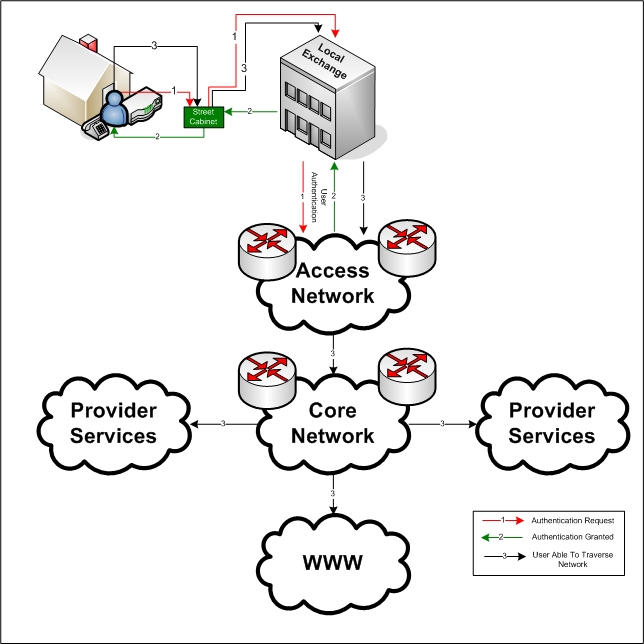
|
Dual Access
In telecommunications, the term dual access has the following meanings: #The connection of a user to two switching centers by separate access lines using a single message routing indicator or telephone number. #In satellite communications, the transmission Transmission may refer to: Medicine, science and technology * Power transmission ** Electric power transmission ** Propulsion transmission, technology allowing controlled application of power *** Automatic transmission *** Manual transmission *** ... of two carriers simultaneously through a single communication satellite repeater. Also, network hardware company D-Link has named technology which allows two simultaneous connections over one cable, for example 1) Internet and 2) provider's local FTP or game servers or IPTV data flow. References * Network access {{Telecomm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded drumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication Connection
A telecommunication circuit is a path in a telecommunications network used to transmit information. Circuits have evolved over time from generally being built on physical connections between individual hardware cables, as in an analog phone switch, to virtual circuits established over packet switching networks. Definitions A telecommunication circuit may be defined as follows: * The complete path between two terminals over which one-way or two-way communications may be provided. * An electronic path between two or more points, capable of providing a single or multiple communication channels. * An electronic closed-loop path among two or more points used for signal transfer. In operational terms, a telecommunication circuit may be capable of transmitting information in only one direction (''simplex'' circuit), or it may be bi-directional (''duplex'' circuit). Bi-directional circuits may support half- duplex operation, when only one end of the channel transmits at any one time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User (telecommunications)
In telecommunications, a user is a person, organization, or other entity that employs the services provided by a telecommunication system, or by an information processing system, for transfer of information. A user functions as a source or final destination of user information, or both. A user ''may'' also be the subscriber, i.e. the customer paying for the service. User is also a person or process accessing an AIS by direct connections (e.g., via terminals) or indirect connections. "Indirect connection" relates to persons who prepare input data or receive output that is not reviewed for content or classification by a responsible individual. Sources * {{FS1037C MS188 * National Information Systems Security Glossary See also * User (computing) A user is a person who utilizes a computer or network service. A user often has a user account and is identified to the system by a username (or user name). Other terms for username include login name, screenname (or screen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switching Center
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital systems to establish telephone calls between subscribers. In historical perspective, telecommunication terms have been used with different semantics over time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. Often, a ''central office'' is defined as a building used to house the inside plant equipment of potentially several telephone exchanges, each serving a certain geographical area. Such an area has also been referred to as the exchange or exchange area. In North America, a central office location may also be identified as a ''wire center'', designating a facility to which a telephone is connected and obtains dial tone. For business and billing purposes, telecommunication carriers defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Access Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality of the records which describe the network. In 2006, according t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Message
A message is a discrete unit of communication intended by the source for consumption by some recipient or group of recipients. A message may be delivered by various means, including courier, telegraphy, carrier pigeon and electronic bus. A message can be the content of a broadcast. An interactive exchange of messages forms a conversation. One example of a message is a press release, which may vary from a brief report or statement released by a public agency to commercial publicity material. History Roles in human communication In communication between humans, messages can be verbal or nonverbal: * A verbal message is an exchange of information using words. Examples include face-to-face communication, telephone calls, voicemails, email etc. * A nonverbal message is communicated through actions or behaviors rather than words, such as conscious or unconscious body language. In computer science There are two main senses of the word "message" in computing: messages be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routing Indicator
In telecommunications, the term routing indicator (RI) has the following meanings: #In a message header, an address, ''i.e.,'' group of characters, that specifies routing instructions for the transmission Transmission may refer to: Medicine, science and technology * Power transmission ** Electric power transmission ** Propulsion transmission, technology allowing controlled application of power *** Automatic transmission *** Manual transmission *** ... of the message to its final destination. A Routing Indicator is a group of letters assigned to identify a station within a tape relay network to facilitate routing of traffic. It indicates the status of the station and may indicate its geographical area. The following factors are reflected in routing indicator assignment: * (a) National or international affiliation and service (when required) of the station. * (b) The geographical area in which the station is located or area from which it is served. * (c) Network status of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Number
A telephone number is a sequence of digits assigned to a landline telephone subscriber station connected to a telephone line or to a wireless electronic telephony device, such as a radio telephone or a mobile telephone, or to other devices for data transmission via the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or other public and private networks. A telephone number serves as an address for switching telephone calls using a system of destination code routing. Telephone numbers are entered or dialed by a calling party on the originating telephone set, which transmits the sequence of digits in the process of signaling to a telephone exchange. The exchange completes the call either to another locally connected subscriber or via the PSTN to the called party. Telephone numbers are assigned within the framework of a national or regional telephone numbering plan to subscribers by telephone service operators, which may be commercial entities, state-controlled administrations, or oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Communications
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communications satelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission (telecommunications)
In telecommunications, transmission is the process of sending or propagating an analog or digital signal via a medium that is wired, wireless, or fiber-optic. Transmission technologies typically refer to physical layer protocol duties such as modulation, demodulation, line coding, equalization, error control, bit synchronization and multiplexing, but it may also involve higher-layer protocol duties, for example, digitizing an analog signal, and data compression. Transmission of a digital message, or of a digitized analog signal, is known as data transmission. Examples of transmission are the sending of signals with limited duration, for example, a block or packet of data, a phone call, or an email. See also *Radio transmitter In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeater
In telecommunications, a repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it. Repeaters are used to extend transmissions so that the signal can cover longer distances or be received on the other side of an obstruction. Some types of repeaters broadcast an identical signal, but alter its method of transmission, for example, on another frequency or baud rate. There are several different types of repeaters; a telephone repeater is an amplifier in a telephone line, an optical repeater is an optoelectronic circuit that amplifies the light beam in an optical fiber cable; and a radio repeater is a radio receiver and transmitter that retransmits a radio signal. A broadcast relay station is a repeater used in broadcast radio and television. Overview When an information-bearing signal passes through a communication channel, it is progressively degraded due to loss of power. For example, when a telephone call passes through a wire telephone line, some of the powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-Link
D-Link Corporation is a Taiwanese multinational networking equipment manufacturing corporation headquartered in Taipei, Taiwan. It was founded in March 1986 in Taipei as ''Datex Systems Inc.'' History D-Link Corporation changed its name from Datex Systems Inc. in 1994, when it went public and when it became the first networking company on the Taiwan Stock Exchange. It is now publicly traded on the TSEC and NSE stock exchanges. In 1988, Datex Systems Inc. released the industry's first peer-to-peer LANSmart Network Operating System, able to run concurrently with early networking systems such as Novell's NetWare and TCP/IP which most small network operating systems could not do at the time. In 2007, it was the leading networking company in the small to medium business (SMB) segment worldwide with 21.9% market share.Compiled from In-Stat Q1 2007 ''Wireless LAN Equipment Market Share Report'' In March 2008, it became the market leader in Wi-Fi product shipments worldwide, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)