|
Daphniidae
Daphniidae is a family of water fleas in the order Anomopoda. Description Members of the family Daphniidae differ from other, similar diplostracans, such as the Macrotrichidae and Moinidae, in that the antennae of females are short and immobile. Ecology The feeding mechanism of the members of the family Daphniidae differs from that of the Macrotrichidae in allowing the animals to engage in filter feeding, rather than having to scrape food from a surface. They have evolved to fill a number of different ecological niches. '' Scapholeberis'' and '' Megafenestra'' contain species adapted to living around the surface film; '' Simocephalus'' species cling to objects while filter feeding; others have developed a pelagic lifestyle. Taxonomy The family Daphniidae contains 121 species in five genera: *'' Ceriodaphnia'' Dana, 1853 *''Daphnia'' O. F. Müller, 1785 *'' Megafenestra'' Dumont & Pensaert, 1983 *'' Scapholeberis'' Schoedler, 1858 *'' Simocephalus'' Schoedler, 1858 The members ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Flea
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms). Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more undescribed. The oldest fossils of diplostracans date to the Jurassic, though their modern morphology suggests that they originated substantially earlier, during the Paleozoic. Some have also adapted to a life in the ocean, the only members of Branchiopoda to do so, even if several anostracans live in hypersaline lakes. Most are long, with a down-turned head with a single median compound eye, and a carapace covering the apparently unsegmented thorax and abdomen. Most species show cyclical parthenogenesis, where asexual reproduction is occasionally supplemented by sexual reproduction, which produces resting eggs that allow the species to survive harsh conditions and disperse to distant habitats. Description They are mostly long, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladocera
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms). Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more undescribed. The oldest fossils of diplostracans date to the Jurassic, though their modern morphology suggests that they originated substantially earlier, during the Paleozoic. Some have also adapted to a life in the ocean, the only members of Branchiopoda to do so, even if several anostracans live in hypersaline lakes. Most are long, with a down-turned head with a single median compound eye, and a carapace covering the apparently unsegmented thorax and abdomen. Most species show cyclical parthenogenesis, where asexual reproduction is occasionally supplemented by sexual reproduction, which produces resting eggs that allow the species to survive harsh conditions and disperse to distant habitats. Description They are mostly long, with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomopoda
Anomopoda is an order of the superorder Diplostraca. These crustaceans, a type of water flea, are members of the class Branchiopoda. The Anomopoda typically have five pairs of thoracic limbs, but sometimes have six pairs. The head of the Anomopoda lacks a clear separation from the trunk and the posterior, while the abdomen area gradually merges with the anterior of the trunk. See also *''Daphnia'' - water fleas *''Rhynchochydorus ''Rhynchochydorus australiensis'' is a species of crustacean in the family Chydoridae. It is the only species in the genus ''Rhynchochydorus''. It is endemic to Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovere ...'' References Cladocera Freshwater crustaceans Arthropod suborders {{Branchiopoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the two. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moinidae
Moinidae is a crustacean family within the order Cladocera. Species within this family are widely occurring, including North America and Africa. In newer classifications, it is sometimes included in the family Daphniidae. Genera These two genera belong to the family Moinidae: * ''Moina ''Moina'' is a genus of crustaceans within the family Moinidae. The genus was first described by W. Baird in 1850. They are referred to as water fleas, but are related to the much larger '' Daphnia magna'' and the larger ''Daphnia pulex''. Th ...'' Baird, 1850 * '' Moinodaphnia'' Herrick, 1887 References Cladocera Crustacean families {{Branchiopoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriodaphnia
''Ceriodaphnia'' is a genus of the Daphniidae; the genus was described in 1853 by James Dwight Dana. It has cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The ext .... Species: * '' Ceriodaphnia dubia'' (Richard, 1894) * '' Ceriodaphnia quadrangula'' (O.F. Müller, 1785) * '' Ceriodaphnia reticulata'' (Jurine, 1820) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6549092 Cladocera Branchiopoda genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapholeberis
''Scapholeberis'' is a genus of small freshwater crustaceans in the family Daphniidae. The genus was described in 1858 by Schoedler and its members have a cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The ext .... Species The genus includes the following species: * '' Scapholeberis armata'' Herrick, 1882 * '' Scapholeberis duranguensis'' Quiroz-Vázquez & Elías-Gutiérrez, 2009 * '' Scapholeberis erinaceus'' Daday, 1903 References External links * * Cladocera {{Branchiopoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrobiologia
''Hydrobiologia'', ''The International Journal of Aquatic Sciences'', is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing 21 issues per year, for a total of well over 4000 pages per year. ''Hydrobiologia'' publishes original research, reviews and opinions investigating the biology of freshwater and marine habitats, including the impact of human activities. Coverage includes molecular-, organism-, community -and ecosystem-level studies dealing with biological research in limnology and oceanography, including systematics and aquatic ecology. In addition to hypothesis-driven experimental research, it presents theoretical papers relevant to a broad hydrobiological audience, and collections of papers in special issues covering focused topics. History ''Hydrobiologia'' changed on the appointment of Henri Dumont to be its editor-in-chief. He introduced peer review, and expanded production from 6 issues per year to more than 20 per year. Koen Martens took over the responsibility as editor-in- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriodaphnia Dubia
''Ceriodaphnia dubia'' is a species of water flea in the class Branchiopoda, living in freshwater lakes, ponds, and marshes in most of the world. They are small, generally less than in length. Males are smaller than females. ''C. dubia'' moves using a powerful set of second antennae, and is used in toxicity testing of wastewater treatment plant effluent water in the United States. Climate change and particularly ultraviolet radiation B may seriously damage ''C. dubia'' populations, as they seems to be more sensitive than other cladocerans such as ''Daphnia pulex ''Daphnia pulex'' is the most common species of water flea. It has a cosmopolitan distribution: the species is found throughout the Americas, Europe, and Australia. It is a model species, and was the first crustacean to have its genome sequenced. ...'' or ''D. pulicaria''''.'' References Cladocera Crustaceans described in 1894 {{branchiopoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museum Of Los Angeles County
The Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County is the largest natural and historical museum in the western United States. Its collections include nearly 35 million specimens and artifacts and cover 4.5 billion years of history. This large collection is comprised not only of specimens for exhibition, but also of vast research collections housed on and offsite. The museum is associated with two other museums in Greater Los Angeles: the Page Museum at the La Brea Tar Pits in Hancock Park and the William S. Hart Ranch and Museum in Newhall. The three museums work together to achieve their common mission: "to inspire wonder, discovery, and responsibility for our natural and cultural worlds." History NHM opened in Exposition Park, Los Angeles, California, United States in 1913 as The Museum of History, Science, and Art. The moving force behind it was a museum association founded in 1910. Its distinctive main building with fitted marble walls and domed and colonnaded rotunda, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portable Document Format
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems.Adobe Systems IncorporatedPDF Reference, Sixth edition, version 1.23 (53 MB) Nov 2006, p. 33. Archiv/ref> Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF has its roots in "The Camelot Project" initiated by Adobe co-founder John Warnock in 1991. PDF was standardized as ISO 32000 in 2008. The last edition as ISO 32000-2:2020 was published in December 2020. PDF files may contain a variety of content besides flat text and graphics including logical structuring elements, interactive elements such as annotations and form-fields, layers, rich media (including video con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
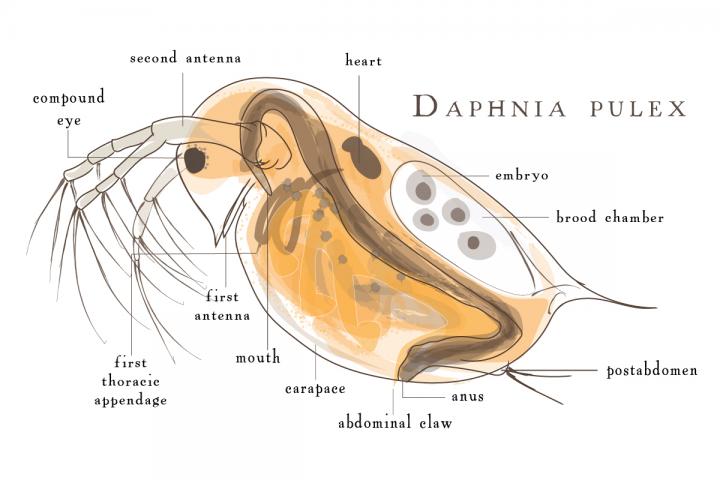
Daphnia Pulex
''Daphnia pulex'' is the most common species of water flea. It has a cosmopolitan distribution: the species is found throughout the Americas, Europe, and Australia. It is a model species, and was the first crustacean to have its genome sequenced. Description ''D. pulex'' is an arthropod whose body segments are difficult to distinguish. It can only be recognised by its appendages (only ever one pair per segment), and by studying its internal anatomy. The head is distinct and is made up of six segments, which are fused together even as an embryo. It bears the mouthparts, and two pairs of antennae, the second pair of which is enlarged into powerful organs used for swimming. No clear division is seen between the thorax and abdomen, which collectively bear five pairs of appendages. The shell surrounding the animal extends posteriorly into a spine. Like most other ''Daphnia'' species, ''D. pulex'' reproduces by cyclical parthenogenesis, alternating between sexual and asexual reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |