|
Douga
The douga or the "dance of the vultures" See p. 52 and p. 56. is a ceremonial dance (and song) among the Mandinka people of West Africa. According to religious scholar Ada Uzoamaka Azodo, its relevance operates on three levels: it is "performed only occasionally at great events, ndmarks the religious revival of this Guinean community; "it shows the dominion of human knowledge, creative skills, and wisdom over matter and bestial instinct", and it "demonstrates ... the promise of resurrection of the dead to life". See p. 52 and p. 59. According to Christopher Miller, it reflects "the hierarchical, casted order of traditional Mande society" (of which the Mandinka are a part) and in essence forms a chain going back to the emperor Sundiata Keita. There is, however, some doubt about to which extent the douga "belongs" to the Mandinka or the Mandé people more generally. Uzo Esonwanne casts doubt on Frantz Fanon's claim that Fodéba Keïta's ''African Dawn'' assigns a kind of ownershi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research In African Literatures
''Research in African Literatures'' is a triannual peer-reviewed academic journal covering African literary studies. It was established in 1970 and is published by Indiana University Press. The editor-in-chief is Kwaku Larbi Korang (Ohio State University). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Arts & Humanities Citation Index *Current Contents ''Current Contents'' is a rapid alerting service database from Clarivate Analytics, formerly the Institute for Scientific Information and Thomson Reuters. It is published online and in several different printed subject sections. History ''Cur .../Arts & Humanities * EBSCO databases * ProQuest databases References External links * Literary magazines published in the United States African studies journals Publications established in 1970 Indiana University Press academic journals {{lit-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bembeya Jazz National
Bembeya Jazz National (originally known as Orchestre de Beyla) is a Guinean jazz group that gained fame in the 1960s for their Afropop rhythms. They are considered one of the most significant bands in Guinean music. Many of their recordings are based on traditional folk music in the country and have been fused with jazz and Afropop style. Featuring guitarist Sekou "Diamond Fingers" Diabaté, who grew up in a traditional griot musical family, the band won over fans in Conakry, Guinea's capital city, during the heady days of that country's newfound independence. Bembeya Jazz fell onto harder times in the 1980s and disbanded for a number of years, but reformed in the late 1990s and toured Europe and North America in the early 2000s. 1960s In the aftermath of the Guinean Independence in 1958 and through the cultural policy of "authenticité", which encouraged cultural pride, numerous bands were created throughout the regions of Guinea. Guinea's President, Ahmed Sékou Touré, disba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minstrel Show
The minstrel show, also called minstrelsy, was an American form of racist theatrical entertainment developed in the early 19th century. Each show consisted of comic skits, variety acts, dancing, and music performances that depicted people specifically of African descent. The shows were performed by mostly white people wearing blackface make-up for the purpose of playing the role of black people. There were also some African-American performers and black-only minstrel groups that formed and toured. Minstrel shows caricatured black people as dim-witted, lazy, buffoonish, superstitious, and happy-go-lucky.The Coon Character , Jim Crow Museum of Racist Memorabilia, Ferris State University. Retrieved 29 January 2016.John Kenrick [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buzzard Lope
The Buzzard Lope is a popular southern States dance dating from the 1890s, included in Minstrel Show repertoire, alongside the cakewalk and juba dance. Ostensibly, it is a representation of "a turkey buzzard getting ready to eat a dead Mule (some report a Cow)", performed with a comic sensibility known as hokum Hokum is a particular song type of American blues music—a humorous song which uses extended analogies or euphemistic terms to make sexual innuendos. This trope goes back to early blues recordings and is used from time to time in modern Ameri .... Reference is made to the dance in the penultimate line of the American blues/folk song "Johnny Brown": Little Johnny Brown, spread your comfort down (2x) Fold one corner, Johnny Brown Fold another corner, Johnny Brown (3x) Take it to your lover, Johnny Brown (2x) Show her your motion, Johnny Brown (2x) Lope like a buzzard, Johnny Brown (2x) Give it to your lover, Johnny Brown (2x) References {{reflist Dances of the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buck Dance
Clogging is a type of folk dance practiced in the United States, in which the dancer's footwear is used percussively by striking the heel, the toe, or both against a floor or each other to create audible rhythms, usually to the downbeat with the heel keeping the rhythm. Clogging is the official state dance of Kentucky and North Carolina. Description In later periods, it was not always called "clogging", being known variously as foot-stomping, buck dancing, clog dancing, jigging, or other local terms. What all these had in common was emphasizing the downbeat of the music by enthusiastic footwork. As for the shoes, many old clogging shoes had no taps and some were made of leather and velvet, while the soles of the shoes were either wooden or hard leather. Clogging can be divided into five major categories: 1) shuffle clogging, 2) cadence clogging, 3) rhythm clogging, 4) stomp clogging, and 5) buck-dancing. The shuffle clogging style is said to be the most popular style for bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gullah People
The Gullah () are an African American ethnic group who predominantly live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and North Carolina, within the coastal plain and the Sea Islands. Their language and culture have preserved a significant influence of Africanisms as a result of their historical geographic isolation and the community's relation to their shared history and identity. Historically, the Gullah region extended from the Cape Fear area on North Carolina's coast south to the vicinity of Jacksonville on Florida's coast. The Gullah people and their language are also called Geechee, which may be derived from the name of the Ogeechee River near Savannah, Georgia. ''Gullah'' is a term that was originally used to designate the creole dialect of English spoken by Gullah and Geechee people. Over time, its speakers have used this term to formally refer to their creole language and distinctive ethnic identity as a people. The Georgia commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Shout
A shout or ring shout is an ecstatic, transcendent religious ritual, first practiced by African slaves in the West Indies and the United States, in which worshipers move in a circle while shuffling and stomping their feet and clapping their hands. Despite the name, shouting aloud is not an essential part of the ritual. The ring shout was Christianized and practiced in some Black churches into the 20th century, and it continues to the present among the Gullah people of the Sea Islands and in "singing and praying bands" associated with many African American United Methodist congregations in Tidewater Maryland and Delaware. A more modern form, known still as a " shout" (or "praise break"), is practiced in many Black churches and non-Black Pentecostal churches to the present day. Description "Shouting" often took place during or after a Christian prayer meeting or worship service. Men and women moved in a circle in a counterclockwise direction, shuffling their feet, clapping, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griot
A griot (; ; Manding: jali or jeli (in N'Ko: , ''djeli'' or ''djéli'' in French spelling); Serer: kevel or kewel / okawul; Wolof: gewel) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician. The griot is a repository of oral tradition and is often seen as a leader due to their position as an advisor to royal personages. As a result of the former of these two functions, they are sometimes called bards. They also act as mediators in disputes. Occurrence and naming Many griots today live in many parts of West Africa and are present among the Mande peoples ( Mandinka or Malinké, Bambara, Soninke etc.), Fulɓe (Fula), Hausa, Songhai, Tukulóor, Wolof, Serer,Unesco. Regional Office for Education in Africa, ''Educafrica, Numéro 11'', (ed. Unesco, Regional Office for Education in Africa, 1984), p. 110Hale, Thomas Albert, ''Griots and Griottes: Masters of Words and Music'', Indiana University Press (1998), p. 176, Mossi, Dagomba, Mauritan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
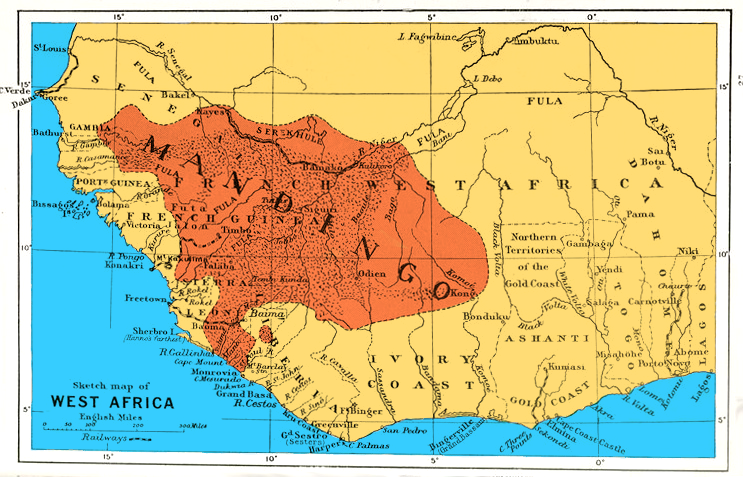
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Senegal to Iv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The African Child
''The African Child'' (French: ''L'Enfant noir'') is an autobiographical French novel by Camara Laye published in 1953. It tells the story of a young African child, Baba, growing up in Guinea. The novel won the Prix Charles Veillon writing prize. It was translated into English by James Kirkup and Ernest Jones and published in the United States by Farrar, Straus and Giroux in 1954 as ''The Dark Child''. In the United Kingdom, this translation was published under the title ''The African Child'' in 1959. It was adapted into a movie called ''L'Enfant noir'' in 1995. Many of the cast in the film were relatives of Laye. The scenes early in the novel, when the young narrator witnesses his father working with gold, have drawn considerable critical attention for their spiritual overtones, but also because of the importance of the douga, the song and dance begun by the griot A griot (; ; Manding: jali or jeli (in N'Ko: , ''djeli'' or ''djéli'' in French spelling); Serer: kevel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camara Laye
Camara Laye (January 1, 1928 – February 4, 1980) was a writer from Guinea. He was the author of ''The African Child'' (''L'Enfant noir''), a novel based loosely on his own childhood, and ''The Radiance of the King'' (''Le Regard du roi''). Both novels are among the earliest major works in Francophone African literature. Camara Laye later worked for the government of newly independent Guinea, but went into voluntary exile over political issues. Early life Camara Laye was born in Kouroussa, a town in what was then the colony of French Guinea. His family were Malinke (a Mandé-speaking ethnicity), and he was born into a system where he had to follow his forefathers footsteps who traditionally worked as blacksmiths and goldsmiths. His mother was from the village of Tindican, and his immediate childhood surroundings were not predominantly influenced by French culture. He attended both Quranic and French elementary schools in Kouroussa. At the age of 15 he went to Conakry, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)