|
Dudley B. Menzies Bridge
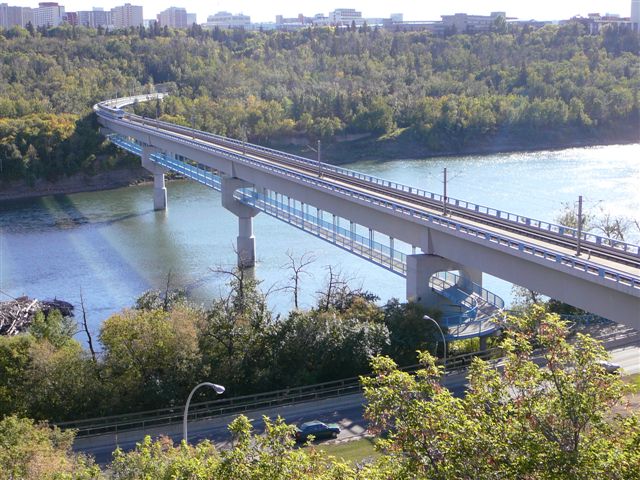
The Dudley B. Menzies Bridge is a dedicated LRT bridge crossing the North Saskatchewan River in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. Named after Edmonton engineer and politician Dudley Blair Menzies, the bridge was the "first concrete segmental box girder bridge in Western Canada". The main deck carries two tracks of the LRT system connecting Government Centre station and the University station. A walkway for pedestrians and bicycles hangs beneath the main spans of the bridge over the river. The American Concrete Institute recognized the joint venture company that built the Dudley B. Menzies Bridge with an Award of Excellence for Design and Construction in Concrete. Gallery File:Edmonton area 004.jpg, Dudley B. Menzies Bridge in front of High Level Bridge, May 2005 File:Edmhighlevel.jpg, Dudley B. Menzies Bridge, September 2006 File:High level Bridge Edmonton Alberta Canada 06-B.jpg, South pier of High Level Bridge, with Dudley B. Menzies Bridge in distance, May 2008 File:High L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Saskatchewan River
The North Saskatchewan River is a glacier-fed river that flows from the Canadian Rockies continental divide east to central Saskatchewan, where it joins with the South Saskatchewan River to make up the Saskatchewan River. Its water flows eventually into the Hudson Bay. The Saskatchewan River system is the largest shared between the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. Its watershed includes most of southern and central Alberta and Saskatchewan. Course The North Saskatchewan River has a length of , and a drainage area of . At its end point at Saskatchewan River Forks it has a mean discharge of . The yearly discharge at the Alberta–Saskatchewan border is more than . The river begins above at the toe of the Saskatchewan Glacier in the Columbia Icefield, and flows southeast through Banff National Park alongside the Icefields Parkway. At the junction of the David Thompson Highway (Highway 11), it initially turns northeast for before switching to a more direct easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Mountain House
Rocky Mountain House is a town in west-central Alberta, Canada. It is approximately west of Red Deer at the confluence of the Clearwater and North Saskatchewan Rivers, and at the crossroads of Highway 22 (Cowboy Trail) and Highway 11 (David Thompson Highway). The surrounding Clearwater County's administration office is located in Rocky Mountain House. History The town has a long history dating to the 18th century with the presence of British and Canadian fur traders during the westward Canadian expansion. In 1799, the Hudson's Bay Company and the North West Company each established the Rocky Mountain House and Acton House fur trading posts. Trade with the local aboriginal peoples continued until 1821 when the companies merged, they continued to trade until 1875 and closed the Rocky Mountain House post. The name of the settlement however remained. The Rocky Mountain House settlement also served as a launching point for many explorers such as David Thompson, in search for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Girder Bridges
A box girder bridge, or box section bridge, is a bridge in which the main beams comprise girders in the shape of a hollow box. The box girder normally comprises prestressed concrete, structural steel, or a composite of steel and reinforced concrete. The box is typically rectangular or trapezoidal in cross-section. Box girder bridges are commonly used for highway flyovers and for modern elevated structures of light rail transport. Although the box girder bridge is normally a form of beam bridge, box girders may also be used on cable-stayed and other bridges. Development of steel box girders In 1919, Major Gifford Martel was appointed head of the Experimental Bridging Establishment at Christchurch, Hampshire, which researched the possibilities of using tanks for battlefield engineering purposes such as bridge-laying and mine-clearing. Here he continued trials on modified Mark V tanks. The bridging component involved an assault bridge, designed by Major Charles Ingli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridges Completed In 1993
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridges In Edmonton
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The '' Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Bridges In Alberta
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Crossings Of The North Saskatchewan River ...
This is a list of crossings of the North Saskatchewan River in the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Alberta from the river's confluence with the South Saskatchewan River upstream to its source. Tables Saskatchewan Alberta Notes References * *{{Google maps, url=https://www.google.ca/maps/@52.9929052,-111.1706652,5.75z, title=North Saskatchewan River in Western Canada, accessdate=November 17, 2016 * North Saskatchewan River The North Saskatchewan River is a glacier-fed river that flows from the Canadian Rockies continental divide east to central Saskatchewan, where it joins with the South Saskatchewan River to make up the Saskatchewan River. Its water flows eventual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groat Bridge
Groat Bridge is a bridge that spans the North Saskatchewan River in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It is a part of Groat Road. The bridge is composed of two spans that are side by side. The original structure was rehabilitated in 1990 and again in 2020. The 2020 $48 million rehabilitation saw the decks of both spans replaced one side at a time, with the new decks placed on the existing piers. The new decks feature an expanded shared-use path on the east side of the bridge ( wide, compared to the original wide sidewalk). Groat bridge connects the communities of River Valley Mayfair on the south end to River Valley Glenora on the north end. See also * List of bridges in Canada This is a list of bridges and viaducts in Canada, including those for pedestrians and vehicular traffic. Historical and architectural interest bridges There are only a few covered bridges left in Canada compared to all those that were built in t ... References External links * Bridges in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Level Bridge (Edmonton)
The High Level Bridge is a bridge that spans the North Saskatchewan River in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. History Located next to the Alberta Legislature Building, the bridge linked the communities of Edmonton and Strathcona, which became one city in 1912. It was designed from the outset to accommodate rail, streetcar, two-way automobile, and pedestrian traffic. The original bridge design included three tracks on the upper deck: The middle track was for CPR trains, and the two outer tracks were for streetcars. The bridge was built by John Gunn and Sons of Winnipeg, who previously built other bridges for Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR). More than 500 workers were employed on the project at its peak, and four men died during the bridge's construction. Fifty steel workers went on strike in October 1912, demanding a 50-cent wage for nine hours of work, instead of 45 cents for ten hours of work. The bridge's upper deck was completed in May 1913. The first CPR train, pulling seven car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bridges In Canada
This is a list of bridges and viaducts in Canada, including those for pedestrians and vehicular traffic. Historical and architectural interest bridges There are only a few covered bridges left in Canada compared to all those that were built in the past. In the Quebec province, if we already counted 1200 in the last century, today there are only 88 remaining. In New Brunswick, 58 covered bridges have been identified. Major road and railway bridges The Canada's longest bridge is the Confederation Bridge in the Gulf of St. Lawrence with a total of between abutments, it's also the world's longest bridge over ice-covered water. More than 5,000 local workers helped with the project, which cost about $1 billion. The Quebec Bridge has been the longest cantilever bridge span in the world since 1917, measuring between its two piles. It helds the record of all-categories longest span in the world until the opening of the Ambassador Bridge, it's the last bridge that broke such a rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city anchors the north end of what Statistics Canada defines as the " Calgary–Edmonton Corridor". As of 2021, Edmonton had a city population of 1,010,899 and a metropolitan population of 1,418,118, making it the fifth-largest city and sixth-largest metropolitan area (CMA) in Canada. Edmonton is North America's northernmost large city and metropolitan area comprising over one million people each. A resident of Edmonton is known as an ''Edmontonian''. Edmonton's historic growth has been facilitated through the absorption of five adjacent urban municipalities ( Strathcona, North Edmonton, West Edmonton, Beverly and Jasper Place) hus Edmonton is said to be a combination of two cities, two towns and two villages./ref> in addition to a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Concrete Institute
The American Concrete Institute (ACI, formerly National Association of Cement Users or NACU) is a non-profit technical society and standards developing organization. ACI was founded in January 1905 during a convention in Indianapolis. The Institute's headquarters are currently located in Farmington Hills, Michigan, USA. ACI's mission is "ACI develops and disseminates consensus-based knowledge on concrete and its uses." ACI History A lack of standards for making concrete blocks resulted in a negative perception of concrete for construction. An editorial by Charles C. Brown in the September 1904 issue of ''Municipal Engineering'' discussed the idea of forming an organization to bring order and standard practices to the industry. In 1905 the National Association of Cement Users was formally organized and adopted a constitution and bylaws. Richard Humphrey was elected its first President. The first committees were appointed at the 1905 convention in Indianapolis and offered prelimina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |