|
DNA-SCARS
DNA-SCARS (short for DNA segments with chromatin alterations reinforcing senescence) are nuclear substructures with persistent DNA damage and DNA damage response proteins found in senescent cells. DNA-SCARS are associated with PML nuclear bodies and the accumulation of activated ATM, ATR, CHK2 and p53 proteins. DNA-SCARS lack most of the characteristics of transient, reversible DNA damage foci, such as single-stranded DNA, active DNA synthesis, and DNA repair proteins RPA and RAD51. Telomere dysfunction-induced foci (TIF) are generally associated with DNA-SCARS. Together with senescence-associated heterochromatin foci (SAHF), DNA-SCARS are one of the most prevalent nuclear markers of cellular senescence. History DNA-SCARS were discovered by Judith Campisi Judith Campisi is an American biochemist and cell biologist. She is a professor of biogerontology at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging. She is also a member of the SENS Research Foundation Advisory Board and an ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Senescence
Cellular senescence is a phenomenon characterized by the cessation of cell division. In their experiments during the early 1960s, Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead found that normal human fetal fibroblasts in culture reach a maximum of approximately 50 cell population doublings before becoming senescent. This process is known as "replicative senescence", or the Hayflick limit. Hayflick's discovery of mortal cells paved the path for the discovery and understanding of cellular aging molecular pathways. Cellular senescence can be initiated by a wide variety of stress inducing factors. These stress factors include both environmental and internal damaging events, abnormal cellular growth, oxidative stress, autophagy factors, among many other things. The physiological importance for cell senescence has been attributed to prevention of carcinogenesis, and more recently, aging, development, and tissue repair. Senescent cells contribute to the aging phenotype, including frailty syndrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
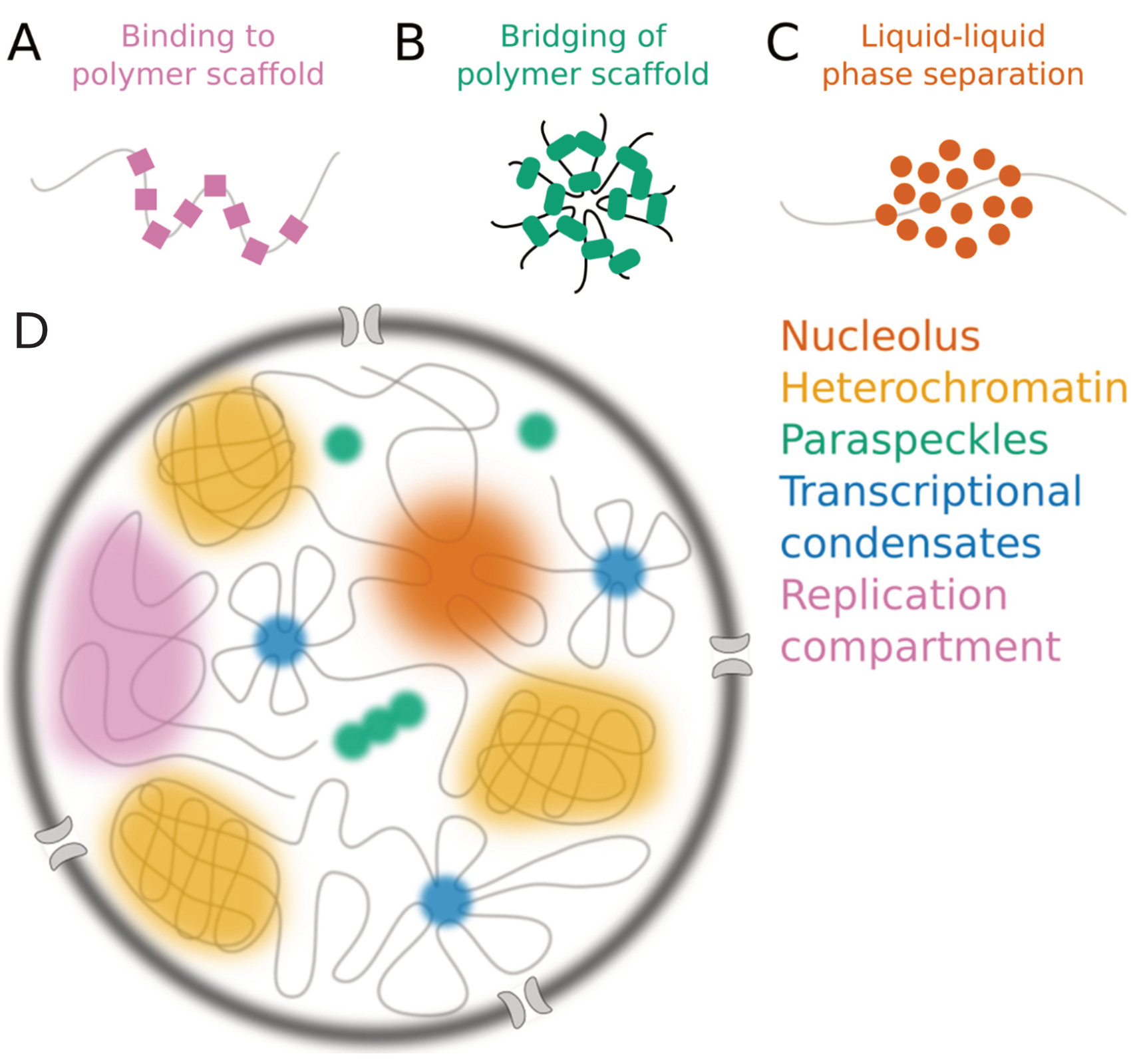
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Dots
Nuclear bodies (also known as nuclear domains, or nuclear dots) are membraneless structures found in the cell nuclei of eukaryotic cells. Nuclear bodies include Cajal bodies, the nucleolus, and promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) nuclear bodies (also called PML oncogenic dots). Nuclear bodies also include ND10s. ND stands for nuclear domain, and 10 refers to the number of dots seen. Nuclear bodies were first seen as prominent interchromatin structures in the nuclei of malignant or hyperstimulated animal cells identified using anti-sp100 autoantibodies from primary biliary cirrhosis and subsequently the promyelocytic leukemia (PML) factor, but appear also to be elevated in many autoimmune and cancerous diseases. Nuclear dots are metabolically stable and resistant to nuclease digestion and salt extraction. A nuclear body subtype is a clastosome suggested to be a site of protein degradation. Structure Simple nuclear bodies (types I and II) and the shells of complex nuclear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
