|
David Ian Stuart
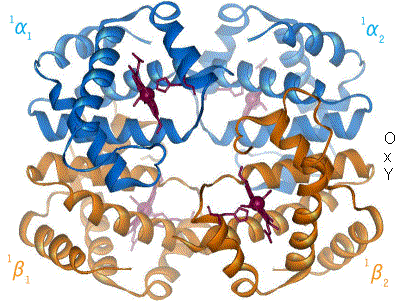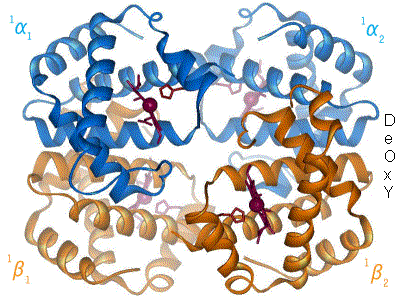
Sir David Ian Stuart (born 8 December 1953) is a Medical Research Council Professor of Structural Biology at the Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics at the University of Oxford where he is also a Fellow of Hertford College, Oxford. He is best known for his contributions to the X-ray crystallography of viruses, in particular for determining the structures of foot-and-mouth disease virus, bluetongue virus and the membrane-containing phages PRD1 (the first structure of an enveloped virus) and PM2. He is also director of Instruct and Life Sciences Director at Diamond Light Source. Education Stuart was born in 1953 in Lancashire. He was educated initially in Helmshore, Lancashire, and then in North Devon, at Barnstaple Grammar School. He studied Biophysics at King's College London, where he graduated with a BSc degree in 1974. He subsequently attended the University of Bristol and completed a PhD degree in the Biochemistry Department in 1979, working on the structure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Biology
Structural biology is a field that is many centuries old which, and as defined by the Journal of Structural Biology, deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization. Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries were primarily only able to study structures to the limit of the naked eye's visual acuity and through magnifying glasses and light microscopes. In the 20th century, a variety of experimental techniques were developed to examine the 3D structures of biological molecules. The most prominent techniques are X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and electron microscopy. Through the discovery of X-rays and its applications to protein crystals, structural biology was revolutionized, as now scientists could obtain the three-dimensional structures of biological molecules in atomic detail. Likewise, NMR spectroscopy allowed information about p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information. Since many materials can form crystals—such as salts, metals, minerals, semiconductors, as well as various inorganic, organic, and biological molecules—X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences among various mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: or ') is the most common Academic degree, degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Because it is an earned research degree, those studying for a PhD are required to produce original research that expands the boundaries of knowledge, normally in the form of a Thesis, dissertation, and defend their work before a panel of other experts in the field. The completion of a PhD is often a requirement for employment as a university professor, researcher, or scientist in many fields. Individuals who have earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree may, in many jurisdictions, use the title ''Doctor (title), Doctor'' (often abbreviated "Dr" or "Dr.") with their name, although the proper etiquette associated with this usage may also be subject to the professional ethics of their own scholarly field, culture, or society. Those who teach at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for programs that generally last three to five years. The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of London in 1860. In the United States, the Lawrence Scientific School first conferred the degree in 1851, followed by the University of Michigan in 1855. Nathaniel Southgate Shaler, who was Harvard's Dean of Sciences, wrote in a private letter that "the degree of Bachelor of Science came to be introduced into our system through the influence of Louis Agassiz, who had much to do in shaping the plans of this School." Whether Bachelor of Science or Bachelor of Arts degrees are awarded in particular subjects varies between universities. For example, an economics student may graduate as a Bachelor of Arts in one university but as a Bachelor of Science in another, and occasionally, both options are offered. Some universities follow the Oxford a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's College London
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public research university located in London, England. King's was established by royal charter in 1829 under the patronage of King George IV and the Duke of Wellington. In 1836, King's became one of the two founding colleges of the University of London. It is one of the oldest university-level institutions in England. In the late 20th century, King's grew through a series of mergers, including with Queen Elizabeth College and Chelsea College of Science and Technology (in 1985), the Institute of Psychiatry (in 1997), the United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy's and St Thomas' Hospitals and the Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery (in 1998). King's has five campuses: its historic Strand Campus in central London, three other Thames-side campuses (Guy's, St Thomas' and Waterloo) nearby and one in Denmark Hill in south London. It also has a presence in Shrivenham, Oxfordshire, for its professional mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Park Community School, Barnstaple
The Park Community School is a coeducational secondary school located in Barnstaple, Devon, England. History and houses It was founded in 1910 as Barnstaple Grammar School, and was the first secondary school to be built by Devon County Council, educating the youth of much of North Devon. The school's name was changed to The Park School in 1973 when the school became a comprehensive. From 2002 to 2003 the school underwent extensive remodelling with a new maths and science building linking the old North and South Buildings, and a new food hall was also built whilst many of the old classrooms were redesigned and refurbished. Previously a foundation school administered by Devon County Council, in February 2019 The Park Community School converted to academy status. The school is now sponsored by the Tarka Learning Partnership. The school used to consist of four houses, each of which was named after a prominent person from Devon: Sir Francis Drake, Hugh Fortescue, 4th Earl Fortes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is a coastal county with cliffs and sandy beaches. Home to the largest open space in southern England, Dartmoor (), the county is predominately rural and has a relatively low population density for an English county. The county is bordered by Somerset to the north east, Dorset to the east, and Cornwall to the west. The county is split into the non-metropolitan districts of East Devon, Mid Devon, North Devon, South Hams, Teignbridge, Torridge, West Devon, Exeter, and the unitary authority areas of Plymouth, and Torbay. Combined as a ceremonial county, Devon's area is and its population is about 1.2 million. Devon derives its name from Dumnonia (the shift from ''m'' to ''v'' is a typical Celtic consonant shift). During the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmshore
Helmshore is a village in the Rossendale Valley, Lancashire, England, south of Haslingden between the A56 and the B6235, north of Manchester. The population at the 2011 census was 5,805. The housing in Helmshore is mixed, with some two-up, two-down terraces, top-and-bottom houses and a few surviving back-to-back cottages. Between the 1970s and 2020 new housing estates have proliferated. History Early history The area around Helmshore is moorland. Post-Ice Age this would have been forested, and bog oak can still be found on the flat peatland tops over 250 metres high. The forest declined in the Neolithic period, and largely disappeared during the Bronze Age, mainly as a result of climatic change although hastened by human activity. There is some evidence of human habitation in the area during the Neolithic period: stone implements found on Bull Hill and in the Musbury valley, and the stones at Thirteen Stone Hill near Grane, and there are a relatively complex network of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly. The non-metropolitan county of Lancashire was created by the Local Government Act 1972. It is administered by Lancashire County Council, based in Preston, and twelve district councils. Although Lancaster is still considered the county town, Preston is the administrative centre of the non-metropolitan county. The ceremonial county has the same boundaries except that it also includes Blackpool and Blackburn with Darwen, which are unitary authorities. The historic county of Lancashire is larger and includes the cities of Manchester and Liverpool as well as the Furness and Cartmel peninsulas, but excludes Bowland area of the West Riding of Yorkshire transferred to the non-metropolitan county in 1974 History Before the county During Roman times the area was part of the Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
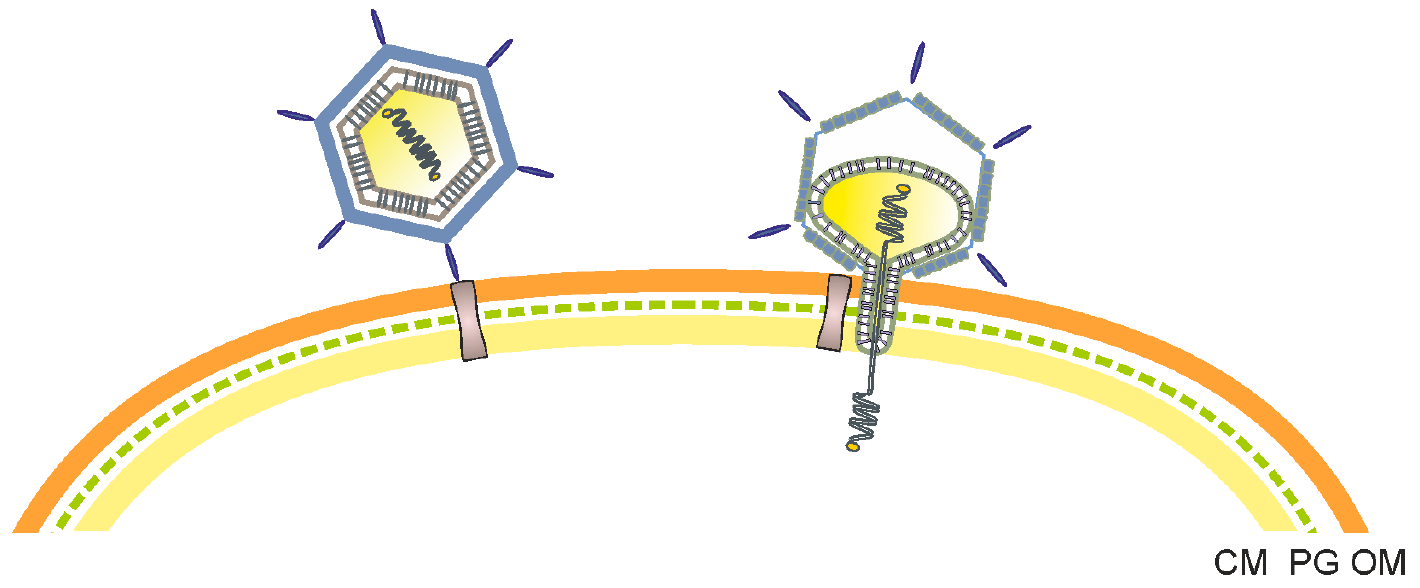
Corticovirus
''Corticovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family '' Corticoviridae''. Corticoviruses are bacteriophages; that is, their natural hosts are bacteria. The genus contains two species. The name is derived from Latin ''cortex'', ''corticis'' (meaning 'crust' or 'bark'). However, prophages closely related to PM2 are abundant in the genomes of aquatic bacteria, suggesting that the ecological importance of corticoviruses might be underestimated. Bacteriophage PM2 was first described in 1968 after isolation from seawater sampled from the coast of Chile. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: * '' Pseudoalteromonas virus Cr39582'' * '' Pseudoalteromonas virus PM2'' Other unassigned phages: * '' Pseudoalteromonas virus GXT1010'' * '' Marinomonas virus YY'' * '' Vibrio virus fNo16'' Virology The virons consist of a round, icosahedral, non-enveloped capsid of a diameter of 60 nm and an internal lipid membrane located between outer and inner protein shell. The shells are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectivirus
''Tectiviridae'' is a family of viruses with 10 species in five genera. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. Tectiviruses have no head-tail structure, but are capable of producing tail-like tubes of ~ 60×10 nm upon adsorption or after chloroform treatment. The name is derived from Latin ''tectus'' (meaning 'covered'). Virology The virions of ''Tectiviridae'' species are non-enveloped, icosahedral and display a pseudo T=25 symmetry. The capsid has two layers. The outer layer is a protein structure of 240 capsid proteins trimers, and the inner one is a proteinaceous lipid membrane which envelopes the virus genome. Apical spikes extending about 20 nanometers (nm) protrude from the icosahedrons vertices. The genome is a single molecule of linear double-stranded DNA of 15 kilo bases in length, and has 30 open reading frames. It forms a tightly packed coil and encodes several structural proteins. It encodes about 30 proteins that are transcribed in operons. At least 9 structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluetongue Disease
Bluetongue disease is a noncontagious, insect-borne, viral disease of ruminants, mainly sheep and less frequently cattle, yaks, goats, buffalo, deer, dromedaries, and antelope. It is caused by ''Bluetongue virus'' (''BTV''). The virus is transmitted by the midges ''Culicoides imicola'', ''Culicoides variipennis'', and other culicoids. Signs In sheep, BTV causes an acute disease with high morbidity and mortality. BTV also infects goats, cattle, and other domestic animals, as well as wild ruminants (for example, blesbuck, white-tailed deer, elk, and pronghorn antelope). Major signs are high fever, excessive salivation, swelling of the face and tongue, and cyanosis of the tongue. Swelling of the lips and tongue gives the tongue its typical blue appearance, though this sign is confined to a minority of the animals. Nasal signs may be prominent, with nasal discharge and stertorous respiration. Some animals also develop foot lesions, beginning with coronitis, with conseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |