Elevation Gain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 In the simplest case of a trip where hikers only travel ''up'' on their way to a single summit, the cumulative elevation gain is simply given by the difference in the summit elevation and the starting elevation. For example, if one starts hiking at a trailhead with elevation , and continues up to a summit of , the cumulative elevation gain is only 5000 ft − 1000 ft = The loss of elevation on the descent is not relevant, because only increases in elevation are considered in this measure.
However, when climbing a mountain with some "ups-and-downs", or traversing several mountains, one must take into account every "up" along the whole route. This even means that the (usually small) uphills on the descent must be counted. For example, consider a mountain whose summit is in elevation, but somewhere on the way up, the trail goes back down . If starting at an elevation of , one gains on the ascent (not 4000 feet, because 250 feet is lost and then has to be "regained"). Additionally, this section of the trail on the overall ascent that goes down 250 feet subsequently goes up on the descent, so it is counted as another gain in elevation. Therefore, the cumulative elevation gain for the trip both up and down the mountain along the same path is .
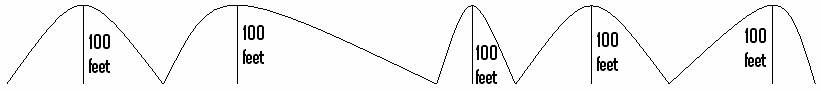
If one hikes over five hills of 100 vertical feet each, the cumulative elevation gain is 5 × () = {{convert, 500, ft, m. Only the uphill sections are counted, not the downhills.
This concept explains why travel on terrain which has more frequent and sharp "ups-and-downs", or is generally more rugged, is usually significantly more strenuous even if the highest absolute elevation reached on any peak is not very great.
In the simplest case of a trip where hikers only travel ''up'' on their way to a single summit, the cumulative elevation gain is simply given by the difference in the summit elevation and the starting elevation. For example, if one starts hiking at a trailhead with elevation , and continues up to a summit of , the cumulative elevation gain is only 5000 ft − 1000 ft = The loss of elevation on the descent is not relevant, because only increases in elevation are considered in this measure.
However, when climbing a mountain with some "ups-and-downs", or traversing several mountains, one must take into account every "up" along the whole route. This even means that the (usually small) uphills on the descent must be counted. For example, consider a mountain whose summit is in elevation, but somewhere on the way up, the trail goes back down . If starting at an elevation of , one gains on the ascent (not 4000 feet, because 250 feet is lost and then has to be "regained"). Additionally, this section of the trail on the overall ascent that goes down 250 feet subsequently goes up on the descent, so it is counted as another gain in elevation. Therefore, the cumulative elevation gain for the trip both up and down the mountain along the same path is .
If one hikes over five hills of 100 vertical feet each, the cumulative elevation gain is 5 × () = {{convert, 500, ft, m. Only the uphill sections are counted, not the downhills.
This concept explains why travel on terrain which has more frequent and sharp "ups-and-downs", or is generally more rugged, is usually significantly more strenuous even if the highest absolute elevation reached on any peak is not very great.
Elevation Gain and 5,000+ Foot Elevation Gain Lists
*
running
Running is a method of terrestrial locomotion allowing humans and other animals to move rapidly on foot. Running is a type of gait characterized by an aerial phase in which all feet are above the ground (though there are exceptions). This is ...
, cycling
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of cycles for transport, recreation, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", or "bikers". Apart from two ...
, and mountaineering
Mountaineering or alpinism, is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending tall mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas. Indoor climbing, sport climbing, a ...
, cumulative elevation gain refers to the sum of every gain in elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vert ...
throughout an entire trip. It is sometimes also known as cumulative gain or elevation gain, or often in the context of mountain travel, simply gain. Another commonly used phrase is total ascent. Elevation losses are not counted in this measure. Cumulative elevation gain, along with round-trip distance, is arguably the most important value used in quantifying the strenuousness of a trip. This is because hiking on flat land (zero elevation gain) is significantly easier than hiking up and down a large mountain with the same round-trip distance. Computation
 In the simplest case of a trip where hikers only travel ''up'' on their way to a single summit, the cumulative elevation gain is simply given by the difference in the summit elevation and the starting elevation. For example, if one starts hiking at a trailhead with elevation , and continues up to a summit of , the cumulative elevation gain is only 5000 ft − 1000 ft = The loss of elevation on the descent is not relevant, because only increases in elevation are considered in this measure.
However, when climbing a mountain with some "ups-and-downs", or traversing several mountains, one must take into account every "up" along the whole route. This even means that the (usually small) uphills on the descent must be counted. For example, consider a mountain whose summit is in elevation, but somewhere on the way up, the trail goes back down . If starting at an elevation of , one gains on the ascent (not 4000 feet, because 250 feet is lost and then has to be "regained"). Additionally, this section of the trail on the overall ascent that goes down 250 feet subsequently goes up on the descent, so it is counted as another gain in elevation. Therefore, the cumulative elevation gain for the trip both up and down the mountain along the same path is .
If one hikes over five hills of 100 vertical feet each, the cumulative elevation gain is 5 × () = {{convert, 500, ft, m. Only the uphill sections are counted, not the downhills.
This concept explains why travel on terrain which has more frequent and sharp "ups-and-downs", or is generally more rugged, is usually significantly more strenuous even if the highest absolute elevation reached on any peak is not very great.
In the simplest case of a trip where hikers only travel ''up'' on their way to a single summit, the cumulative elevation gain is simply given by the difference in the summit elevation and the starting elevation. For example, if one starts hiking at a trailhead with elevation , and continues up to a summit of , the cumulative elevation gain is only 5000 ft − 1000 ft = The loss of elevation on the descent is not relevant, because only increases in elevation are considered in this measure.
However, when climbing a mountain with some "ups-and-downs", or traversing several mountains, one must take into account every "up" along the whole route. This even means that the (usually small) uphills on the descent must be counted. For example, consider a mountain whose summit is in elevation, but somewhere on the way up, the trail goes back down . If starting at an elevation of , one gains on the ascent (not 4000 feet, because 250 feet is lost and then has to be "regained"). Additionally, this section of the trail on the overall ascent that goes down 250 feet subsequently goes up on the descent, so it is counted as another gain in elevation. Therefore, the cumulative elevation gain for the trip both up and down the mountain along the same path is .
If one hikes over five hills of 100 vertical feet each, the cumulative elevation gain is 5 × () = {{convert, 500, ft, m. Only the uphill sections are counted, not the downhills.
This concept explains why travel on terrain which has more frequent and sharp "ups-and-downs", or is generally more rugged, is usually significantly more strenuous even if the highest absolute elevation reached on any peak is not very great.
Technology
Cumulative elevation gain can be recorded usingGPS device
A satellite navigation device (satnav device) is a user equipment that uses one or more of several global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) to calculate the device's geographical position and provide navigational advice.
Depending on the s ...
s such as Garmin
Garmin Ltd. (shortened to Garmin, stylized as GARMIN, and formerly known as ProNav) is an American, Swiss-domiciled multinational technology company founded in 1989 by Gary Burrell and Min Kao in Lenexa, Kansas, United States, with headquart ...
or Strava
Strava is an American internet service for tracking physical exercise which incorporates social network features. It is mostly used for cycling and running using Global Positioning System data. Strava uses a freemium model with some features on ...
.
See also
* Naismith's ruleReferences
Elevation Gain and 5,000+ Foot Elevation Gain Lists
*
National Three Peaks Challenge
The National Three Peaks Challenge is an event in which participants attempt to climb the highest mountains of England, Scotland and Wales within 24 hours. It is frequently used to fundraising, raise money for charitable organisations. Walkers c ...
- use of phrase 'total ascent'
Mountaineering
Vertical position