|
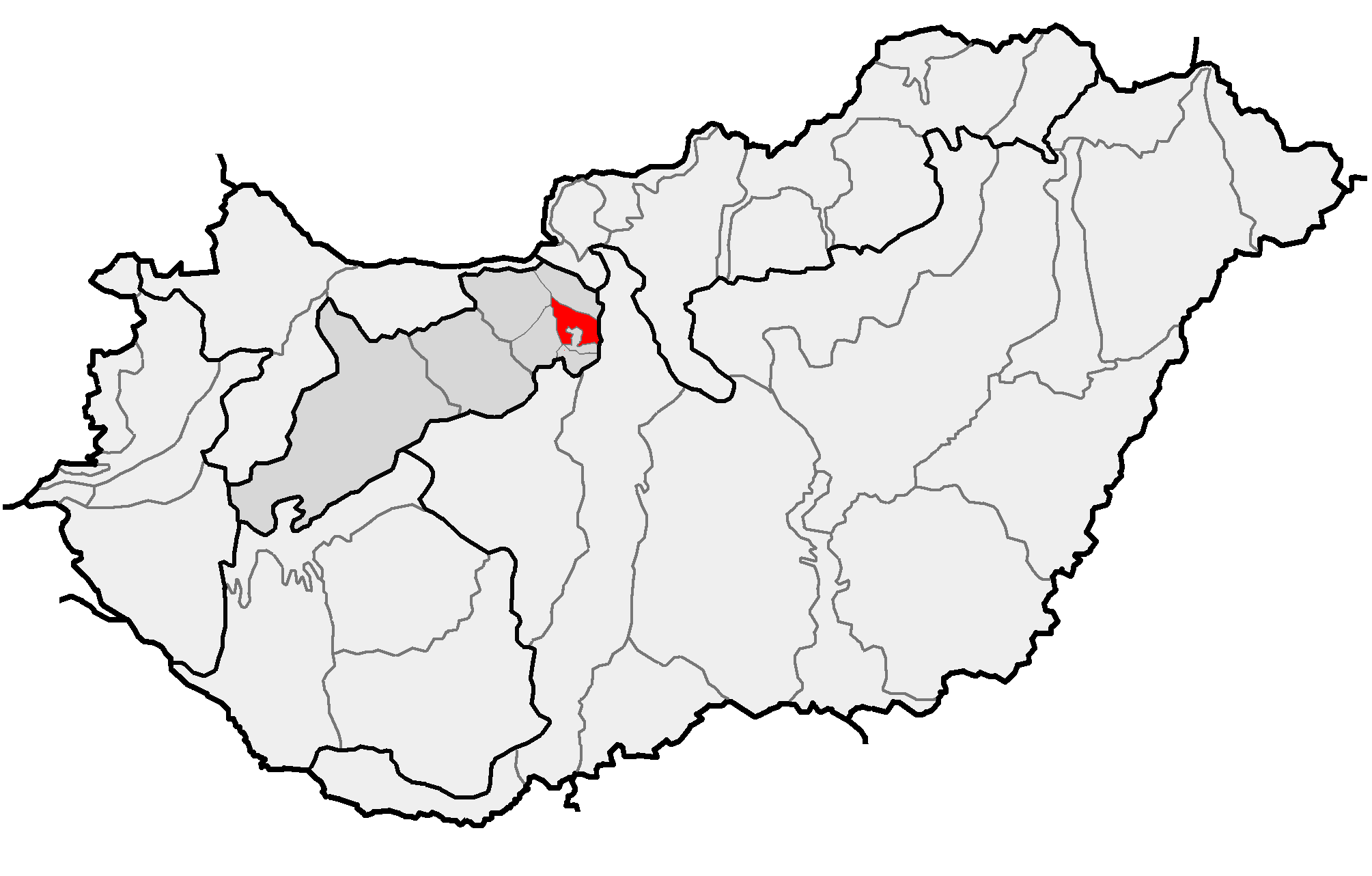
Dunazug Mountains
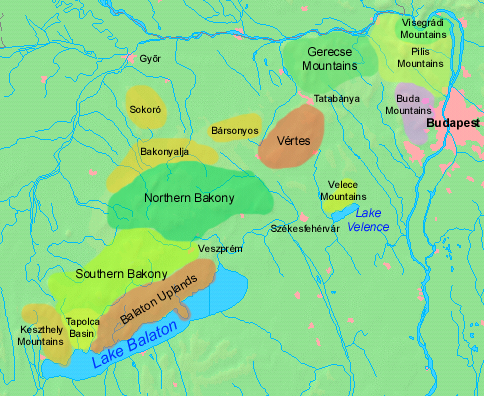
Dunazug Mountains (Hu: ''Dunazug hegyvidék'') is a part of Transdanubian Mountains in Hungary. It is the easternmost part of the mountains that connects it to the Danube Bend and the capital. The name itself also comes from the river (in Hungarian ''Duna''), while ''zug'' means ''recess'', ''corner''. The highest peak is ''Pilis-tető'', about 750 metres, The mountains are made up of sedimentary rock, mainly limestone. Parts of the mountains * Gerecse Mountains *Pilis Mountains * Buda Hills The Buda Hills ( Hungarian: ''Budai-hegység'') are a low mountain range of numerous hills which dot the Buda side of Budapest, capital of Hungary. The most famous ones located within city limits are Gellért Hill, Castle Hill, Rózsadomb, , Jà ... Gallery File:Turistajelzés a Vértesben.jpg File:Gerecse pelifoldszentkeresztnel.JPG File:Gerecse látképe.jpg File:View of János Hill from Kis-Hárs Hill.JPG Sources (In Hungarian) *https://vandorbot.hu/dunazug-hegyvidek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transdanubian Mountains
__NOTOC__ The Transdanubian Mountains (sometimes also referred to as ''Bakony Forest, Dunántúl Highlands, Highlands of Dunántúl, Highlands of Transdanubia, Mountains of Dunántúl, Mountains of Transdanubia, Transdanubian Central Range, Transdanubian Hills, Transdanubian Midmountains'' or ''Transdanubian Mid-Mountains'', ) are a mountain range in Hungary covering about 7000 km2. Its highest peak is the ''Pilis'', with a height of . Parts of the mountains *Bakony ** ''Southern Bakony'' ** ''Northern Bakony'' *** Keszthely Plateau *** Tapolca Basin *** Balaton Uplands **** Bakonyalja **** Sokoró Hills *Vértes Mountains ** Vértesalja (Bársonyos) *Velence Hills * Dunazug Mountains **Gerecse Mountains **Buda Hills ** Pilis Mountains Visegrád Mountains are often considered a part of it for geopolitical reasons, but geographically they are part of the North Hungarian Mountains. Gallery File:Gulács01.jpg File:Pliocene Volcanoes near Lake Balaton in Hungary.jpg File: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 9 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, the official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic language and among the few non-Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr. The territory of present-day Hungary has for centuries been a crossroads for various peoples, including Celts, Romans, Germanic tribes, Huns, West Slavs and the Avars. The foundation of the Hungarian state was established in the late 9th century AD with the conquest of the Carpathian Basin by Hungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube Bend
The Danube Bend ( hu, Dunakanyar) is a curve of the Danube in Hungary, close to the town of Visegrád. Geology The present-day U-shaped loop is probably the result of an eruption of the volcano stretching over the whole area some 15 million years ago. The caldera of Keserűs Hill-volcano, with the associated lava dome formed a later eroded central in the north. The river follows the southern edge of this caldera. The region This region is touristically very significant. The landscape and the river attracts a lot of visitors both from the homeland and abroad. The most important towns are Visegrád, Szentendre and Budapest, while on the other (left) bank of the river can be found Vác, Nagymaros and some smaller towns, villages. The islands of the region are also interesting, mainly the large Szentendrei-sziget and Margaret Island (Margitsziget) within the capital city. Gallery Catedral of Vác.jpg, The Cathedral of Vác Visegrad danube.jpg, Szentendrei-sziget RedBio T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a city and county, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,303,786; it is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celtic settlement transformed into the Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Lower Pannonia. The Hungarians arrived in the territory in the late 9th century, but the area was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241–42. Re-established Buda became one of the centres of Renaissance humanist culture by the 15th century. The Battle of Mohács, in 1526, was followed by nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule. After the reconquest of Buda in 1686, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus (organic matter). The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transdanubian Medium Mountains Map
Transdanubian may refer to: * relative term, designating someone or something related to any region ''beyond'' the Danube river (lat. ''trans-'' / beyond, over), depending on a point of observation * Transdanubian Bulgaria, historical designation for regions under former Bulgarian rule to the north from the Danube river * Transdanubian Hungary, designation for Hungarian regions to the west of the Danube river ** Transdanubian Mountains (Hungary), mountains in Transdanubian regions of Hungary ** Battle of the Transdanubian Hills, a World War II battle (1945) fought in Transdanubian regions of Hungary * Transdanubian Romania, designation for Romanian regions to the east of the Danube river (North Dobruja) * ''Transdanubian Serbia'', designation for Serbian regions to the north of the Danube river (Serbian Banat and Serbian BaÄŤka) * ''Transdanubian Vienna'' (''Transdanubien'' in Viennese German), designation for Vienna city districts to the northeast of the Danube river (Donaustadt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerecse Mountains
Gerecse is a mountain range in north-western Hungary, that belongs to the Transdanubian Mountains Geography The range lies in the Central Transdanubian region and connects Vértes Hills with Pilis Mountains in Komárom-Esztergom County, between the town of Tatabánya and the Danube River. Gerecse occupies an area of 850 km2 (20,300 ha). The highest point is ''Nagy-Gerecse'' at 634 m. The main rock is limestone and chalk. Biology Deciduous oak forests cover the lower slopes, with submontane species of Quercus, Carpinus, Fagus, and at higher altitudes karst scrub. The area is 70% forest, 5% scrubland, 10% grassland, and 15% artificial landscapes. Yearly sunshine duration is around 1,980 hours. The average annual temperature above the height of 350 meters is 9.5 C (in January -2,8 C). The average annual precipitation is 640 millimeters. Gallery Image:Farkasvölgy.jpg, Farkasvölgy (Wolf-valley) Image:Forest in Gerecse Mountains.jpg, Forest in the Gerecse Image:Pusztam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilis Mountains
Pilis Mountains is a mountainous region in the Transdanubian Mountains. Its highest peak is ''Pilis-tető'' at . It is a popular hiking destination in Hungary. It is the direct southern neighbour of the Visegrád Mountains which are based on volcanic rocks while Pilis is sedimentary. History of the region The region used to be a hunting area for the mediaeval kings. Numerous hunting lodges have survived. One of the most frequented areas was around the village Pilisszentkereszt. Mountains of the range * , the second highest point of Transdanubia Transdanubia ( hu, Dunántúl; german: Transdanubien, hr, Prekodunavlje or ', sk, Zadunajsko :sk:Zadunajsko) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary. Administrative divisions Trad .... * * Csikóváralja References Transdanubian Mountains Biosphere reserves of Hungary {{Hungary-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buda Hills
The Buda Hills ( Hungarian: ''Budai-hegység'') are a low mountain range of numerous hills which dot the Buda side of Budapest, capital of Hungary. The most famous ones located within city limits are Gellért Hill, Castle Hill, Rózsadomb, , János Hill, and Eagle Hill. These hills consist of both nature and residential areas. Geology The Budaörs dolomite of Anisian-Carnian age (Triassic period) is the oldest formation which crops out in the Buda Hills. Younger Triassic succession is composed of cherty dolomite and limestone (basin facies), and dolomite combined with limestone (platform facies). The Trassic surface is composed of karstified carbonates, which are overlain by an Upper Eocene succession made of conglomerate beds. During the period from the terminal Cretaceous to Priabonian, the area was a karstic terrestrial environment displaying distinct relief differences. It was also the time when Triassic formations were eroded. The continental period (ended by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |