|
Dynamics Explorer 1
Dynamics Explorer 1 (DE-1 or Explorer 62) was a NASA high-altitude mission, launched on 3 August 1981, and terminated on 28 February 1991. It consisted of two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere. Mission The Dynamics Explorer mission's general objective is to investigate the strong interactive processes coupling the hot, tenuous, convecting plasmas of the magnetosphere and the cooler, denser plasmas and gases corotating in the Earth's ionosphere, upper atmosphere, and plasmasphere. Two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, were launched together and were placed in polar coplanar orbits, permitting simultaneous measurements at high and low altitudes in the same field-line region. The DE-1 spacecraft (high-altitude mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 63
Dynamics Explorer 2 (DE-2 or Explorer 63) was a NASA low-altitude mission, launched on 3 August 1981. It consisted of two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere. Mission The DE 2 spacecraft (low-altitude mission) complemented the high-altitude mission Dynamics Explorer 1 and was placed into an orbit with a perigee sufficiently low to permit measurements of neutral composition, temperature, and wind. The apogee was high enough to permit measurements above the interaction regions of suprathermal ions, and also plasma flow measurements at the feet of the magnetospheric field lines. The Dynamics Explorer mission is to investigate the strong interactive processes coupling the hot, tenuous, convecting plasmas of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Physics
Space physics, also known as solar-terrestrial physics or space-plasma physics, is the study of plasmas as they occur naturally in the Earth's upper atmosphere (aeronomy) and within the Solar System. As such, it encompasses a far-ranging number of topics, such as heliophysics which includes the solar physics of the Sun, the solar wind, planetary magnetospheres and ionospheres, auroras, cosmic rays, and synchrotron radiation. Space physics is a fundamental part of the study of space weather and has important implications in not only to understanding the universe, but also for practical everyday life, including the operations of communications and weather satellites. Space physics is distinct from astrophysical plasma and the field of astrophysics, which studies similar plasma phenomena beyond the Solar System. Space physics utilizes in situ measurements from high altitude rockets and spacecraft, in contrast to astrophysical plasma that relies deduction of theory and astronomical obse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auroral Oval
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of brilliant lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals, or dynamic flickers covering the entire sky. Auroras are the result of disturbances in the magnetosphere caused by the solar wind. Major disturbances result from enhancements in the speed of the solar wind from coronal holes and coronal mass ejections. These disturbances alter the trajectories of charged particles in the magnetospheric plasma. These particles, mainly electrons and protons, precipitate into the upper atmosphere (thermosphere/ exosphere). The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emit light of varying colour and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of accelerati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Analyzer
An electrostatic analyzer or ESA is an instrument used in ion optics that employs an electric field to allow the passage of only those ions or electrons that have a given specific energy. It usually also focuses these particles (concentrates them) into a smaller area. ESA’s are typically used as components of space instrumentation, to limit the scanning (sensing) energy range and, thereby also, the range of particles targeted for detection and scientific measurement. The closest analogue in photon optics is a filter. Radial cylindrical analyzer Electrostatic analyzers are designed in different configurations. A simple version is a radial cylindrical analyzer, which consists of two curved parallel plates at different potentials. Ions or electrons enter the analyzer at one end and either pass through the other end or collide with the walls of the analyzer, depending on their initial energy. In these types of analyzers, only the radial component of the velocity of a charged particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISEE-1
The ISEE-1 (International Sun-Earth Explorer-A or ISEE-A) was an Explorer-class mother spacecraft, International Sun-Earth Explorer-1, was part of the mother/daughter/heliocentric mission (ISEE-1, ISEE-2, ISEE-3). ISEE-1 was a space probe used to study magnetic fields near the Earth. ISEE-1 was a spin-stabilized spacecraft and based on the design of the prior IMP (Interplanetary Monitoring Platform) series of spacecraft. ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 were launched on 22 October 1977, and they re-entered on 26 September 1987. Mission The purposes of the mission were: (1) to investigate solar-terrestrial relationships at the outermost boundaries of the Earth's magnetosphere, (2) to examine in detail the structure of the solar wind near the Earth and the shock wave that forms the interface between the solar wind and the Earth's magnetosphere, (3) to investigate motions of and mechanisms operating in the plasma sheets, and (4) to continue the investigation of cosmic rays and solar flar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomagnetic Storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The disturbance that drives the magnetic storm may be a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or (much less severely) a co-rotating interaction region (CIR), a high-speed stream of solar wind originating from a coronal hole. