|
Drawworks
A drawworks is the primary hoisting machinery component of a rotary drilling rig. Its main function is to provide a means of raising and lowering the traveling block. The wire-rope drill line winds on the drawworks drum and over the crown block to the traveling block, allowing the drill string to be moved up and down as the drum turns. The segment of drill line from the drawworks to the crown block is called the "fast line". The drill line then enters the first sheave of the crown block and makes typically 6 to 12 passes between the crown block and traveling block pulleys for mechanical advantage. The line then exits the last sheave on the crown block and is fastened to a derrick leg on the other side of the rig floor. This section of drill line is called the "dead line." A modern drawworks consists of five main parts: the drum, the power source, the reduction gear, the brake, and the auxiliary brake. The apparatus can be powered by AC or DC, or the drawworks may be c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winch
A winch is a mechanical device that is used to pull in (wind up) or let out (wind out) or otherwise adjust the tension of a rope or wire rope (also called "cable" or "wire cable"). In its simplest form, it consists of a spool (or drum) attached to a hand crank. Traditionally, winches on ships accumulated wire or rope on the drum; those that do not accumulate, and instead pass on the wire/rope (see yacht photo above), are called capstans. Despite this, sailboat capstans are most often referred to as winches. Winches are the basis of such machines as tow trucks, steam shovels and elevators. More complex designs have gear assemblies and can be powered by electric, hydraulic, pneumatic or internal combustion drives. It might include a solenoid brake and/or a Mechanical brake stretch wrapper, mechanical brake or ratchet (device), ratchet and pawl which prevents it unwinding unless the pawl is retracted. The rope may be stored on the winch. When trimming a line on a sailboat, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
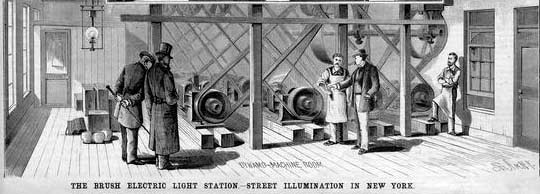
Drilling Rig
A drilling rig is an integrated system that drills wells, such as oil or water wells, or holes for piling and other construction purposes, into the earth's subsurface. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill water wells, oil wells, or natural gas extraction wells, or they can be small enough to be moved manually by one person and such are called augers. Drilling rigs can sample subsurface mineral deposits, test rock, soil and groundwater physical properties, and also can be used to install sub-surface fabrications, such as underground utilities, instrumentation, tunnels or wells. Drilling rigs can be mobile equipment mounted on trucks, tracks or trailers, or more permanent land or marine-based structures (such as oil platforms, commonly called 'offshore oil rigs' even if they don't contain a drilling rig). The term "rig" therefore generally refers to the complex equipment that is used to penetrate the surface of the Earth's crust. Small to medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traveling Block
A traveling block is the freely moving section of a block and tackle that contains a set of pulleys or sheaves through which the drill line (wire rope) is threaded oreevedand is opposite (and under) the crown block (the stationary section). The combination of the traveling block, crown block and wire rope drill line gives the ability to lift weights in the hundreds of thousands of pounds. On larger drilling rigs, when raising and lowering the derrick, line tensions over a million pounds are not unusual. See also * List of components of oil drilling rigs This article lists the main components of a petroleum onshore drilling rig. Offshore drilling rigs have similar elements, but are configured with a number of different drilling systems to suit drilling in the marine environment. The equipment a ... {{Petroleum-stub Oilfield terminology Drilling technology Petroleum engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill Line
In a drilling rig, the drill line is a multi-thread, twisted ''wire'' rope that is threaded oreevedthrough in typically 6 to 12 parts between the traveling block and crown block to facilitate the lowering and lifting of the drill string into and out of the wellbore. On larger diameter lines, traveling block loads of over a ''million'' pounds are possible. To make a connection is to add another segment of drill pipe onto the top the drill string. A segment is added by pulling the kelly above the rotary table, stopping the mud pump, hanging off the drill string in the rotary table, unscrewing the kelly from the drill pipe below, swinging the kelly over to permit connecting it to the top of the new segment (which had been placed in the mousehole Mousehole (; kw, Porthenys) is a village and fishing port in Cornwall, England, UK. It is approximately south of Penzance on the shore of Mount's Bay. The village is in the civil parish of Penzance. An islet called St Clement's Isle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Block
A crown block is the stationary section of a block and tackle that contains a set of pulleys or sheaves through which the drill line (wire rope) is threaded oreevedand is opposite and above the traveling block. The combination of the traveling block, crown block and wire rope drill line gives the ability to lift weights in the hundreds of thousands of pounds. When running heavy casing (borehole), casing strings hook loads occasionally exceed one million pounds. See also * List of components of oil drilling rigs {{Petroleum-stub Oilfield terminology Drilling technology Petroleum engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulley
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that does not transfer power to a shaft, but is used to guide the cable or exert a force, the supporting shell is called a block, and the pulley may be called a sheave. A pulley may have a groove or grooves between flanges around its circumference to locate the cable or belt. The drive element of a pulley system can be a rope, cable, belt, or chain. The earliest evidence of pulleys dates back to Ancient Egypt in the Twelfth Dynasty (1991-1802 BCE) and Mesopotamia in the early 2nd millennium BCE. In Roman Egypt, Hero of Alexandria (c. 10-70 CE) identified the pulley as one of six simple machines used to lift weights. Pulleys are assembled to form a block and tackle in order to provide mechanical advantage to apply large forces. Pulleys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the ''law of the lever.'' Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. An ideal mechanism transmits power without adding to or subtracting from it. This means the ideal machine does not include a power source, is frictionless, and is constructed from rigid bodies that do not deflect or wear. The performance of a real system relative to this ideal is expressed in terms of efficiency factors that take into account departures from the ideal. Lever The lever is a movable bar that pivots on a fulcrum attached to or positioned on or across a fixed point. The lever operates by applying forces at different distances from the fulcrum, or pivot. The location of the fulcrum determines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derrick
A derrick is a lifting device composed at minimum of one guyed mast, as in a gin pole, which may be articulated over a load by adjusting its guys. Most derricks have at least two components, either a guyed mast or self-supporting tower, and a boom hinged at its base to provide articulation, as in a ''stiffleg'' derrick. The most basic type of derrick is controlled by three or four lines connected to the top of the mast, which allow it both to move laterally and cant up and down. To lift a load, a separate line runs up and over the mast with a hook on its free end, as with a crane. Forms of derricks are commonly found aboard ships and at docking facilities. Some large derricks are mounted on dedicated vessels, and known as floating derricks and sheerlegs. The term derrick is also applied to the framework supporting a drilling apparatus in an oil rig. The derrick derives its name from a type of gallows named after Thomas Derrick, an Elizabethan era English executioner. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill Floor
The drill floor is the heart of any drilling rig. This is the area where the drill string begins its trip into the earth. It is traditionally where joints of pipe (fluid conveyance), pipe are assembled, as well as the BHA (bottom hole assembly), drilling bit, and various other tools. This is the primary work location for roughnecks and the driller (oil), driller. The drill floor is located directly under the derrick. The floor is a relatively small work area in which the rig crew conducts operations, usually adding or removing drillpipe to or from the drillstring. The rig floor is the most dangerous location on the rig because heavy iron is moved around there. Drill string connections are made or broken on the drill floor, and the driller's console for controlling the major components of the rig are located there. Attached to the rig floor is a small metal room, the doghouse, where the rig crew can meet, take breaks and take refuge from the elements during idle times. External li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
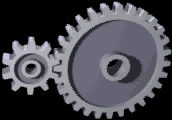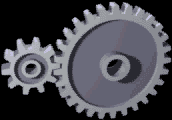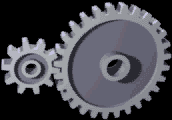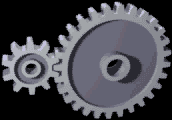
Gear
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa. In certain applications, like guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square waves. Audio a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)