|
Dudhwa Range
The Dundwa Range (Hindi and dundwā shrinkhalā) is a subrange of the Sivalik Hills in western Nepal and northern Uttar Pradesh, India. It separates the Outer Terai of Balarampur and Shravasti districts in Uttar Pradesh from Deukhuri Valley in Nepal's Dang-Deukhuri and eastern Banke districts. The international border follows the southern edge of this range, leaving a zone of forested Bhabar inside Uttar Pradesh. The Dundwas diverge from other Sivalik ranges at 27°52'N, 83°14'Ein western Kapilvastu, extending 160 km W and WNW across Dang Deukhuri District and into Banke -- within 20 km of Nepalganj -- before descending into the alluvial plains. The Dundwas divert the Rapti some 100 km west before the river resumes its southward course toward the Ganges. Nepal's main E-W Mahendra Highway climbs 400 metres from the Outer Terai to cross this range at 28°47'N, 82°49'E. Summit elevations diminish from east to west with some exceeding 1,400m near the eastern e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindi
Hindi ( Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India. Hindi is the '' lingua franca'' of the Hindi Belt. It is also spoken, to a lesser extent, in other parts of India (usually in a simplified or pidginised variety such as Bazaar Hindustani or Haflong Hindi). Outside India, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
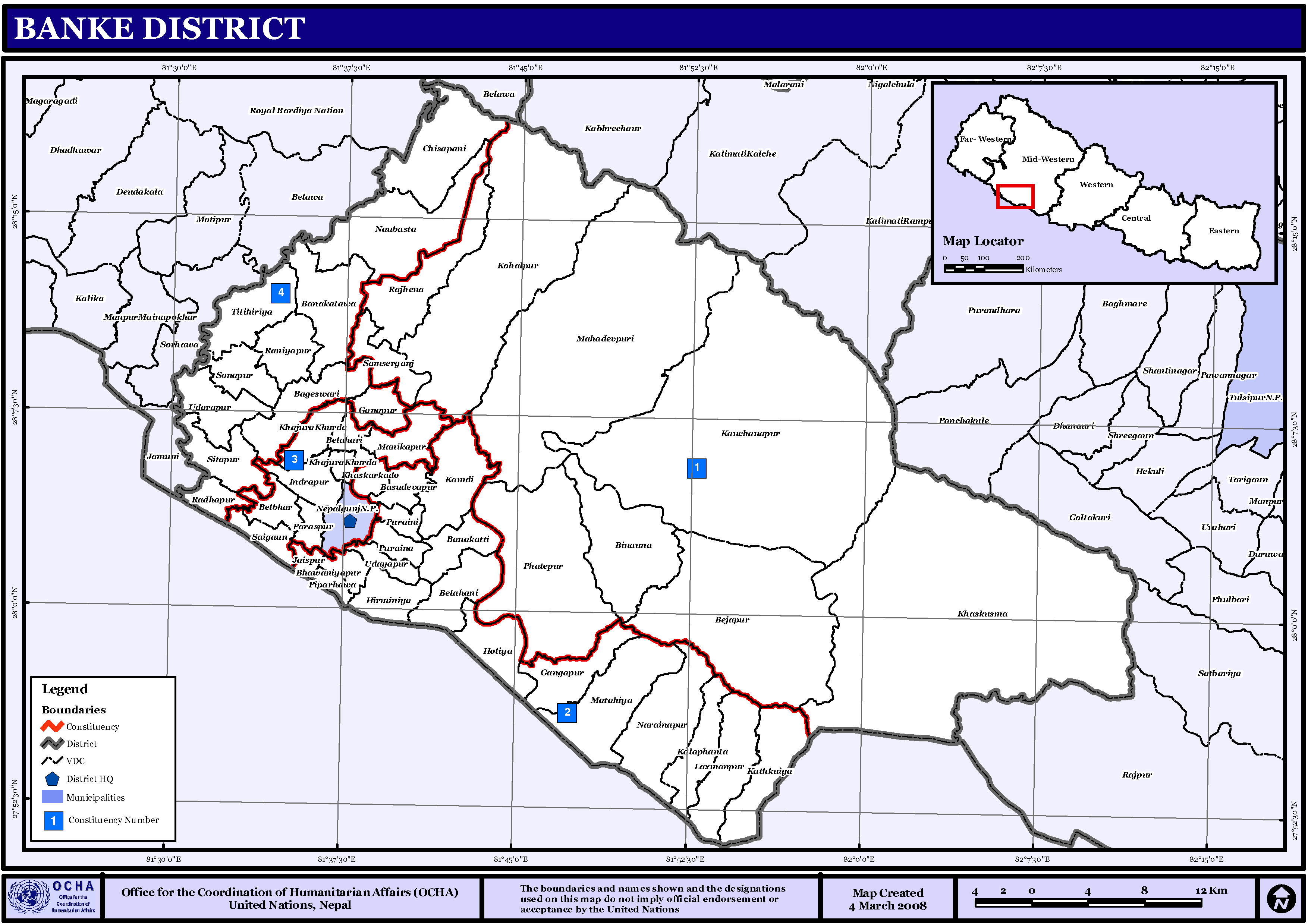
Banke District
Banke District ( ne, बाँके जिल्ला , a part of Lumbini Province, is one of the 77 districts of Nepal. The district, located in midwestern Nepal with Nepalganj as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 385,840 in 2001 and 491,313 in 2011. There are three main cities in the Banke District: Nepalganj, Kohalpur and Khajura Bajaar. Geography and Climate Banke is bordered on the west by ''Bardiya district''. ''Rapti zone's'' ''Salyan'' and ''Dang Deukhuri Districts'' border to the north and east. To the south lies ''Uttar Pradesh'', India, a country in Asia; specifically ''Shravasti'' and ''Bahraich districts'' of ''Awadh''. East of Nepalganj the international border follows the southern edge of the ''Dudhwa Range'' of the ''Siwaliks''. Most of the district is drained by the ''Rapti'', except the district's western edge is drained by the ''Babai''. Rapti and Babai cross into Uttar Pradesh, a state in India, Nepal's neighbori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Uttar Pradesh
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of India
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Nepal
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of The Himalayas
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koilabas
Koilabas is a bazaar town situated in Gadhawa Rural Municipality in Dang Deokhuri District in Lumbini Province of south-western Nepal. The town is situated on the southern edge of the Dudhwa Range of the Siwaliks, at Nepal's border with Uttar Pradesh 5 km from the village Jarwa on the other side. Indian and Nepalese nationals may cross the border unrestricted however there is a customs checkpoint for goods. Koilabas has regular bus service to Tulsipur on the Gorakhpur-Gonda Loop of Indian Railways. From Koilabas, goods are transshipped over the Dudhwas to Dang and Deukhuri Valleys, then on into hill districts Pyuthan, Rolpa and Salyan. Before Nepal's east–west Mahendra Highway was built in the 1990s, Koilabas was also a transit hub. It was often easier if less direct to use Indian trains to travel east or west to reach other parts of Nepal than to traverse a seemingly endless series of north–south mountain valleys on foot. Hindi or Awadhi Awadhi (; ), also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahendra Highway
Mahendra Highway (), also called East-West Highway () runs across the Terai geographical region of Nepal, from Mechinagar in the east to Bhim Datta in the west, cutting across the entire width of the country. It is the longest highway in Nepal and was constructed by cooperation of various countries. Overview The highway is mostly a single lane in each direction. It is a major infrastructure element because east–west travel was previously limited to the Hulaki Highway built during the Rana regime, expensive and limited air travel, or Nepalese trains and buses. The highway crosses the Terai from east to west for over . Connecting Nepal from Kakarbhitta ( Mechinagar Municipality) to West Mahendra Nagar in the east, this is the longest highway in Nepal till now. Bharatpur city and Chitwan valley are located towards the central part of this highway. The major destinations along and around the highway are Mechinagar, Bhadrapur, Itahari, Janakpur, Bharatpur, Butwal, Siddha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly river. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna, the lower stream of the Brahmaputra, and eventually the Meghna, forming the major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Rapti River
West Rapti, also known as the Kuwano drains Rapti Zone in Mid-Western Region, Nepal, then Awadh and Purvanchal regions of Uttar Pradesh state, India before joining the Ghaghara—a major left bank tributary of the Ganges known as the Karnali inside Nepal. The West Rapti is notable for ''janajati'' ethnic groups – Kham Magar among its highland sources and then Tharu in Inner Terai Deukhuri Valley, for its irrigation and hydroelectric potential, and for recurrent floods that led to its nickname "Gorakhpur's Sorrow". History As ancient Airavati river Aciravati, Achirvati or Airavati is the ancient name for a river has been identified with the modern Rapti, flowing through what is now Nepal and the northern portion of Uttar Pradesh. The Chinese pilgrim Xuanzang knew it as A-chi-lo. Jain texts mention it as Eravai. The ancient city of Sravasti, once capital of Kosala Kingdom, stood on the western bank of the Achirvati. The river was a tributary of the Sarayu. It w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepalganj
Nepalgunj (), also spelled Nepalganj, is a Sub-Metropolitan City in Banke District, Nepal. It lies on the Terai plains near the southern border with Bahraich district in Uttar Pradesh, India. Nepalgunj is 153 kilometers south-west of Ghorahi and 16 km south of Kohalpur. Former Village Development Committee: Udayapur, Bhawaniyapur, Piprahawa, Jaispur, Paraspur, Indrapur, Khaskarkado, Bashudevpur, Manikapur and Puraina were added to territory in order to make it Sub metropolitan city on 2071 Paush 28 and later Puraini was also added in list on 2072 Paush 21. Further, while restructuring of local levels nationwide, ward no. 23 (former Indrapur VDC) was taken out to Janaki Rural Municipality and ward no. 7 of Hirminiya VDC was added to Nepalgunj. Demographics The 2011 census counted 73,779 inhabitants with 20% growth since 2001. Currently it is estimated around 1,60,000 inhabitants in Nepalgunj city. Culture and religion Nepalgunj has a diverse culture with peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapilvastu District
Kapilvastu district ( ne, कपिलवस्तु जिल्ला ), often Kapilbastu, is one of the districts of Lumbini Province, Nepal. The district, with Kapilbastu municipality as its district headquarters, covers an area of and in 2001 had a population of 481,976, which increased to 571,936 in 2011 and later according 2021 census it further increased to 686,739 Kapilvastu district has 3 number of seats for central whereas 6 seats for state level elections. Geography and climate The district is situated at a height of above sea level. Geographically, the district can be divided into the low land plains of Terai and the low Chure hills. Kapilvastu is bounded by Rupandehi District to the east, Dang Deukhuri District in Rapti zone to the northwest, Arghakhanchi District to the north, Balrampur district, Awadh region, Uttar Pradesh, India to the west and Siddharthnagar district, Purvanchal region, Uttar Pradesh to the south. The summer is hot with temperature above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