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. During solar maximum, geomagnetic storms occur more often, with the majority driven by CMEs. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth's magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 (approximately ) or root-power ratio of 10 (approximately ). The unit expresses a relative change or an absolute value. In the latter case, the numeric value expresses the ratio of a value to a fixed reference value; when used in this way, the unit symbol is often suffixed with letter codes that indicate the reference value. For example, for the reference value of 1 volt, a common suffix is " V" (e.g., "20 dBV"). Two principal types of scaling of the decibel are in common use. When expressing a power ratio, it is defined as ten times the logarithm in base 10. That is, a change in ''power'' by a factor of 10 corresponds to a 10 dB change in level. When expressing root-power quantities, a change in ''ampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
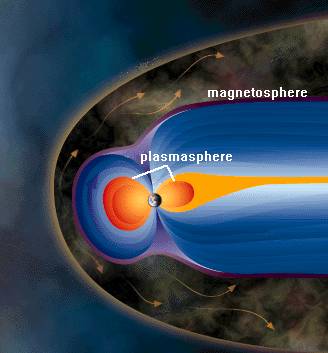
Plasmasphere
The plasmasphere, or inner magnetosphere, is a region of the Earth's magnetosphere consisting of low-energy (cool) plasma. It is located above the ionosphere. The outer boundary of the plasmasphere is known as the plasmapause, which is defined by an order of magnitude drop in plasma density. In 1963 American scientist Don Carpenter and Soviet astronomer proved the plasmasphere and plasmapause's existence from the analysis of very low frequency (VLF) whistler wave data. Traditionally, the plasmasphere has been regarded as a well behaved cold plasma with particle motion dominated entirely by the geomagnetic field and, hence, co-rotating with the Earth. History The discovery of the plasmasphere grew out of the scientific study of whistlers, natural phenomena caused by very low frequency (VLF) radio waves. Whistlers were first heard by radio operators in the 1890s. British scientist Llewelyn Robert Owen Storey had shown lightning generated whistlers in his 1953 PhD dissertation. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siple Station
Siple Station was a research station in Antarctica (), established in 1973 by Stanford's STAR Lab, to perform experiments that actively probed the magnetosphere using very low frequency (VLF) waves. Its location was selected to be near the Earth's south magnetic pole, and the thick ice sheet allowed for a relatively efficient dipole antenna at VLF (very low frequency – 3 kHz range) frequencies. John Katsufrakis of Stanford University was the "father" of the station and the VLF experiment sponsored by Stanford. There were two stations, Siple I and later Siple II, circa 1979, built above the original which was eventually crushed by the ice. The original Siple I station had a four-person winter over crew and the later Siple II station had an eight-person winter over crew. The Siple II station used a 300 kW Kato square wound generator powered by a Caterpillar D353 engine to power the VLF (Jupiter) transmitter which transmitted to a receiver in Roberval, Canada. At the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time. The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction with an SI prefix such as kilo (1 kbit/s = 1,000 bit/s), mega (1 Mbit/s = 1,000 kbit/s), giga (1 Gbit/s = 1,000 Mbit/s) or tera (1 Tbit/s = 1,000 Gbit/s). The non-standard abbreviation bps is often used to replace the standard symbol bit/s, so that, for example, 1 Mbps is used to mean one million bits per second. In most computing and digital communication environments, one byte per second (symbol: B/s) corresponds to 8 bit/s. Prefixes When quantifying large or small bit rates, SI prefixes (also known as metric prefixes or decimal prefixes) are used, thus: Binary prefixes are sometimes used for bit rates. The International Standard ( IEC 80000-13) specifies different a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape Recorder
An audio tape recorder, also known as a tape deck, tape player or tape machine or simply a tape recorder, is a sound recording and reproduction device that records and plays back sounds usually using magnetic tape for storage. In its present-day form, it records a fluctuating signal by moving the tape across a tape head that polarizes the magnetic domains in the tape in proportion to the audio signal. Tape-recording devices include the reel-to-reel tape deck and the cassette deck, which uses a cassette for storage. The use of magnetic tape for sound recording originated around 1930 in Germany as paper tape with oxide lacquered to it. Prior to the development of magnetic tape, magnetic wire recorders had successfully demonstrated the concept of magnetic recording, but they never offered audio quality comparable to the other recording and broadcast standards of the time. This German invention was the start of a long string of innovations that have led to present-day magnetic t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)