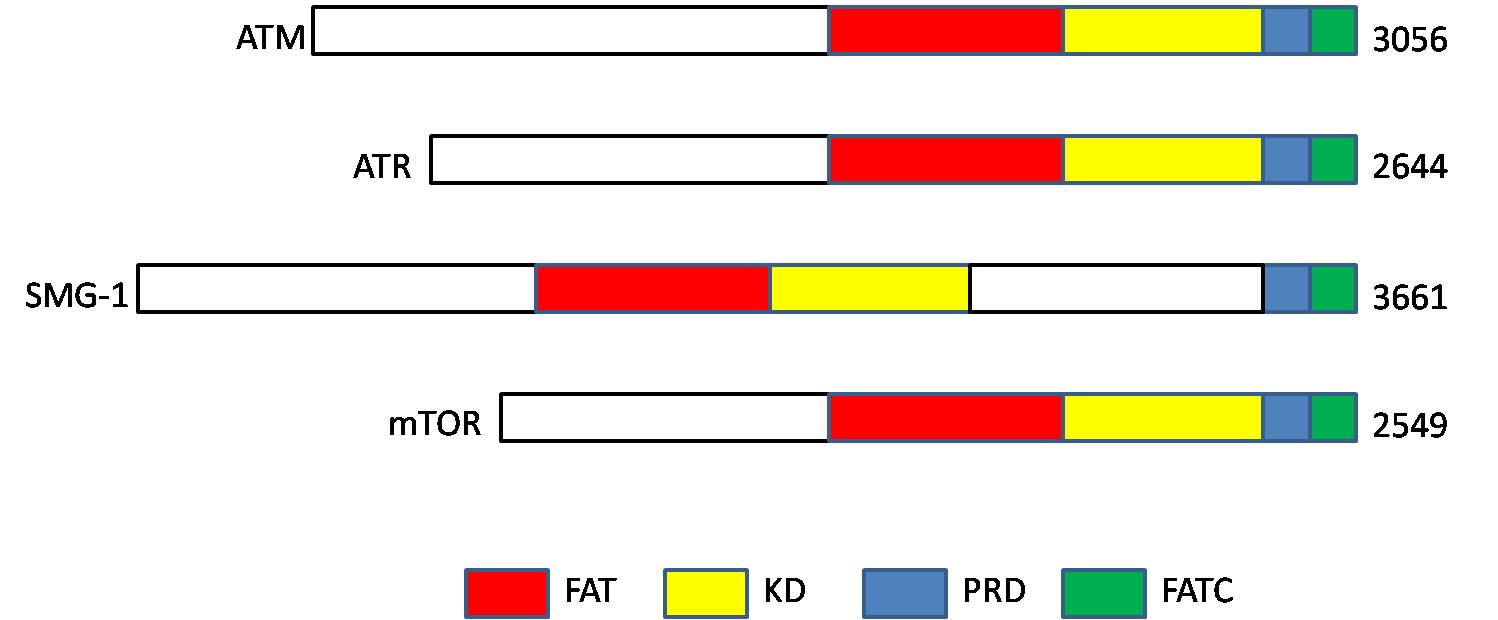
Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated
ATM serine/threonine kinase or Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, symbol ATM, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis. Several of these targets, including p53, CHK2, BRCA1, NBS1 and H2AX are tumor suppressors. In 1995, the gene was discovered by Yosef Shiloh who named its product ATM since he found that its mutations are responsible for the disorder ataxia–telangiectasia#Cause, ataxia–telangiectasia. In 1998, the Shiloh and Michael B. Kastan, Kastan laboratories independently showed that ATM is a protein kinase whose activity is enhanced by DNA damage. Introduction Throughout the cell cycle DNA is monitored for damage. Damages result from errors during DNA replication, replication, by-products of metabolism, general toxic drugs or ionizing radiation. The cell cycle has diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataxia Telangiectasia And Rad3 Related
Serine/threonine-protein kinase ATR also known as ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein (ATR) or FRAP-related protein 1 (FRP1) is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''ATR'' gene. It is a large kinase of about 301.66 kDa. ATR belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. ATR is activated in response to single strand breaks, and works with ATM to ensure genome integrity. Function ATR is a serine/ threonine-specific protein kinase that is involved in sensing DNA damage and activating the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest in eukaryotes. ATR is activated in response to persistent single-stranded DNA, which is a common intermediate formed during DNA damage detection and repair. Single-stranded DNA occurs at stalled replication forks and as an intermediate in DNA repair pathways such as nucleotide excision repair and homologous recombination repair. ATR is activated during more persistent issues with DNA damage; w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHK2
CHEK2 (Checkpoint kinase 2) is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the protein CHK2, a serine-threonine kinase. CHK2 is involved in DNA repair, cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Mutations to the CHEK2 gene have been linked to a wide range of cancers. Gene location The CHEK2 gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 22 at position 12.1. Its location on chromosome 22 stretches from base pair 28,687,742 to base pair 28,741,904. Protein structure The CHEK2 protein encoded by the CHEK2 gene is a serine threonine kinase. The protein consists of 543 amino acids and the following domains: * N-terminal SQ/TQ cluster domain (SCD) * Central forkhead-associated (FHA) domain * C-terminal serine/threonine kinase domain (KD) The SCD domain contains multiple SQ/TQ motifs that serve as sites for phosphorylation in response to DNA damage. The most notable and frequently phosphorylated site being Thr68. CHK2 appears as a monomer in its inactive state. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication Protein A
Replication protein A (RPA) is the major protein that binds to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) in eukaryotic cells. In vitro, RPA shows a much higher affinity for ssDNA than RNA or double-stranded DNA. RPA is required in replication, recombination and repair processes such as nucleotide excision repair and homologous recombination. It also plays roles in responding to damaged DNA. Structure RPA is a heterotrimer, composed of the subunits RPA1 (RPA70) (70kDa subunit), RPA2 (RPA32) (32kDa subunit) and RPA3 (RPA14) (14kDa subunit). The three RPA subunits contain six OB-folds (oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding),with DNA-binding domains (DBD) designated DBDs A-F, that bind RPA to single-stranded DNA. DBDs A, B, C and F are located on RPA1, DBD D is located on RPA2, and DBD E is located on RPA3. DBDs C, D, and E make up the trimerization core of the protein with flexible linker regions connecting them all together. Due to these flexible linker regions RPA is considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAD51
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 is a protein encoded by the gene ''RAD51''. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assists in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to the bacterial RecA, Archaeal RadA and yeast Rad51. The protein is highly conserved in most eukaryotes, from yeast to humans. Variants Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene, which encode distinct proteins, have been reported. Transcript variants utilizing alternative polyA signals exist. Family In mammals, seven recA-like genes have been identified: Rad51, Rad51L1/B, Rad51L2/C, Rad51L3/D, XRCC2, XRCC3, and DMC1/Lim15. All of these proteins, with the exception of meiosis-specific DMC1, are essential for development in mammals. Rad51 is a member of thRecA-like NTPases Function In humans, RAD51 is a 339-amino acid protein that plays a major role in homologous recombination of DNA during double strand break r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judith Campisi
Judith Campisi is an American biochemist and cell biologist. She is a professor of biogerontology at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging. She is also a member of the SENS Research Foundation Advisory Board and an adviser at the Lifeboat Foundation. She is co-editor in chief of the ''Aging Journal,'' together with Mikhail Blagosklonny and David Sinclair, and founder of the pharmaceutical company Unity Biotechnology. She is listed in '' Who's Who in Gerontology''. She is widely known for her research on how senescent cells influence aging and cancer — in particular the Senescence Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP). Career Campisi got her B.A. in Chemistry in 1974 and Ph.D. in Biochemistry in 1979 from the State University of New York at Stony Brook and completed her postdoctoral training at the Harvard Medical School in 1982. She initially joined the Boston University Medical School, and moved onto the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory as a Senior Scientist in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |