|
DEMOnstration Power Station
DEMO refers to a proposed class of nuclear fusion experimental reactors that are intended to demonstrate the net production of electric power from nuclear fusion. Most of the ITER partners have plans for their own DEMO-class reactors. With the possible exception of the EU and Japan, there are no plans for international collaboration as there was with ITER. Plans for DEMO-class reactors are intended to build upon the ITER experimental nuclear fusion reactor. The most well-known and documented DEMO-class reactor design is that of the European Union (EU). The following parameters have been used as a baseline for design studies: the EU DEMO should produce at least 2000 megawatts (2 gigawatts) of fusion power on a continuous basis, and it should produce 25 times as much power as required for scientific breakeven, which does not include the power required to operate the reactor. The EU DEMO design of 2 to 4 gigawatts of thermal output will be on the scale of a modern electric power s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EUROfusion Schematic Diagram Of Fusion Power Plant
EUROfusion is a consortium of national fusion research institutes located in the European Union, the UK, Switzerland and Ukraine. It was established in 2014 to succeed the European Fusion Development Agreement ( EFDA) as the umbrella organisation of Europe's fusion research laboratories. The consortium is currently funded by the Euratom Horizon 2020 programme. Organisation The EUROfusion consortium agreement has been signed by 30 research organisations and universities from 25 European Union countries plus Switzerland, Ukraine and the United Kingdom. The EUROfusion's Programme Management Unit offices located in Garching, near Munich (Germany), are hosted by the Max Planck Institute of Plasma Physics (IPP). The IPP is also the seat for the co-ordinator of EUROfusion. Activities EUROfusion funds fusion research activities in accordance with thRoadmap to the realisation of fusion energy The Roadmap outlines the most efficient way to realise fusion electricity by 2050. Research carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor
The China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor (中国聚变工程实验堆, CFETR) is a proposed tokamak fusion reactor, which uses a magnetic field in order to confine plasma and generate energy. Presently, tokamak devices are leading candidates for the construction of a viable and practical thermonuclear fusion reactor. These reactors may be used to generate sustainable energy whilst ensuring a low environmental impact and a smaller carbon footprint than fossil fuel-based power plants. The CFETR utilises and intends to build upon pre-existing nuclear fusion research from the ITER program in order to address the gaps between ITER and the next generation thermonuclear plant and successor reactor class to ITER, the Demonstration Power Plant (DEMO). Presently, three domestic fusion test reactors are in operation in China. These include EAST in ASIPP at Hefei, HL-2A(M) at the Southwestern Institute of Physics (SWIP) at Chengdu and J-TEXT located at Huazhong University of Science and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
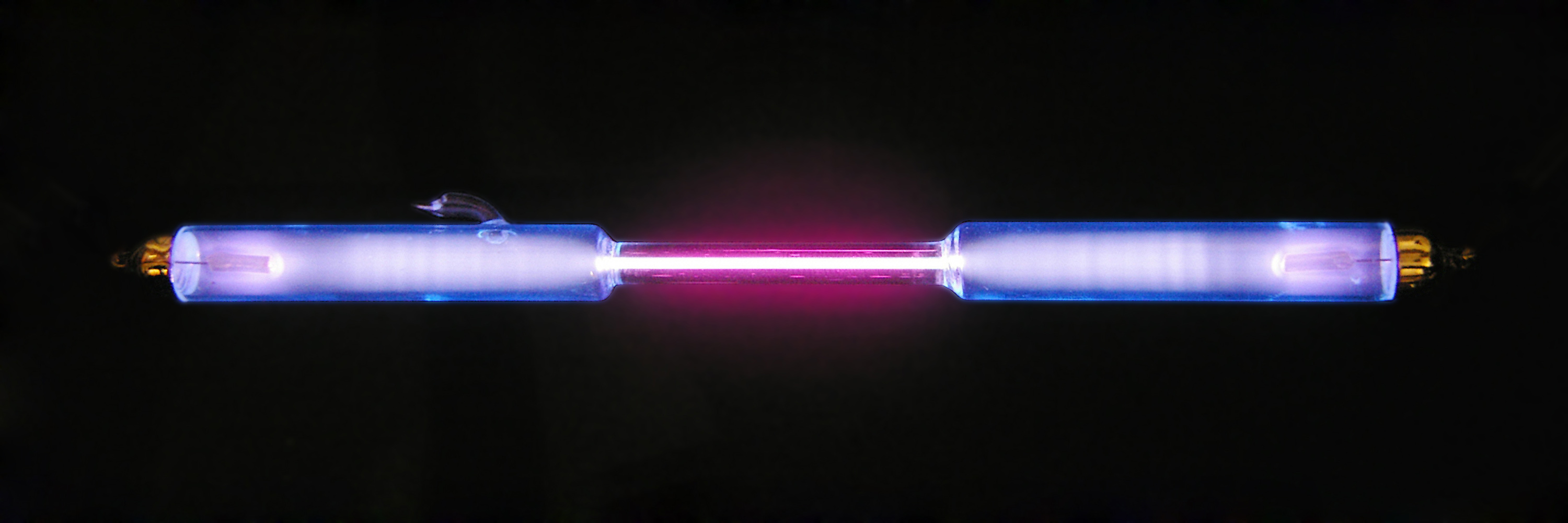
Helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling and melting point are the lowest among all the elements. It is the second lightest and second most abundant element in the observable universe ( hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant). It is present at about 24% of the total elemental mass, which is more than 12 times the mass of all the heavier elements combined. Its abundance is similar to this in both the Sun and in Jupiter, due to the very high nuclear binding energy (per nucleon) of helium-4, with respect to the next three elements after helium. This helium-4 binding energy also accounts for why it is a product of both nuclear fusion and radioactive decay. The most common isotope of helium in the universe is helium-4, the vast majority of which was forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. An atom is composed of a positively charged nucleus, with a cloud of negatively charged electrons surrounding it, bound together by electrostatic force. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force. The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of () for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about for uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 26,634 (uranium atomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of the common isotope hydrogen-1 (''protium'') contains one proton and zero neutrons, and that of hydrogen-2 (''deuterium'') contains one proton and one neutron. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare on Earth. The atmosphere has only trace amounts, formed by the interaction of its gases with cosmic rays. It can be produced artificially by irradiating lithium metal or lithium-bearing ceramic pebbles in a nuclear reactor and is a low-abundance byproduct in normal operations of nuclear reactors. Tritium is used as the energy source in radioluminescent lights for watches, gun sights, numerous instruments and tools, and even novelty items such as self-illuminating key chains. It is used in a medical and scientific setting as a radioacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom of deuterium among all atoms of hydrogen (see heavy water). Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% by number (0.0312% by mass) of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another (see Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water). ( Tritium is yet another hydrogen isotope, with two neutrons, that is far more rare and is radioactive.) The name ''deuterium'' is derived from the Greek , meaning "second", to denote the two particles composing the nucleus. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEMO Power Plant Schematic
Demo, usually short for demonstration, may refer to: Music and film *Demo (music), a song typically recorded for reference rather than release * ''Demo'' (Behind Crimson Eyes), a 2004 recording by the band Behind Crimson Eyes * ''Demo'' (Deafheaven album), a 2010 EP by Deafheaven * ''Demo'' (The Flat liners Album), a 2002 album by the band The Flatliners * ''Demo'' (Miss May I album), a 2008 recording by the metalcore band Miss May I *"Demo", a 1990 single by Die Krupps * "Demo" (P-Model song), a 1979 recording by songwriters Susumu Hirasawa and Yasumi Tanaka *''Demo (Skinless)'', a 1994 recording by the band Skinless * ''Demo 2004'' (Year of No Light album), a 2004 recording by Year of No Light *'' Demo #2'', an unreleased recording by Neutral Milk Hotel *''Demo'', 2008 debut EP by Yuna Computing and technology *Demo (computer programming), a multimedia spectacle of programming skill * The Demo, a computer demonstration in 1968, sometimes called "the mother of all demos" * DEM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFMIF
The International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility, also known as IFMIF, is a projected material testing facility in which candidate materials for the use in an energy producing fusion reactor can be fully qualified. IFMIF will be an accelerator-driven neutron source producing a high intensity fast neutron flux with a spectrum similar to that expected at the first wall of a fusion reactor using a deuterium-lithium nuclear reaction. The IFMIF project was started in 1994 as an international scientific research program, carried out by Japan, the European Union, the United States, and Russia, and managed by the International Energy Agency. Since 2007, it has been pursued by Japan and the European Union under the Broader Approach Agreement in the field of fusion energy research, through the IFMIF/EVEDA project, which conducts engineering validation and engineering design activities for IFMIF. The construction of IFMIF is recommended in the European Roadmap for Research Infrastruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Llewellyn Smith
Sir Christopher Hubert Llewellyn Smith (born 19 November 1942) is an Emeritus Professor of Physics at the University of Oxford. Education Llewellyn Smith was educated at the University of Oxford (BA) and completed his Doctor of Philosophy degree in theoretical physics at New College, Oxford in 1967. Career and research After his DPhil he worked at the Lebedev Physical Institute in Moscow, CERN and then the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory before returning to Oxford in 1974. Llewellyn Smith was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1984. While Chairman of Oxford Physics (1987–92), he led the merger of five different departments into a single Physics Department. Smith was Director General of CERN from 1994 to 1998. Thereafter he served as Provost and President of University College London (1999–2002). Awards and honours Llewellyn Smith received the James Clerk Maxwell Medal and Prize in 1979, and Glazebrook Medal and Prize of the Institute of Physics in 1999 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a U.S. multiprogram science and technology national laboratory sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and administered, managed, and operated by UT–Battelle as a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) under a contract with the DOE, located in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. Established in 1943, ORNL is the largest science and energy national laboratory in the Department of Energy system (by size) and third largest by annual budget. It is located in the Roane County section of Oak Ridge, Tennessee. Its scientific programs focus on materials, nuclear science, neutron science, energy, high-performance computing, systems biology and national security, sometimes in partnership with the state of Tennessee, universities and other industries. ORNL has several of the world's top supercomputers, including Frontier, ranked by the TOP500 as the world's most powerful. The lab is a leading neutron and nuclear power re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Atomics
General Atomics is an American energy and defense corporation headquartered in San Diego, California, specializing in research and technology development. This includes physics research in support of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion energy. The company also provides research and manufacturing services for remotely operated surveillance aircraft, including the Predator drones, airborne sensors, and advanced electric, electronic, wireless, and laser technologies. History General Atomics (GA) was founded on July 18, 1955, in San Diego, California, by Frederic de Hoffmann with assistance from notable physicists Edward Teller and Freeman Dyson. Originally the company was part of the General Atomic division of General Dynamics "for harnessing the power of nuclear technologies for the benefit of mankind". GA's first offices were in the General Dynamics facility on Hancock Street in San Diego. GA also used a schoolhouse on San Diego's Barnard Street as its temporary headquarte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |