[ ISEE-1 and ]ISEE-2
The ISEE-2 (International Sun-Earth Explorer-B or ISEE-B) was an Explorer-class daughter spacecraft, International Sun-Earth Explorer-2, was part of the mother/daughter/heliocentric mission (ISEE-1, ISEE-2, ISEE-3). ISEE-2 was a space probe use ...
were launched on 22 October 1977, and they re-entered on 26 September 1987.[ ]
Mission

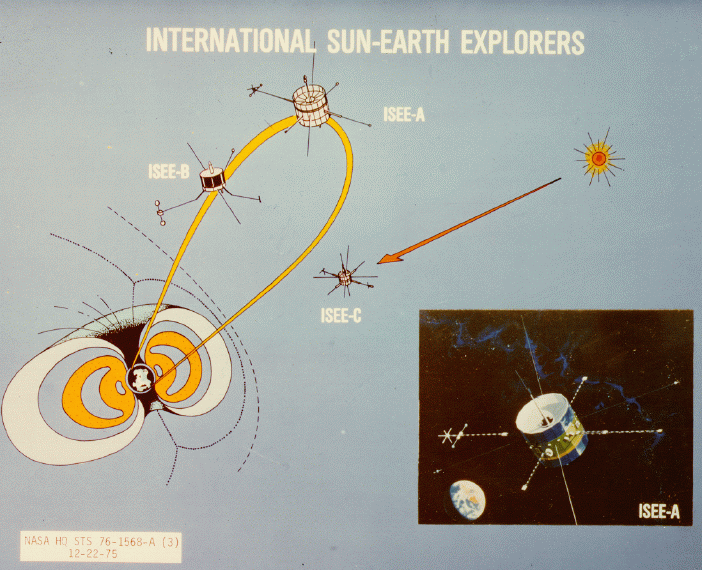 The purposes of the mission were: (1) to investigate solar-terrestrial relationships at the outermost boundaries of the
The purposes of the mission were: (1) to investigate solar-terrestrial relationships at the outermost boundaries of the Earth's magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dyn ...
, (2) to examine in detail the structure of the solar wind near the Earth and the shock wave that forms the interface between the solar wind and the Earth's magnetosphere, (3) to investigate motions of and mechanisms operating in the plasma sheets, and (4) to continue the investigation of cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s and solar flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phe ...
effects in the interplanetary region near 1 AU. The three spacecraft carried a number of complementary instruments for making measurements of plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
s, energetic particles, waves, and fields. The mission thus extended the investigations of previous IMP spacecraft. The mother/daughter portion of the mission consisted of two spacecraft (ISEE-1 and ISEE-2) with station-keeping capability in the same highly eccentric geocentric orbit with an apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any ellip ...
of 23 Earth radii
Earth radius (denoted as ''R''🜨 or R_E) is the distance from the center of Earth to a point on or near its surface. Approximating the figure of Earth by an Earth spheroid, the radius ranges from a maximum of nearly (equatorial radius, deno ...
(Re).[ ] During the course of the mission, the ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 orbit parameters underwent short-term and long-term variations due to solar and lunar
Lunar most commonly means "of or relating to the Moon".
Lunar may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lunar'' (series), a series of video games
* "Lunar" (song), by David Guetta
* "Lunar", a song by Priestess from the 2009 album ''Prior t ...
perturbations. These two spacecraft maintained a small separation distance, and made simultaneous coordinated measurements to permit separation of spatial from temporal irregularities in the near-Earth solar wind, the bow shock
In astrophysics, a bow shock occurs when the magnetosphere of an astrophysical object interacts with the nearby flowing ambient plasma such as the solar wind. For Earth and other magnetized planets, it is the boundary at which the speed of ...
, and inside the magnetosphere. By maneuvering ISEE-2, the inter-spacecraft separation as measured near the Earth's bow shock was allowed to vary between and ; its value is accurately known as a function of time and orbital position.European Space Research Organisation
The European Space Research Organisation (ESRO) was an international organisation founded by 10 European nations with the intention of jointly pursuing scientific research in space. It was founded in 1964. As an organisation ESRO was based on a ...
(ESRO) (later European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
(ESA)) designed to study the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic f ...
and the solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sola ...
. At least 32 institutions were involved, and the focus was on understanding magnetic fields. ISEE-1 and ISEE-3 were built by NASA, while ISEE-2 was built by ESA. All three had complementary instruments supported by the same group of over 100 scientists.
Spacecraft
ISEE-1 was a cylinder at 16 sided of of diameter and of in height.[ ] The spacecraft were spin stabilized, with the spin vectors maintained nominally within 1° of perpendicular to the ecliptic plane
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic again ...
, pointing north. The spin rates were nominally 19.75 rpm
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionl ...
for ISEE-1 and 19.8 rpm for ISEE-2, so that there was a slow differential rotation between the two spacecraft. The ISEE-1 body-mounted solar array provided approximately 175 watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Wa ...
s initially and 131 watts after three years, at 28 volts during normal operation. The ISEE-1 data rate was 4096 bps most of the time and 16384 bit/s during one orbit out of every five (with some exceptions).
Experiments
DC and low frequency electric fields, double-probe (0.19-1900 Hz)
This experiment was intended to study quasi-static electric fields and low-frequency plasma waves in the plasmasphere
The plasmasphere, or inner magnetosphere, is a region of the Earth's magnetosphere consisting of low-energy (cool) plasma. It is located above the ionosphere. The outer boundary of the plasmasphere is known as the plasmapause, which is defined ...
, magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynam ...
, magnetosheath
The magnetosheath is the region of space between the magnetopause and the bow shock of a planet's magnetosphere. The regularly organized magnetic field generated by the planet becomes weak and irregular in the magnetosheath due to interaction with ...
, and solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sola ...
. The double-probe floating-potential technique was applied using long-wire antenna probes with an effective electric field baseline of . The DC differential voltage was measured 8 or 32 times per second, depending on bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time.
The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction w ...
. In addition, the DC field was measured at selected azimuthal angles relative to the Sun and the magnetic field, and the peak value of delta-v
Delta-''v'' (more known as "change in velocity"), symbolized as ∆''v'' and pronounced ''delta-vee'', as used in spacecraft flight dynamics, is a measure of the impulse per unit of spacecraft mass that is needed to perform a maneuver such as ...
and its azimuthal angle
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north.
Mathematicall ...
s were measured. Low-frequency waves were measured in eight frequency bands as follows: 0.19 to 0.6, 0.6 to 1.9, 1.9 to 6, 6 to 19, 19 to 60, 60 to 190, 190 to 600, and 600 to 1900 Hz. The DC-mode measurements had a two-step, variable-gain amplifier controlled from the ground. The resolution in the highest gain state was 0.5E-6 V/m. The AC measurement electronics consisted of two amplifier sections. One amplifier was used for low-frequency channels, and one for high-frequency channels. Gain lines for each amplifier were independently controllable from the ground. In the highest-gain mode, each analyzer channel had a sensitivity of 0.04E-6 V/m (rms). The experiment could be run in either a Sun-sensor synchronized or a free state as controlled from the ground. In addition, the AC portion could be run in an averaging mode, or an alternating averaging and peak-amplitude-detection mode keyed to the telemetry readout sequence.[ ]
Electron and Proton Fluxes in the Outer Magnetosphere (1.5-300 keV)
This experiment was designed to determine, by using identical instrumentation (see ISEE-2) on the mother/daughter spacecraft, the spatial extent, propagation velocity, and temporal behavior of a wide variety of particle phenomena. Electrons were measured at 2 and 6 keV and in two bands: 8 to 200 keV and 30 to 200 keV. Protons were measured at 2 and 6 keV and in three bands: 8 to 200 keV, 30 to 200 keV, and 200 to 380 keV. The 30 keV threshold could be commanded to 15 or 60 keV. Identical instrumentation on each spacecraft consisted of a pair of surface-barrier semiconductor detector
A semiconductor detector in ionizing radiation detection physics is a device that uses a semiconductor (usually silicon or germanium) to measure the effect of incident charged particles or photons.
Semiconductor detectors find broad applicati ...
telescopes (one with a foil and one without a foil) and four fixed-voltage cylindrical electrostatic analyzer An electrostatic analyzer or ESA is an instrument used in ion optics that employs an electric field to allow the passage of only those ions or electrons that have a given specific energy. It usually also focuses these particles (concentrates the ...
s (two for electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
s and two for proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
s). Channel multipliers were used as detectors with the fixed-voltage analyzers. The telescopes had a viewing cone with a 40° half-angle, oriented at about 20° to the spin axis.[ ]
Energetic Ion Mass Spectrometer (0-17 keV/q; 1 AMU to > 150 AMU)
The objective of this investigation was to determine the ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
composition and energy spectra of the plasma within the magnetosphere, magnetosheath, and solar wind, and to determine the angular distribution of the plasma in the magnetosheath. An energetic ion mass spectrometer was flown that had an electrostatic energy analyzer followed by a combined cylindrical electrostatic/magnetic mass analyzer. A combination of electron multipliers was used as the detector. The energy-per-unit-charge range measured was from 0 to 17 keV/Q. The mass-per-unit-charge range measured extended from 1 to 150 u/Q.[ ]
Fast Plasma Experiment (FPE) and Solar Wind Ion Experiment (SWE)
This experiment was designed, in conjunction with a similar instrument (1977-102B-01) provided by G. Paschmann of Max Planck Institute
Max or MAX may refer to:
Animals
* Max (dog) (1983–2013), at one time purported to be the world's oldest living dog
* Max (English Springer Spaniel), the first pet dog to win the PDSA Order of Merit (animal equivalent of OBE)
* Max (gorilla) (1 ...
for flight on the daughter spacecraft, to study the plasma velocity distribution and its spatial and temporal variations in the solar wind, bow shock, magnetosheath, magnetopause
The magnetopause is the abrupt boundary between a magnetosphere and the surrounding plasma. For planetary science, the magnetopause is the boundary between the planet's magnetic field and the solar wind. The location of the magnetopause is d ...
, magnetotail
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body
An astronomical object, c ...
, and magnetosphere. The FPE consists of three high efficience 90° spherical section electrostatic analyzers using large secondary emitters and discrete dynode multipliers to detect analyzed particles. Two of them, viewing in opposite directions, produce complete 2D velocity distribution measurements of both protons and electrons every spacecraft revolution. A third FPE analyzer with a divided emitter measures 3D distributions at a slower rate. Protons from 50 eV to 40 keV and electrons from 5 eV to 20 keV were measured The experiment operated in two ranges, with energy resolution for the several steps in each range of 10% of the center energy level. The Solar Wind Experiment (SWE) measures solar wind ions. It is composed of two 150° spherical section analyzers using the same set of plates. The two acceptance fans are tilted with respect to each other so that 3D characteristics of the ion distributions can be derived. The ion experiment had degraded by April 1980 and the density values are suspected to be too low in later years. To protect the instrument, this experiment was turned off whenever the spacecraft was below . The Fast Plasma Experiment (FPE) had degraded by January 1978.[ ]
Gamma-Ray Bursts (Time History)
This experiment was designed to recognize and record the time history of gamma-ray burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are immensely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most energetic and luminous electromagnetic events since the Big Bang. Bursts can last from ten milli ...
s. Two sensors were used: a -diameter, CsI scintillator system and a 6-cm2, solid-state (Cadmium telluride
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) is a stable crystalline compound formed from cadmium and tellurium. It is mainly used as the semiconducting material in cadmium telluride photovoltaics and an infrared optical window. It is usually sandwiched with ca ...
(CdTe)) array. An intensity increase in either of the sensors could cause a trigger signal to occur, freezing the circulating memory of the immediate past counting-rate history and filling another memory with the counting rates for 1 minute following the trigger signal. The time of the trigger signal and its location in the temporal history were also stored in memory. All stored information was then read out at a very low bit rate during the succeeding several hours. Three trigger signals were used based on total counts in 4 ms, 32 ms, and 256 ms. Six memories were used, three before and three after the trigger signal, yielding storage of 1/64, 1/8, and 1 minute of data each to provide detailed rise-time information.[ ]
Low Energy Cosmic Ray Experiment
This instrument, carried on both ISEE-1 and ISEE-3, was designed to measure solar, interplanetary, and magnetospheric energetic ions in numerous bands within the energy range 2 keV/charge to 80 MeV/nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number (nucleon number).
Until the 1960s, nucleons were ...
, and electrons in four contiguous bands from 75 to 1300 keV. At the lower energies, charge states of heavy ions in the high-speed (> ) solar wind were determined. In the range 0.3 to 80 MeV/nucleon, the energy spectra, anisotropies, and composition of energetic ions were determined. In the limited range 0.4 to 6 MeV/nucleon, simultaneous determination of ionic and nuclear charge was possible. The instrument consisted of three different sensor systems. "ULECA" (ultralow-energy charge analyzer) was an electrostatic analyzer An electrostatic analyzer or ESA is an instrument used in ion optics that employs an electric field to allow the passage of only those ions or electrons that have a given specific energy. It usually also focuses these particles (concentrates the ...
with solid-state detectors. Its energy range was approximately 3 to 560 keV/charge. "ULEWAT" (ultralow-energy wide-angle telescope) was a double dE/dx vs E, thin-window, flow-through proportional counter/solid-state detector telescope covering the range 0.2 to 80 MeV/nucleon (Fe). "ULEZEQ" (ultralow-energy Z, E, and Q) was a combination of an electrostatic analyzer and a dE/dx vs E system with a thin-window proportional counter and a position-sensitive solid-state detector. The energy range was 0.4 to 6 MeV/nucleon. Data was obtained in 45° sectors.[ ]
Low-Energy Proton and Electron Differential Energy Analyzer (LEPEDEA)
This experiment was designed to study, by means of identical instrumentation on the mother/daughter spacecraft, the spatial and temporal variations of the solar wind and magnetosheath electrons and ions. Protons and electrons in the energy range from 1 eV to 45 keV were measured in 64 contiguous energy bands with an energy resolution (delta E/E) of 0.16. A quadrispherical low-energy proton and electron differential energy analyzer (LEPEDEA), employing seven continuous channel electron multipliers in each of its two (one for protons and one for electrons) electrostatic analyzers was flown on both the mother and the daughter spacecraft. All but 2% of the 4-pi-sr solid angle was covered for particle velocity vectors. A Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborated w ...
was also included, with a conical field of view of 40° full-angle, perpendicular to the spin axis. This detector was sensitive to electrons with E>45 keV, and to protons with E>600 keV.[ ]
Medium Energy Particles Experiment (METE)
This experiment was designed to identify and to study plasma instabilities responsible for acceleration, source and loss mechanisms, and boundary and interface phenomena throughout the orbital range of the mother/daughter satellites. A proton telescope and an electron spectrometer were flown on each spacecraft to measure detailed energy spectrum and angular distributions. These detectors used silicon surface-barrier, totally depleted solid-state devices of various thicknesses, areas, and configurations. Protons in 8 or 16 channels between 20 keV and 1.2 MeV, and electrons in 8 or 16 channels between 20 keV and 1 MeV, were measured. A separate solid-state detector system measured the energy spectra and pitch-angle distributions of alpha particles and heavy ions in the energy range above 125 keV per nucleon.[ ]
Plasma (Total Electron) Density by Radio Techniques
This experiment measured the plasma electron density near the mother satellite and also the total electron content between the mother (ISEE-1) and the daughter (ISEE-2) spacecraft. The experiment consisted of two distinct parts. The mother spacecraft carried an experiment (the sounder) to detect resonances of the ambient plasma. After an antenna had been momentarily excited at one of the characteristic frequencies of the plasma in which it was immersed, a pronounced "ringing" was observed. These resonances occurred at the plasma frequency, the upper hybrid resonance, the cyclotron frequency
Cyclotron resonance describes the interaction of external forces with charged particles experiencing a magnetic field, thus already moving on a circular path. It is named after the cyclotron, a cyclic particle accelerator that utilizes an oscillati ...
and its harmonics, and the measurement of their frequencies permitted the determination of several plasma parameters, including the electron density. In this experiment, the transmitter was designed to step through 128 sub-bands, covering the characteristic resonance frequencies of the plasma, from 0.3 to 50.9-kHz, and from 0 to 353-kHz. The integrated density between the mother and the daughter was obtained from a second experiment (the propagation experiment) that measured the phase delay introduced by the ambient plasma onto a wave of frequency about 683-kHz transmitted from the mother and received on the daughter (experiment 1977-102A-06). The phase was compared against a phase-coherent signal transmitted from the mother to the daughter by modulation onto a carrier of frequency high enough to be unaffected by the ambient plasma (272.5-MHz). Due to perturbations to other experiments, active operation was on a limited duty cycle.[ ]
Plasma waves: electric and magnetic fields spectra, flux, direction (5.62 Hz-31.1 khz)
This experiment, in conjunction with a similar (but simpler) experiment (1977-102B-05) on ISEE-2, was designed to measure wave phenomena occurring within the magnetosphere and solar wind. Three electric dipole antennas (, and ) and a triaxial search-coil antenna were used. The instrumentation consisted of four main elements: (1) a narrow-band sweep-frequency receiver with 32 frequency steps in each of four bands from 100-Hz to 400-kHz, a complete sweep required 32 seconds; (2) a high-time-resolution spectrum analyzer with 20 channels from 5.62-Hz to 31.1-kHz for electric field and 14 identical channels from 5.62-Hz to 10-kHz for magnetic field information, the electric and magnetic channels were sampled simultaneously; (3) a wave-normal analyzer to provide components for computing the wave normal and the Poynting flux, this analyzer had a 10-Hz bandwidth, and covered 32 frequencies from 100-Hz to 5-kHz; and (4) a wide-band receiver to condition electric and magnetic waveforms for transmission to the ground via the special-purpose analog transmitter, this receiver also provided the signals for long-baseline-interferometer measurements between ISEE-1 and ISEE-2. There were two basic frequency channels: 10-Hz to 1-kHz and 650-Hz to 10 or 40-kHz. In addition, the frequency range could be shifted by a frequency-conversion scheme to any of eight ranges up to 2-MHz.[ ]
Quasi-static and low-frequency electric fields (0.1-200 mV/m, frequency < 1000Hz)
The objective of this experiment was to study quasi-static and low-frequency electric fields in the plasmasphere, magnetosphere, magnetosheath, and solar wind. Measurements were made of the potential difference between a pair of diameter vitreous carbon spheres which were separated by and mounted on the ends of wire booms in the satellite spin plane. To attempt to overcome the spacecraft sheath (a potential problem which plagues all electric field detectors), an electron gun for changing the spacecraft potential was included, and all exposed spacecraft surfaces were made electrically conducting. The instrument was designed to be sensitive to fields from 0.1 to 200 mV/m in the frequency band of 0 to 12-Hz. The experiment also measured the electric field component of waves at frequencies below 1000-Hz.[ ]
Triaxial Fluxgate Magnetometer
The magnetic fields investigation selected for ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 had as its principal objectives the study of the magnetic signatures of magnetospheric phenomena and magnetohydrodynamic waves in and around the magnetosphere, and to provide supporting data for other experiments on the spacecraft such as the electric field, particle and plasma wave investigations. In this triaxial fluxgate magnetometer, three ring-core sensors in an orthogonal triad were enclosed in a flipper mechanism at the end of the magnetometer boom. The electronics unit was on the main body of the spacecraft at the foot of the boom. The magnetometer had two operating ranges of ± 8192 nT and ± 256 nT in each vector component. The data were digitized and averaged within the instrument to provide increased resolution and to provide Nyquist filter
A Nyquist filter is an electronic filter used in TV receivers to equalize the video characteristics. The filter is named after the Swedish–US engineer Harry Nyquist (1889–1976).
VSB
In analogue TV broadcasting the visual radio frequency (RF ...
ing. There were two modes for the transmission of the averaged data. In the double-precision mode of operation, 16-bit samples of data were transmitted. This provided a maximum resolution of ± 1/4 nT or 1/128 nT in the low-sensitivity and high-sensitivity ranges. In the single-precision mode, any 8 consecutive bits of the above 16 bits were selected by ground command for transmission and the telemetry bandwidths of the magnetometer were doubled. This bandwidth varied from 2-Hz for the low-telemetry-rate, double-precision experiment mode to 32-Hz for the high-telemetry-rate, single-precision experiment mode. Operation of this experiment was near nominal until spacecraft re-entry on 26 September 1987. Users of data from this experiment should be aware of the fact that the averaging of 12-bit samples to create 16-bit samples worked well in the spin plane, but in situations during which the field along the spin axis was quiet relative to the size of a digital window, the magnetometer returned only a 12-bit sample. This was particularly noticeable when the spacecraft was in the solar wind and the instrument was operated in its low gain (8192 nT) range, and when the spacecraft was in quiet regions of the magnetosphere in the low gain mode. The former situation limited the resolution of the field measured to 4 nT in the double precision mode in which the magnetometer usually was operated, and the latter situation created, as the spacecraft moved through the large gradient in the Earth's magnetic field, a stairstep pattern of field changes of size 4 nT which may be mistaken for waves. Another operational anomaly was the saturation of a sensor during gain changes. At these times, the 3 components of the magnetic field were deduced from one spin tone and the field along the spin axis, limiting the temporal resolution of the instrument to below the spin frequency. Every effort was made to minimize zero level errors, clerical errors and other data processing anomalies within the available resources. However, these resources were very constrained and funding ceased before the entire submitted data set could be checked.[ ]
Vector Electron Spectrometer Experiment
This experiment studied the transport coefficients of turbulence in the collisionless plasma represented by the interplanetary medium and magnetosheath, low-energy solar electron events, and bow-shock-associated electrons. Two triaxial systems of 127° cylindrical electrostatic analyzers were used to make three-dimensional measurements of the electron distribution function. There were three modes of operation, with the following nominal energy ranges: solar wind, 7 to 500 eV; magnetosheath, 10 eV to 2 keV; and magnetotail and solar, 105 eV to 7.05 keV. The energy resolution (delta E/E) was 0.07. The entire set of six simultaneous spectrometer measurements was taken while the satellite rotated through 60°. Each spectrometer consisted of a curved-plate analyzer and two channeltron detectors.[ ]
Very low frequency (1-32 kHz) Wave-Particle Interactions in the Magnetosphere
This experiment was intended to provide data to study interactions between discrete Very low frequency
Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave a ...
(VLF) waves and energetic particles in the magnetosphere. The VLF waves were produced by a ground-based transmitter. Injection of the waves beyond the ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an ...
was assured by transmitter location in a region where the magnetic lines of force are open: in this case, the Siple Station
Siple Station was a research station in Antarctica (), established in 1973 by Stanford's STAR Lab, to perform experiments that actively probed the magnetosphere using very low frequency (VLF) waves. Its location was selected to be near the Earth' ...
, Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
. The injected signal and any stimulated VLF emissions were recorded through a loop antenna by a 1 to 32-kHz broadband receiver on the satellite. The observed parameters were the intensities of received radio frequency waves as a function of time.[ ]
Orbit
ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 remained near the Earth. ISEE-3 was the first spacecraft to be placed in a halo orbit
A halo orbit is a periodic, three-dimensional orbit near one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics. Although a Lagrange point is just a point in empty space, its peculiar characteristic is that it ca ...
at the Earth-Sun Lagrange point and it was later deployed into a heliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit (also called circumsolar orbit) is an orbit around the barycenter of the Solar System, which is usually located within or very near the surface of the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in the Solar System, and the Sun i ...
.[
]
Atmospheric entry
Both ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 re-entered the Earth's atmosphere during orbit 1518 on 26 September 1987. Seventeen of 21 on-board experiments were operational at the end.
See also
* ISEE-2
The ISEE-2 (International Sun-Earth Explorer-B or ISEE-B) was an Explorer-class daughter spacecraft, International Sun-Earth Explorer-2, was part of the mother/daughter/heliocentric mission (ISEE-1, ISEE-2, ISEE-3). ISEE-2 was a space probe use ...
* International Cometary Explorer
The International Cometary Explorer (ICE) spacecraft (designed and launched as the International Sun-Earth Explorer-3 (ISEE-3) satellite), was launched 12 August 1978, into a heliocentric orbit. It was one of three spacecraft, along with the mo ...
(ISEE-3)
* 1977 in spaceflight
* List of heliophysics missions
This is a list of missions supporting heliophysics, including solar observatory missions, solar orbiters, and spacecraft studying the solar wind.
References
{{Orbital launches in 1977
Explorers Program
NASA space probes
Spacecraft which reentered in 1987
Spacecraft launched in 1977

 The purposes of the mission were: (1) to investigate solar-terrestrial relationships at the outermost boundaries of the
The purposes of the mission were: (1) to investigate solar-terrestrial relationships at the outermost boundaries of the