|
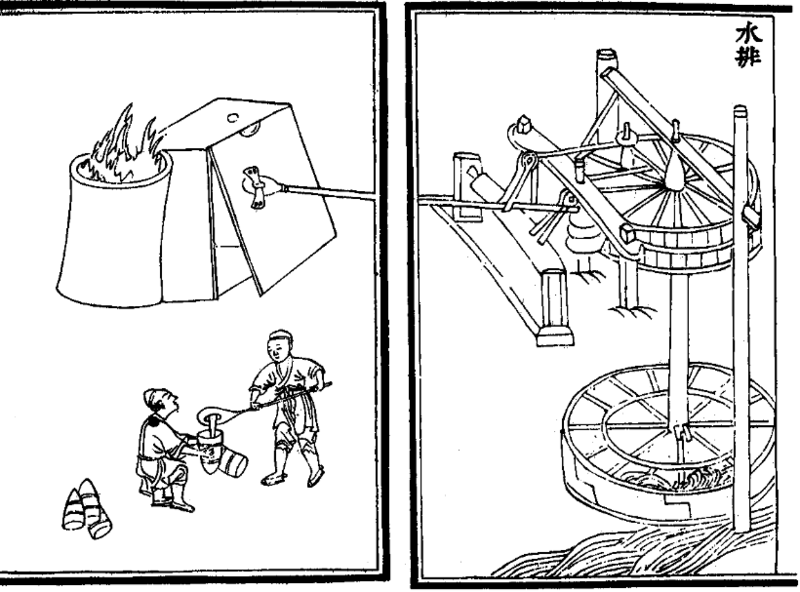
Du Shi
Du Shi (, d. 38'' Book of Later Han'', vol. 31Crespigny, 183.) was a Chinese hydrologist, inventor, mechanical engineer, metallurgist, and politician of the Eastern Han Dynasty. Du Shi is credited with being the first to apply hydraulic power (i.e. a waterwheel) to operate bellows (air-blowing device) in metallurgy. His invention was used to operate piston-bellows of the blast furnace and then cupola furnace in order to forge cast iron, which had been known in China since the 6th century BC. He worked as a censorial officer and administrator of several places during the reign of Emperor Guangwu of Han. He also led a brief military campaign in which he eliminated a small bandit army under Yang Yi (d. 26). Life Early career Although the year of his birth is uncertain, it is known that Du Shi was born in Henei, Henan province. Du Shi became an Officer of Merit in his local commandery before receiving an appointment in 23 as a government clerk under Gengshi Emperor (r. 23–25) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty - Waterwheels And Smelting
Yuan may refer to: Currency * Yuan (currency), the basic unit of currency in historic and contemporary mainland China and Taiwan **Renminbi, the current currency used in mainland China, whose basic unit is yuan ** New Taiwan dollar, the current currency used in Taiwan, whose basic unit is yuán in Mandarin ** Manchukuo yuan, the unit of currency that was used in the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo Governmental organ * "Government branch" or "Court" (), the Chinese name for a kind of executive institution. Government of Taiwan * Control Yuan * Examination Yuan * Executive Yuan * Judicial Yuan * Legislative Yuan Government of Imperial China * Xuanzheng Yuan, or Bureau of Buddhist and Tibetan Affairs during the Yuan dynasty * Lifan Yuan during the Qing dynasty Dynasties * Yuan dynasty (元朝), a dynasty of China ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan ** Northern Yuan dynasty (北元), the Yuan dynasty's successor state in northern China and the Mongolian Plateau People and languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commandery (China)
A jùn (郡) was a historical administrative division of China from the Eastern Zhou (c. 7th century BCE) until the early Tang dynasty (c. 7th century CE). It is usually translated as a commandery. Countries around China have adopted administrative divisions based on or named after the ''jùn''. History and development China Eastern Zhou During the Eastern Zhou's Spring and Autumn period from the 8th to 5th centuries BCE, the larger and more powerful of the Zhou's vassal states—including Qin, Jin and Wei—began annexing their smaller rivals. These new lands were not part of their original fiefs and were instead organized into counties (''xiàn''). Eventually, jun were developed as marchlands between the major realms. Despite having smaller populations and ranking lower on the official hierarchies, the jun were larger and boasted greater military strength than the counties. As each state's territory gradually took shape in the 5th- to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanguo Zhi
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). It is widely regarded as the official and authoritative source historical text for that period. Written by Chen Shou in the third century, the work synthesizes the histories of the rival states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu in the Three Kingdoms period into a single compiled text. The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is the main source of influence for the 14th century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms,'' considered one of the great four novels of Chinese classical literature. Major chunks of the records have been translated into English, but the tome has yet to be fully translated. Origin and structure The ''Records of the Grand Historian'', ''Book of Han'' and ''Book of the Later Han'', and the ''Records ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty Hydraulic Mill For Grain
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetition and variation of sections. Written words created specifically for music, or for which music is specifically created, are called lyrics. If a pre-existing poem is set to composed music in classical music it is an art song. Songs that are sung on repeated pitches without distinct contours and patterns that rise and fall are called chants. Songs composed in a simple style that are learned informally "by ear" are often referred to as folk songs. Songs that are composed for professional singers who sell their recordings or live shows to the mass market are called popular songs. These songs, which have broad appeal, are often composed by professional songwriters, composers, and lyricists. Art songs are composed by trained classical composers fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Excellencies
The Three Ducal Ministers (), also translated as the Three Dukes, Three Excellencies, or the Three Lords, was the collective name for the three highest officials in Ancient China and Imperial China. These posts were abolished by Cao Cao in 208 AD and replaced with the position of Grand Chancellor. Overview Each minister was responsible for different areas of government, but the boundaries were often blurred. Together, the Three Ducal Ministers were the emperor's closest advisors. Toward the end of a dynasty, the positions were often sold to men of wealth to raise state revenue. Starting in the late Shang dynasty and Zhou dynasty, the top three were: * Grand Preceptor (); * Grand Tutor (); * Grand Protector (). During the Western Han dynasty, the three positions were: * Chancellor () * Grand Secretary (); * Grand Commandant (). In the Eastern Han dynasty, the names of the Three Ducal Ministers were changed to: * Minister of War (); * Minister of the Masses (); * Minister ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamation ground or land fill. In some jurisdictions, including parts of the United States, the term "reclamation" can refer to returning disturbed lands to an improved state. In Alberta, Canada, for example, reclamation is defined by the provincial government as "The process of reconverting disturbed land to its former or other productive uses." In Oceania, it is frequently referred to as land rehabilitation. History One of the earliest large-scale projects was the Beemster Polder in the Netherlands, realized in 1612 adding of land. In Hong Kong the Praya Reclamation Scheme added of land in 1890 during the second phase of construction. It was one of the most ambitious projects ever taken during the Colonial Hong Kong era.Bard, Solomon. 002 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanyang, Henan
Nanyang is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Henan province, China. The city with the largest administrative area in Henan, Nanyang borders Xinyang to the southeast, Zhumadian to the east, Pingdingshan to the northeast, Luoyang to the north, Sanmenxia to the northwest, the province of Shaanxi to the west, and the province of Hubei to the south. Dinosaur egg fossils have been discovered in the Nanyang Basin. The 35,000 capacity Nanyang Sports Centre Stadium is the main (football) venue in the city. Names In the name "Nanyang" (), ''Nan'' () means south, and ''Yang'' (/) means sun—the south side of a mountain, or the north side of a river, in Chinese is called ''Yang''. The name came from Nanyang Commandery, a commandery established in the region during the Warring States period. Before the name "Nanyang" became associated with the city itself, it was referred to as "Wan" (). History Nanyang was the capital of the state of Shen in the first millennium BCE. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runan Commandery
Runan Commandery ( zh, 汝南郡) was a Chinese commandery from Han dynasty to Tang dynasty, located in modern Henan and Anhui provinces. The name referred to its location to the south of Ru River (汝水), a historical river that flowed into the Huai. Runan was part of the Huaiyang Kingdom in early Western Han dynasty. In 156 BC, Runan was granted to Liu Fei, son of the reigning Emperor Jing as a principality. A year later, Fei's fief was changed to Jiangdu (江都), and Runan became a commandery. In late Western Han dynasty, it administered 37 counties, Pingyu (平輿), Yang'an (陽安), Yangcheng (陽城), Liqiang (郦強), Fubo (富波), Nüyang (女陽), Tongyang (鮦陽), Wufang (吳房), Ancheng (安成), Nandun (南頓), Langling (朗陵), Xiyang (細陽), Yichun (宜春), Nüyin (女陰), Xincai (新蔡), Xinxi (新息), Quyang (灈陽), Qisi (期思), Shenyang (慎陽), Shen (慎), Zhaoling (召陵), Yiyang (弋陽), Xiping (西平), Shangcai (上蔡), Qin (浸), Xi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pei Commandery
Pei Commandery ( zh, 沛郡) was a Chinese commandery from Han dynasty to Northern Qi dynasty. Its territory was located in present-day northern Anhui and northwestern Jiangsu, as well as part of Shandong and Henan. Pei was established in early Western Han on an area formerly known as Sishui Commandery (泗水郡) during the Qin dynasty, and received its name from Pei County, Liu Bang's home county. The seat was at Xiang (相), in modern Huaibei, Anhui. The commandery was part of the vassal Kingdom of Chu during its early years, however, during Emperor Jing's reign, the imperial forces defeated Chu in the Rebellion of Seven States and revoked the territory. In 117 BC, part of Pei was split off to form the new Linhuai Commandery. In 2 AD, the commandery consisted of 37 counties: Xiang (相), Longkang (龍亢), Zhu (竹), Guyang (穀陽), Xiao (蕭), Xiang (向), Zhi (銍), Guangqi (廣戚), Xiacai (下蔡), Feng (豐), Dan (鄲), Qiao (譙), Qi (蘄), Zhuan (颛), Zheyu (輒與), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Standard Beijing Mandarin, Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the Yellow River civilization, birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far East, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating natural disasters in China, floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedong Commandery
Hedong Commandery () was a historical region in the Qin and Han dynasties of ancient China. Hedong was located to the east of the Yellow River in Shanxi (around present-day Yuncheng). History Hedong Commandery was established by the Qin state during the Warring States Period. Its seat was Anyi, the former capital of Wei. During the Western Han dynasty, It administered 24 counties: Anyi (安邑), Dayang (大陽), Yishi (猗氏), Xie (解), Puban (蒲反), Hebei (河北), Zuoyi (左邑), Fenyin (汾陰), Wenxi (聞喜), Huoze (濩澤), Duanshi (端氏), Linfen (臨汾), Yuan (垣), Pishi (皮氏), Changxiu (長脩), Pingyang (平陽), Xiangling (襄陵), Zhi (彘), Yang (楊), Beiqu (北屈), Puzi (蒲子), Jiang (絳), Hunie (狐讘) and Qi (騏). In 2 AD, the commandery had a population of 962,912, in 236,896 households. During the Cao Wei dynasty, a separate Pingyang Commandery was formed from several counties of Hedong. In early Jin dynasty, Hedong administered nine counties, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang, Henan, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five out of six urban districts (except the Jili District not continuously urbanized) and Yanshi District, now being conurbated. Situated on the Central Plain (China), central plain of China, Luoyang is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#East Asia, oldest cities in China and one of the History of China#Ancient China, cradles of Chinese civilization. It is the earliest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |