|
Dune Dam
Dune Dam is a long sand dune that lies at the western end of Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, near the confluence of the Chaco and Escavada Washs. The dune was created by winds that brought sand up the Chaco River. When the dune was large enough, it dammed the Chaco Wash and created a small and shallow lake near the Ancestral Puebloan great house, Penasco Blanco. Archeological evidence suggests that the dune was breached around 900 CE. Chacoans filled the breach with masonry sometime in the early 11th century, and built an accompanying reservoir lined with stones that was visible until 1920. The dam stopped Chaco Wash from further deepening, which helped raise the water table in the canyon, aiding Chacoan farming. The absence of a lacustrine plain A lacustrine plain or lake plain is a plain formed due to the past existence of a lake and its accompanying sediment accumulation. Lacustrine plains can be formed through one of three major mechanisms: glacial drainage, differential uplift, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat regions covered with wind-swept sand or dunes with little or no vegetation are called ''ergs'' or ''sand seas''. Dunes occur in different shapes and sizes, but most kinds of dunes are longer on the stoss (upflow) side, where the sand is pushed up the dune, and have a shorter ''slip face'' in the lee side. The valley or trough between dunes is called a ''dune slack''. Dunes are most common in desert environments, where the lack of moisture hinders the growth of vegetation that would otherwise interfere with the development of dunes. However, sand deposits are not restricted to deserts, and dunes are also found along sea shores, along streams in semiarid climates, in areas of glacial outwash, and in other areas where poorly cemented sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaco Culture National Historical Park
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote canyon cut by the Chaco Wash. Containing the most sweeping collection of ancient ruins north of Mexico, the park preserves one of the most important pre-Columbian cultural and historical areas in the United States. Between AD 900 and 1150, Chaco Canyon was a major center of culture for the Ancestral Puebloans. Chacoans quarried sandstone blocks and hauled timber from great distances, assembling fifteen major complexes that remained the largest buildings ever built in North America until the 19th century. Evidence of archaeoastronomy at Chaco has been proposed, with the "Sun Dagger" petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example. Many Chacoan buildings may have been aligned to capture the solar and lunar cycles, requiring generations of astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escavada Wash
Escavada Wash is a tributary of the Chaco Wash, in Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, United States. It flows south and west from its origin near Lybrook and meets the Chaco Wash at the west end of the canyon. Several small Ancestral Puebloan The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, an ... archeological sites border the wash, which is located north of the Chacoan great house Pueblo Alto. References Bibliography * Chaco Canyon Chaco Culture National Historical Park Colorado Plateau Geography of New Mexico Arroyos and washes of the United States {{NewMexico-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Puebloans
The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, were an ancient Native American culture that spanned the present-day Four Corners region of the United States, comprising southeastern Utah, northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, and southwestern Colorado. They are believed to have developed, at least in part, from the Oshara tradition, which developed from the Picosa culture. The people and their archaeological culture are often referred to as ''Anasazi'', meaning "ancient enemies", as they were called by Navajo. Contemporary Puebloans object to the use of this term, with some viewing it as derogatory. The Ancestral Puebloans lived in a range of structures that included small family pit houses, larger structures to house clans, grand pueblos, and cliff-sited dwellings for defense. They had a complex network linking hundreds of communities and population centers across the Colorado Plateau. They held a distinct knowledge of celestial sciences that found form in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great House (pueblo)
A great house is a large, multi-storied Ancestral Puebloan structure; they were built between 850 and 1150. Whereas the term "great house" typically refers to structures in Chaco Canyon, they are also found in more northerly locations in the San Juan Basin, including the Mesa Verde region. The purpose of the structures is unclear, but may have been to house large numbers of people, religious leaders, or royalty. They were designed and constructed to provide shelter to inhabitants in an arid climate and had protective walls and small windows. History and purpose Great house construction flourished during the late 11th and early 12th centuries, and may have begun as early as 800. Mesa Verdeans usually built their great houses on the site of older villages. The earliest examples of structures similar to great houses have been found along the Mimbres River in New Mexico. Archeologists differ as to their purpose, but they might have been residences for large numbers of people, or cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacustrine Plain
A lacustrine plain or lake plain is a plain formed due to the past existence of a lake and its accompanying sediment accumulation. Lacustrine plains can be formed through one of three major mechanisms: glacial drainage, differential uplift, and inland lake creation and drainage. Lake plains can have various uses depending on where and how they form. Over time, in regions where a lake once existed, as water drains or evaporates from the lake, the deposited sediments are left behind, resulting in a level plain of land where the lake once existed. The soil of the plain may constitute fertile and productive farmland due to the previous accumulation of lacustrine sediments; in other cases, it may become a wetland or a desert. Background Lacustrine plains are plains formed when lakes filled with sediments are drained. There are several reasons why drainage might occur, but in all cases the water in the lake is lost, leaving behind a level land of sediments. The resulting plain is an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In New Mexico
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaco Canyon
Chaco Culture National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park in the American Southwest hosting a concentration of pueblos. The park is located in northwestern New Mexico, between Albuquerque and Farmington, in a remote canyon cut by the Chaco Wash. Containing the most sweeping collection of ancient ruins north of Mexico, the park preserves one of the most important pre-Columbian cultural and historical areas in the United States. Between AD 900 and 1150, Chaco Canyon was a major center of culture for the Ancestral Puebloans. Chacoans quarried sandstone blocks and hauled timber from great distances, assembling fifteen major complexes that remained the largest buildings ever built in North America until the 19th century. Evidence of archaeoastronomy at Chaco has been proposed, with the "Sun Dagger" petroglyph at Fajada Butte a popular example. Many Chacoan buildings may have been aligned to capture the solar and lunar cycles, requiring generations of astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
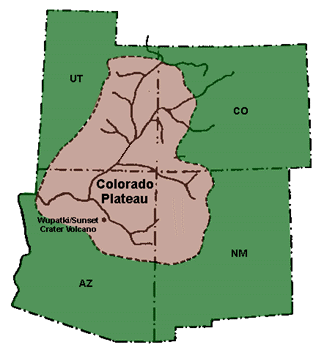
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)