, located on the long arm of chromosome 9 at position 33.3. It was originally identified as a regulator of genes encoding cytochrome P450 steroid hydroxylases, however, further roles in endocrine function have since been discovered. Structure The ''NR5A1'' gene encodes a 461-amino acid protein that shares several conserved domains consistent with members of the nuclear receptor subfamily. The N-terminal domain includes two zinc fingers and is responsible for DNA binding via specific recognition of target sequences. Variations of AGGTCA DNA motifs allows SF-1 to interact with the major groove of the DNA helix and monomerically bind. Following binding, trans-activation of target genes depends on recrui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NRIP1
Nuclear receptor-interacting protein 1 (NRIP1) also known as receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NRIP1'' gene. Function Nuclear receptor interacting protein 1 (NRIP1) is a nuclear protein that specifically interacts with the hormone-dependent activation domain AF2 of nuclear receptors. Also known as RIP140, this protein is a key regulator which modulates transcriptional activity of a variety of transcription factors, including the estrogen receptor. RIP140 has an important role in regulating lipid and glucose metabolism, and regulates gene expression in metabolic tissues including heart, skeletal muscle, and liver. A major role for RIP140 in adipose tissue is to block the expression of genes involved in energy dissipation and mitochondrial uncoupling, including uncoupling protein 1 and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1b. Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRa) can activate RIP140 during adipogenesis, by means of direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COPS2
COP9 signalosome complex subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COPS2'' gene. It encodes a subunit of the COP9 signalosome. Interactions COPS2 has been shown to interact with: * DAX1, * IRF8 Interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) also known as interferon consensus sequence-binding protein (ICSBP), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IRF8'' gene. IRF8 is a transcription factor that plays critical roles in the regulation of ..., * NIF3L1, and * THRA. References External links * * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-15-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SREBF1
Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) also known as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SREBF1'' gene. This gene is located within the Smith–Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. The isoforms are SREBP-1a and SREBP-1c (the latter also called ADD-1). SREBP-1a is expressed in the intestine and spleen, whereas SREBP-1c is mainly expressed in liver, muscle, and fat (among other tissues). Expression The proteins encoded by this gene are transcription factors that bind to a sequence in the promoter of different genes, called sterol regulatory element-1 (SRE1). This element is a decamer (oligomer with ten subunits) flanking the LDL receptor gene and other genes involved in, for instance, sterol biosynthesis. The protein is synthesized as a precursor that is attached to the nuclear membrane and endoplas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroidogenic Factor 1
The steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) protein is a transcription factor involved in sex determination by controlling activity of genes related to the reproductive glands or gonads and adrenal glands. This protein is encoded by the NR5A1 gene, a member of the nuclear receptor subfamily, located on the long arm of chromosome 9 at position 33.3. It was originally identified as a regulator of genes encoding cytochrome P450 steroid hydroxylases, however, further roles in endocrine function have since been discovered. Structure The ''NR5A1'' gene encodes a 461-amino acid protein that shares several conserved domains consistent with members of the nuclear receptor subfamily. The N-terminal domain includes two zinc fingers and is responsible for DNA binding via specific recognition of target sequences. Variations of AGGTCA DNA motifs allows SF-1 to interact with the major groove of the DNA helix and monomerically bind. Following binding, trans-activation of target genes depends on recrui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis. The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Gland
In vertebrate anatomy, the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland, about the size of a chickpea and weighing, on average, in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain. The hypophysis rests upon the hypophyseal fossa of the sphenoid bone in the center of the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded by a small bony cavity (sella turcica) covered by a Dura mater, dural fold (diaphragma sellae). The anterior pituitary (or adenohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that regulates several physiological processes including stress, growth, reproduction, and lactation. The intermediate lobe synthesizes and secretes melanocyte-stimulating hormone. The posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) is a lobe of the gland that is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the pituitary stalk (also called the infundibular stalk or the infundibulum). Hormones secreted from the pitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
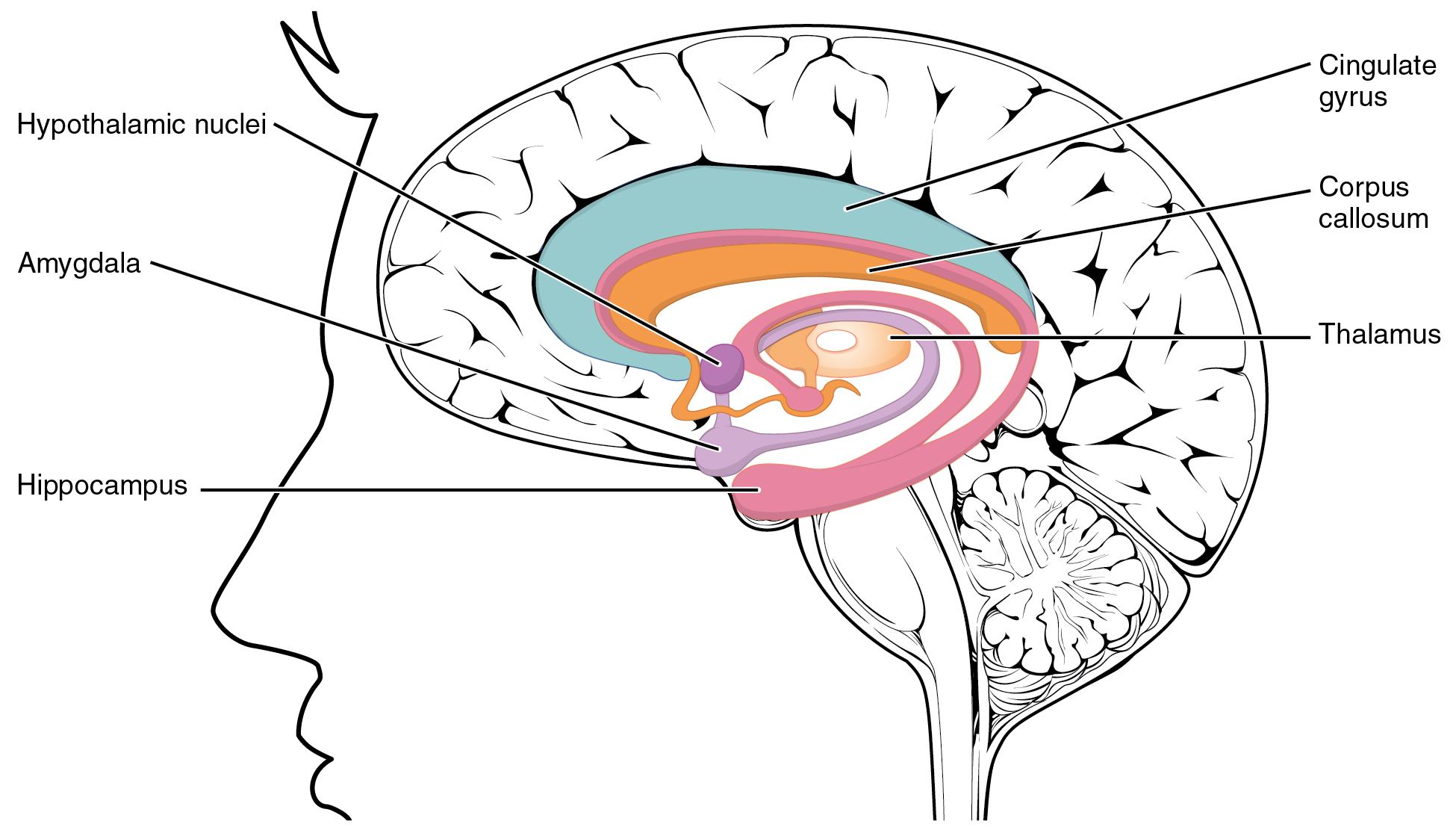
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ... part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an Almond#Nut, almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain Metabolism, metabolic biological process, processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It biosynthesis, synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |