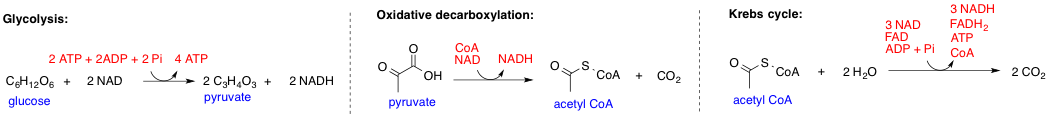|
DrugBank
The DrugBank database is a comprehensive, freely accessible, online database containing information on drugs and drug targets created and maintained by the University of Alberta and The Metabolomics Innovation Centre located in Alberta, Canada. As both a bioinformatics and a cheminformatics resource, DrugBank combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. DrugBank has used content from Wikipedia; Wikipedia also often links to Drugbank, posing potential circular reporting issues. The DrugBank Online website is available to the public as a free-to-access resource. However, use and re-distribution of content from DrugBank Online or the underlying DrugBank Data, in whole or part, and for any purpose requires a license. Academic users can apply for a free license for certain use cases while all other users require a paid license. The latest release of the database (vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugbank Logo
The DrugBank database is a comprehensive, freely accessible, online database containing information on drugs and drug targets created and maintained by the University of Alberta and The Metabolomics Innovation Centre located in Alberta, Canada. As both a bioinformatics and a cheminformatics resource, DrugBank combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. DrugBank has used content from Wikipedia; Wikipedia also often links to Drugbank, posing potential circular reporting issues. The DrugBank Online website is available to the public as a free-to-access resource. However, use and re-distribution of content from DrugBank Online or the underlying DrugBank Data, in whole or part, and for any purpose requires a license. Academic users can apply for a free license for certain use cases while all other users require a paid license. The latest release of the database (vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Withdrawn Drug
Drugs or medicines may be withdrawn from commercial markets because of risks to patients, but also because of commercial reasons (e.g. lack of demand and relatively high production costs). Where risks or harms is the reason for withdrawal, this will usually have been prompted by unexpected adverse effects that were not detected during Phase III clinical trials, i.e. they were only made apparent from postmarketing surveillance data collected from the wider community over longer periods of time. This list is not limited to drugs that were ever approved by the FDA. Some of them (lumiracoxib, rimonabant, tolrestat, ximelagatran and ximelidine, for example) were approved to be marketed in Europe but had not yet been approved for marketing in the US, when side effects became clear and their developers pulled them from the market. Some drugs in this list (e.g. LSD) were never approved for marketing in the US or Europe. Significant withdrawals Withdrawn clinical trial drugs *RG7795, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FooDB
FooDB (The Food Database) is a freely available, open-access database containing chemical (micronutrient and macronutrient) composition data on common, unprocessed foods. It also contains extensive data on flavour and aroma constituents, food additives as well as positive and negative health effects associated with food constituents. The database contains information on more than 28,000 chemicals found in more than 1000 raw or unprocessed food products. The data in FooDB was collected from many sources including textbooks, scientific journals, on-line food composition or nutrient databases, flavour and aroma databases and various on-line metabolomic databases. This literature-derived information has been combined with experimentally derived data measured on thousands of compounds from more than 40 very common food products through the Alberta Food Metabolome Project which is led by David S. Wishart. Users are able to browse through the FooDB data by food source, name, descriptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChEMBL
ChEMBL or ChEMBLdb is a manually curated chemical database of bioactive molecules with drug-like properties. It is maintained by the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), based at the Wellcome Trust Genome Campus, Hinxton, UK. The database, originally known as StARlite, was developed by a biotechnology company called Inpharmatica Ltd. later acquired by Galapagos NV. The data was acquired for EMBL in 2008 with an award from The Wellcome Trust, resulting in the creation of the ChEMBL chemogenomics group at EMBL-EBI, led by John Overington. Scope and access The ChEMBL database contains compound bioactivity data against drug targets. Bioactivity is reported in Ki, Kd, IC50, and EC50. Data can be filtered and analyzed to develop compound screening libraries for lead identification during drug discovery. ChEMBL version 2 (ChEMBL_02) was launched in January 2010, including 2.4 million bioassay measurements covering 622,824 com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug injection, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption (skin), absorption via a dermal patch, patch on the skin, suppository, or sublingual administration, dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to pharmacotherapy, treat, cure, preventive healthcare, prevent, or medical diagnosis, diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Pathways
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function. Different metabolic pathways function based on the position within a eukaryotic cell and the significance of the pathway in the given compartment of the cell. For instance, the, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation all take place in the mitochondrial membrane. In contrast, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid biosynthesis all occur in the cytosol of a cell. There are two types of metabolic pathways that are character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relational Query
A relational database is a (most commonly digital) database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using the SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and maintaining the database. History The term "relational database" was first defined by E. F. Codd at IBM in 1970. Codd introduced the term in his research paper "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". In this paper and later papers, he defined what he meant by "relational". One well-known definition of what constitutes a relational database system is composed of Codd's 12 rules. However, no commercial implementations of the relational model conform to all of Codd's rules, so the term has gradually come to describe a broader class of database systems, which at a minimum: # Present the data to the user as relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteome
The proteome is the entire set of proteins that is, or can be, expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time. It is the set of expressed proteins in a given type of cell or organism, at a given time, under defined conditions. Proteomics is the study of the proteome. Types of proteomes While proteome generally refers to the proteome of an organism, multicellular organisms may have very different proteomes in different cells, hence it is important to distinguish proteomes in cells and organisms. A cellular proteome is the collection of proteins found in a particular cell type under a particular set of environmental conditions such as exposure to hormone stimulation. It can also be useful to consider an organism's complete proteome, which can be conceptualized as the complete set of proteins from all of the various cellular proteomes. This is very roughly the protein equivalent of the genome. The term ''proteome'' has also been used to refer to the collectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BLAST
Blast or The Blast may refer to: * Explosion, a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner *Detonation, an exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front Film * ''Blast'' (1997 film), starring Andrew Divoff * ''Blast'' (2000 film), starring Liesel Matthews * ''Blast'' (2004 film), an action comedy film * ''Blast!'' (1972 film) or ''The Final Comedown'', an American drama * ''BLAST!'' (2008 film), a documentary about the BLAST telescope * '' A Blast'', a 2014 film directed by Syllas Tzoumerkas Magazines * ''Blast'' (magazine), a 1914–15 literary magazine of the Vorticist movement * ''Blast'' (U.S. magazine), a 1933–34 American short-story magazine * ''The Blast'' (magazine), a 1916–17 American anarchist periodical Music * Blast (American band), a hardcore punk band * Blast (Russian band), an indie band * ''Blast'' (album), by Holly Johnson, 1989 * ''The Blast'' (album), by Yuvan Shankar Raja, 1999 * " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Sensitive
Case or CASE may refer to: Containers * Case (goods), a package of related merchandise * Cartridge case or casing, a firearm cartridge component * Bookcase, a piece of furniture used to store books * Briefcase or attaché case, a narrow box to carry paperwork * Computer case, the enclosure for a PC's main components * Keep case, DVD or CD packaging * Pencil case * Phone case, protective or vanity accessory for mobile phones ** Battery case * Road case or flight case, for fragile equipment in transit * Shipping container or packing case * Suitcase, a large luggage box * Type case, a compartmentalized wooden box for letterpress typesetting Places * Case, Laclede County, Missouri * Case, Warren County, Missouri * Case River, a Kabika tributary in Ontario, Canada * Case Township, Michigan * Case del Conte, Italy People * Case (name), people with the surname (or given name) * Case (singer), American R&B singer-songwriter and producer (Case Woodard) Arts, entertainment, and media * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMILES
The simplified molecular-input line-entry system (SMILES) is a specification in the form of a line notation for describing the structure of chemical species using short ASCII strings. SMILES strings can be imported by most molecule editors for conversion back into two-dimensional drawings or three-dimensional models of the molecules. The original SMILES specification was initiated in the 1980s. It has since been modified and extended. In 2007, an open standard called OpenSMILES was developed in the open-source chemistry community. History The original SMILES specification was initiated by David Weininger at the USEPA Mid-Continent Ecology Division Laboratory in Duluth in the 1980s. Acknowledged for their parts in the early development were "Gilman Veith and Rose Russo (USEPA) and Albert Leo and Corwin Hansch (Pomona College) for supporting the work, and Arthur Weininger (Pomona; Daylight CIS) and Jeremy Scofield (Cedar River Software, Renton, WA) for assistance in programming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |