|
Dương Đình Nghệ
Dương Đình Nghệ (Chữ Hán: 楊廷藝; pinyin: ''Yáng Tíngyì''; 874 – March 937; some sources record Dương Diên Nghệ, Chữ Hán: 楊延藝) was the jiedushi of Tĩnh Hải quân in around 931 AD. He was a skillful, talented general under Khúc Hạo, descendant of the Khúc clan who ruled Vietnam autonomously while it was technically under Chinese control for three generations. He cornered the Southern Han garrison inside Đại La and defeated their relief force, afterwards establishing himself as jiedushi. Dương Đình Nghệ was killed eventually by his general Kiều Công Tiễn who then moved up to the post of governor/administrator. This brief void left the region without rulers, until Kiều fled and Dương's son-in-law Ngô Quyền established the Ngô dynasty The Ngô dynasty (; Chữ Nôm: 茹吳) was a dynasty that ruled Tĩnh Hải quân (Jinghai) in northern Vietnam from 939 to 968. The dynasty was founded by Ngô Quyền, who led Vietnamese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dương Tam Kha
Dương Tam Kha ( 楊 三 哥), formally King Ping of Yang ( 楊 平 王), later known as the Duke of Chương Dương (章陽公) (died 10 August 980), was king of the Ngô dynasty from 944 to 950.''Đại Việt sử lược'', vol. 1''Nguyễn Minh Tường (2006), Book title "Về sự nghiệp và vị thế của Dương Tam Kha trong lịch sử dân tộc ở thế kỷ X", Nghiên cứu Lịch sử, số 9 (365), Page 36-42, Viện Sử học, Hà Nội, Chapter 9.''趙久安, 《遺民: 文革烙印了我的階級》, 新銳文創, 2012, 234 pages, Page 79-215, , 978986591531/ref>华业, 世界历史读这本就够了, Beijing Book Co. Inc, 2012, , 978799901850/ref> Early years Dương Tam Kha was one of Dương Đình Nghệ's sons, brother of Ngô Quyền's wife, empress Dương. According to ''Đại Việt sử lược'' (History annals of Dai Viet), his birth name was Dương Chủ Tướng ( 楊 主 將), but according to '' History of Song'', his name was Dương ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally written in Chinese form, to learners already familiar with the Latin alphabet. The system includes four diacritics denoting tones, but pinyin without tone marks is used to spell Chinese names and words in languages written in the Latin script, and is also used in certain computer input methods to enter Chinese characters. The word ' () literally means "Han language" (i.e. Chinese language), while ' () means "spelled sounds". The pinyin system was developed in the 1950s by a group of Chinese linguists including Zhou Youguang and was based on earlier forms of romanizations of Chinese. It was published by the Chinese Government in 1958 and revised several times. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) adopted pinyin as an international standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
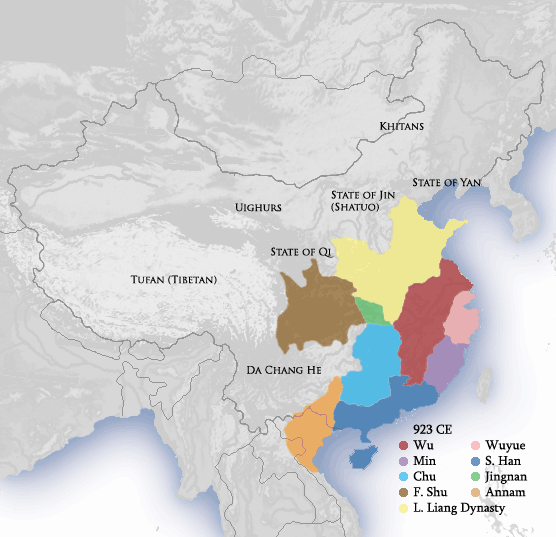
10th Century In Vietnam
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
937 Deaths
Year 937 ( CMXXXVII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * A Hungarian army invades Burgundy, and burns the city of Tournus. Then they go southwards to Italy, pillaging the environs of Naples, Benevento and Monte Cassino. When the Hungarians return home, they are attacked in the Apennine Mountains by Lombard forces, losing their plunder (approximate date). * July 11 – King Rudolph II of Burgundy dies after a 25-year reign, and is succeeded by his 12-year-old son Conrad I ("the Peaceful"). His wife, Queen Bertha, takes effective control of unified Burgundy, transferring its capital to Arles (that Burgundian kingdom was later known from the 12th century as the Kingdom of Arles). * King Otto I refuses to give land to his older (illegitimate) half-brother Thankmar, who gains the support of Eberhard III (duke of Franconia) and Wichmann the Elder, and seizes the fortress of Eresb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Han Jiedushi Of Jinghai Circuit
Southern may refer to: Businesses * China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China * Southern Airways, defunct US airline * Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US * Southern Airways Express, Memphis-based passenger air transportation company, serving eight cities in the US * Southern Company, US electricity corporation * Southern Music (now Peermusic), US record label * Southern Railway (other), various railways * Southern Records, independent British record label * Southern Studios, recording studio in London, England * Southern Television, defunct UK television company * Southern (Govia Thameslink Railway), brand used for some train services in Southern England Media * ''Southern Daily'' or ''Nanfang Daily'', the official Communist Party newspaper based in Guangdong, China * ''Southern Weekly'', a newspaper in Guangzhou, China * Heart Sussex, a radio station in Sussex, England, previously known as "Southern FM" * 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of Vietnam
Throughout the history of Vietnam, many names were used in reference to Vietnam. History Throughout the history of Vietnam, official and unofficial names have been used in reference to the territory of Vietnam. Vietnam was called Văn Lang during the Hồng Bàng dynasty, Âu Lạc under Thục dynasty, Nam Việt during the Triệu dynasty, Vạn Xuân during the Early Lý dynasty, Đại Cồ Việt during the Đinh dynasty and Early Lê dynasty. Starting in 1054, Vietnam was called Đại Việt (Great Việt). During the Hồ dynasty, Vietnam was called Đại Ngu. Việt Nam ( in Vietnamese) is a variation of Nam Việt (Southern Việt), a name that can be traced back to the Triệu dynasty (2nd century BC, also known as Nanyue Kingdom). The word "Việt" originated as a shortened form of Bách Việt, a word used to refer to a people who lived in what is now southern China in ancient times. The word "Việt Nam", with the syllables in the modern order, first appears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngô Dynasty
The Ngô dynasty (; Chữ Nôm: 茹吳) was a dynasty that ruled Tĩnh Hải quân (Jinghai) in northern Vietnam from 939 to 968. The dynasty was founded by Ngô Quyền, who led Vietnamese forces in the Battle of Bạch Đằng River against the Chinese Southern Han dynasty in 938. Around 930, as Ngô Quyền rose to power, northern Vietnam was militarily occupied by the Southern Han and was treated as an autonomous province and vassal state of Later Tang Dynasty, referred to as Tĩnh Hải quân. Every year the Jiedushi of Tĩnh Hải quân had to pay tribute to its Chinese master in exchange for peace and political support. At the beginning of the 10th century, China was domestically plagued and weakened by civil war during what is known as the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Chinese were preoccupied with these civil struggles and lost their grip on Tĩnh Hải quân periodically. Tĩnh Hải quân took advantage of this opportunity and proclaimed its independenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Han
Southern Han (; 917–971), officially Han (), originally Yue (), was one of the ten kingdoms that existed during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was located on China's southern coast, controlling modern Guangdong and Guangxi. The kingdom greatly expanded its capital Xingwang Fu (, present-day Guangzhou). It attempted but failed to annex the independent polity of Jinghai which was controlled by the Vietnamese. Founding of the Southern Han Liu Yin was named regional governor and military officer by the Tang court in 905. Though the Tang fell two years later, Liu did not declare himself the founder of a new kingdom as other southern leaders had done. He merely inherited the title of Prince of Nanping in 909. It was not until Liu Yin's death in 917 that his brother, Liu Yan, declared the founding of a new kingdom, which he initially called "Yue" (); he changed the name to Han () in 918. This was because his surname Liu () was the imperial surname of the Han dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khúc Clan
The Khúc family or Khúc clan ( vi, Họ Khúc, Chữ nôm: 𣱆曲; ) was a succession of native leaders who ruled over Tĩnh Hải quân during the late Tang dynasty until the Five Dynasties period. The Chinese Tang dynasty took control of the region of Jiaozhi (Giao Châu; roughly corresponding to the area of the modern Red River Delta) in 621 from the preceding Sui dynasty. Later, the Tang dynasty established 12 provinces and 59 districts under the Protectorate of Annan. Effective control exercised by the Tang dynasty lasted until the 10th century, when Khúc Thừa Dụ took over as ''jiedushi'' in 905. By 906 an autonomous region in Vietnam was established under the Khúc clan in Tống Bình (near modern-day Hanoi), paving the way for total Vietnamese independence from China under Đinh Bộ Lĩnh. Preconditions The Tang took control of the northern Vietnamese region of Jiaozhi (Giao Chi; roughly corresponding to the area of the modern Red River Delta). Periodical rebel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiedushi
The ''jiedushi'' (), or jiedu, was a title for regional military governors in China which was established in the Tang dynasty and abolished in the Yuan dynasty. The post of ''jiedushi'' has been translated as "military commissioner", "legate", or "regional commander". Originally introduced in 711 to counter external threats, the ''jiedushi'' were posts authorized with the supervision of a defense command often encompassing several prefectures, the ability to maintain their own armies, collect taxes and promote and appoint subordinates. Powerful ''jiedushi'' eventually became ''fanzhen'' rulers (''de facto'' warlords) and overrode the power of the central government of Tang. An early example of this was An Lushan, who was appointed ''jiedushi'' of three regions, which he used to start the An Lushan Rebellion that abruptly ended the golden age of the Tang dynasty. Even after the difficult suppression of that rebellion, some ''jiedushi'' such as the Three Fanzhen of Hebei were all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chữ Hán
Chữ Hán (𡨸漢, literally "Chinese characters", ), Chữ Nho (𡨸儒, literally "Confucian characters", ) or Hán tự (漢字, ), is the Vietnamese term for Chinese characters, used to write Văn ngôn (which is a form of Classical Chinese used in Vietnam during the feudal period) and Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary in Vietnamese language, was officially used in Vietnam after the Red River Delta region was incorporated into the Han dynasty and continued to be used until the early 20th century (111 BC – 1919 AD). Terminology * Stroke - nét * Stroke order - Bút thuận (筆順) * Radical - Bộ thủ (部首) * Regular script - Khải thư (楷書) * Simplified characters - chữ giản thể (𡨸簡體) * Traditional characters - chữ phồn thể (𡨸繁體) * Văn ngôn - Literary Chinese (文言) * Hán văn - synonym of Literary Chinese (漢文) * Kangxi radicals - Bộ thủ Khang Hi History In the late 3rd century BC, the newly established Qin dynasty made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngô Quyền
Ngô Quyền ( vi-hantu, 吳權) (April 17, 898 – February 14, 944), often referred to as Tiền Ngô Vương (前吳王; "First King of Ngô"), was a warlord who later became the founding king of the Ngô dynasty of Vietnam. He reigned from 939 to 944. In 938, he defeated the Southern Han dynasty at the Battle of Bạch Đằng River north of modern Haiphong. The battle is usually remembered in Vietnamese national history as it ended 1,000 years of Chinese rule over Vietnam dating back to 111 BC under the Western Han dynasty. A central district in modern Haiphong is named after him. Early life and career Ngô Quyền was born in 898 AD in Đường Lâm (modern-day Sơn Tây District, Hanoi of northern Vietnam) during the Tang dynasty. He was the son of Ngô Mân, an influential official in Phong, Annan (today Phu Tho province). Ngô Mân's ancestor was Wu Ridai (Ngô Nhật Đại), a local tribal chief from Fuluzhou, Annan (Modern-day Ha Tinh Province). In 722, Wu Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |