|
Dudipatsar Trail
The Dudipatsar Trail is an approximately hiking trail in the Lulusar-Dudipatsar National Park of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, in northern Pakistan. The trail goes along a tributary of the Kunhar River called Poorbi Narr in the northern Kaghan Valley. The headwater for the particular tributary is the Dudipat Lake and the trail has a cumulative elevation gain of . The average time taken to complete the trail is 5 to 8 hours. Overview The trail is entirely within the national park and passes through multiple life zones of the park, from lowland forests to alpine meadows of wildflowers. As the trail climbs up to the plateau, hikers see different wildlife in the region including marmots and different species of birds. The trail is of medium difficulty. The overall elevation gain isn't great but climbing at high altitude makes the trail more demanding. During the course of the trail, one encounters boulders, meadows, plateaus, snow (in early summer) and streams. The trail and the surr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lulusar-Dudipatsar National Park
Lulusar-Dodipat National Park is located in the Kaghan Valley in Mansehra District of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The park was created in 2003. The scenic Dudipatsar Lake and Lulusar Lake and peaks are in the park. Flora and fauna The flora includes the trees, shrubs, perennials, and herbs of the Himalayan Western Himalayan subalpine conifer forests and higher elevation Western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows ecoregions. Some of the park's fauna includes the snow leopard, black bear, marmot, weasel, lynx, leopard, Himalayan snowcock, and the snow partridge. The park's lakes and wetlands habitats are of significant ecological importance for resident fauna and migratory waterfowl. Access The road is accessible by cars and motorbikes. The 2005 Kashmir earthquake in North Pakistan made access more difficult. However, since 2006 the Pakistan government has taken steps to restore tourism in the Kaghan Valley, including rebuilding and new tourism facilities and infrastruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
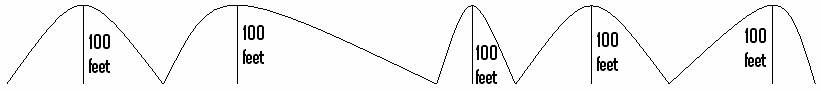
Elevation Gain
In running, cycling, and mountaineering, cumulative elevation gain refers to the sum of every gain in elevation throughout an entire trip. It is sometimes also known as cumulative gain or elevation gain, or often in the context of mountain travel, simply gain. Another commonly used phrase is total ascent. Elevation losses are not counted in this measure. Cumulative elevation gain, along with round-trip distance, is arguably the most important value used in quantifying the strenuousness of a trip. This is because hiking on flat land (zero elevation gain) is significantly easier than hiking up and down a large mountain with the same round-trip distance. Computation In the simplest case of a trip where hikers only travel ''up'' on their way to a single summit, the cumulative elevation gain is simply given by the difference in the summit elevation and the starting elevation. For example, if one starts hiking at a trailhead with elevation , and continues up to a summit of , the cumu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudipatsar Trail
The Dudipatsar Trail is an approximately hiking trail in the Lulusar-Dudipatsar National Park of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, in northern Pakistan. The trail goes along a tributary of the Kunhar River called Poorbi Narr in the northern Kaghan Valley. The headwater for the particular tributary is the Dudipat Lake and the trail has a cumulative elevation gain of . The average time taken to complete the trail is 5 to 8 hours. Overview The trail is entirely within the national park and passes through multiple life zones of the park, from lowland forests to alpine meadows of wildflowers. As the trail climbs up to the plateau, hikers see different wildlife in the region including marmots and different species of birds. The trail is of medium difficulty. The overall elevation gain isn't great but climbing at high altitude makes the trail more demanding. During the course of the trail, one encounters boulders, meadows, plateaus, snow (in early summer) and streams. The trail and the surr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marmots
Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, when they hibernate underground. They are the heaviest members of the squirrel family. Description Marmots are large rodents with characteristically short but robust legs, enlarged claws which are well adapted to digging, stout bodies, and large heads and incisors to quickly process a variety of vegetation. While most species are various forms of earthen-hued brown, marmots vary in fur coloration based roughly on their surroundings. Species in more open habitat are more likely to have a paler color, while those sometimes found in well- forested regions tend to be darker. Marmots are the heaviest members of the squirrel family. Total length varies typically from about and body mass averages about in spring in the smaller species and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildflower
A wildflower (or wild flower) is a flower that grows in the wild, meaning it was not intentionally seeded or planted. The term implies that the plant probably is neither a hybrid nor a selected cultivar that is in any way different from the way it appears in the wild as a native plant, even if it is growing where it would not naturally. The term can refer to the flowering plant as a whole, even when not in bloom, and not just the flower. "Wildflower" is not an exact term. More precise terms include ''native species'' (naturally occurring in the area, see flora), ''exotic'' or, better, ''introduced species'' (not naturally occurring in the area), of which some are labelled ''invasive species'' (that out-compete other plants – whether native or not), ''imported'' (introduced to an area whether deliberately or accidentally) and ''naturalized'' (introduced to an area, but now considered by the public as native). In the United Kingdom, the organization Plantlife International in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Meadow
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets lower until it reaches sea level, and alpine tundra merges with polar tundra. The high elevation causes an adverse climate, which is too cold and windy to support tree growth. Alpine tundra transitions to sub-alpine forests below the tree line; stunted forests occurring at the forest-tundra ecotone are known as ''Krummholz''. With increasing elevation it ends at the snow line where snow and ice persist through summer. Alpine tundra occurs in mountains worldwide. The flora of the alpine tundra is characterized by dwarf shrubs close to the ground. The cold climate of the alpine tundra is caused by adiabatic cooling of air, and is similar to polar climate. Geography Alpine tundra occurs at high enough altitude at any latitude. Portions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Zone
The life zone concept was developed by C. Hart Merriam in 1889 as a means of describing areas with similar plant and animal communities. Merriam observed that the changes in these communities with an increase in latitude at a constant elevation are similar to the changes seen with an increase in elevation at a constant latitude. The life zones Merriam identified are most applicable to western North America, being developed on the San Francisco Peaks, Arizona and Cascade Range of the northwestern USA. He tried to develop a system that is applicable across the North American continent, but that system is rarely referred to. The life zones that Merriam identified, along with characteristic plants, are as follows: * Lower Sonoran (low, hot desert): creosote bush, Joshua tree * Upper Sonoran (desert steppe or chaparral): sagebrush, scrub oak, Colorado pinyon, Utah juniper * Transition (open woodlands): ponderosa pine * Canadian (fir forest): Rocky Mountain Douglas fir, quaking aspe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudipatsar
Dudipatsar Lake ( ur, ), also known as Dudipat Lake, is a lake encircled by snow clad peaks in Lulusar-Dudipatsar National Park. The lake lies in the north end of the Kaghan Valley, in the Mansehra District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, in northern Pakistan. Geography The lake's water is greenish blue hue and very cold, at an elevation of . The surrounding mountains, with snow patches in the shady dales, average around in elevation. Their natural habitat is in the Western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows ecoregion. Lulusar Lake, also in the park, is the primary headwaters of the Kunhar River. Saiful Muluk National Park, with Saif ul Maluk Lake, is adjacent in the long Kaghan Valley region and together the parks protect . Wildlife The lake and its wetlands habitats are of significant ecological importance for resident fauna and migratory waterfowl. Some of the park's fauna includes the snow leopard, black bear, marmot, weasel, lynx, leopard, Himalayan snowcock, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ps, خېبر پښتونخوا; Urdu, Hindko: خیبر پختونخوا) commonly abbreviated as KP or KPK, is one of the Administrative units of Pakistan, four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, northwestern region of the country, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa is the smallest province of Pakistan by land area and the Demographics of Pakistan, third-largest province by population after Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab and Sindh. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan to the south, Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab to the south-east and province of Gilgit-Baltistan to the north and north-east, as well as Islamabad Capital Territory to the east, Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Autonomous Territory of Azad Jammu and Kashmir to the north-east. It shares an Durand Line, international border with Afghanistan to the west. Khyber Pakhtunkhwa is known as a tourist hot spot for adventurers and explorers and has a varied landsca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaghan Valley
The Kaghan Valley ( ur, ) is an alpine valley located in the Mansehra District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The valley covers a distance of across northern Pakistan, rising from its lowest elevation of to its highest point at the Babusar Pass around . Landslides triggered by the devastating 2005 Kashmir earthquake destroyed many passes leading into the valley, though roads have since been largely rebuilt. The Kaghan is a highly popular tourist attraction. Geography The Kaghan Valley is located in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan (formerly known as the North-West Frontier Province), and borders the Pakistani-administered territories of Gilgit-Baltistan and Azad Jammu and Kashmir to the north and east, respectively. The 155-kilometre-long valley is enveloped by the Lower Himalayan mountain range, resulting in an alpine climate and the prevalence of pine forests and alpine meadows. Alongside the flow of the Kunhar River, the valley features glaciers, crystal-like clear lakes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |