|
Doswelliidae
Doswelliidae is an extinct family of carnivorous archosauriform reptiles that lived in North America and Europe during the Middle to Late Triassic period. Long represented solely by the heavily-armored reptile ''Doswellia'', the family's composition has expanded since 2011, although two supposed South American doswelliids ('' Archeopelta'' and '' Tarjadia'') were later redescribed as erpetosuchids. Doswelliids were not true archosaurs, but they were close relatives and some studies have considered them among the most derived non-archosaurian archosauriforms. They may have also been related to the Proterochampsidae, a South American family of crocodile-like archosauriforms. Description Doswelliids are believed to be semiaquatic carnivores similar to crocodilians in appearance, as evidenced by their short legs and eyes and nostrils which are set high on the head, though the putative member '' Scleromochlus'' has been interpreted as a frog-like hopper by one study. They had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archeopelta
''Archeopelta'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous archosaur from the late Middle or early Late Triassic period (late Ladinian to early Carnian stage). It was a 2 m (6 ft) long predator which lived in what is now southern Brazil. Its exact phylogenetic placement within Archosauriformes is uncertain; it was originally classified as a doswelliid, but subsequently it was argued to be an erpetosuchid archosaur. Discovery It is only known from the holotype CPEZ-239a, which consists of partial skeleton (including vertebrae, partial right front and hind limbs, a partial hip, and an undetermined bone which may be part of a tibia) and braincase. It was found in the Santa Maria 1 Sequence, previously known as the Santa Maria Formation, in Chiniquá region, São Pedro do Sul of Rio Grande do Sul State. It was first named by Julia B. Desojo, Martín D. Ezcurra and César L. Schultz in 2011 and the type species is ''Archeopelta arborensis''. The generic name comes from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterochampsia
Proterochampsia is a clade of early archosauriform reptiles from the Triassic period. It includes the Proterochampsidae (e.g. '' Proterochampsa'', '' Chanaresuchus'' and '' Tropidosuchus'') and probably also the Doswelliidae. Nesbitt (2011) defines Proterochampsia as a stem-based taxon that includes '' Proterochampsa'' and all forms more closely related to it than ''Euparkeria'', ''Erythrosuchus'', ''Passer domesticus'' (the House Sparrow), or ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). Therefore, the inclusion of Doswelliidae in it is dependent upon whether ''Doswellia'' and '' Proterochampsa'' form a monophyletic group to the exclusion of Archosauria and other related groups. Description Nesbitt (2011) found that Proterochampsians share several distinguishing characteristics, or synapomorphies. A prominent ridge runs along the length of the jugal, a bone below the eye. Another ridge is present on the quadratojugal, a bone positioned toward the back of the skull behind the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
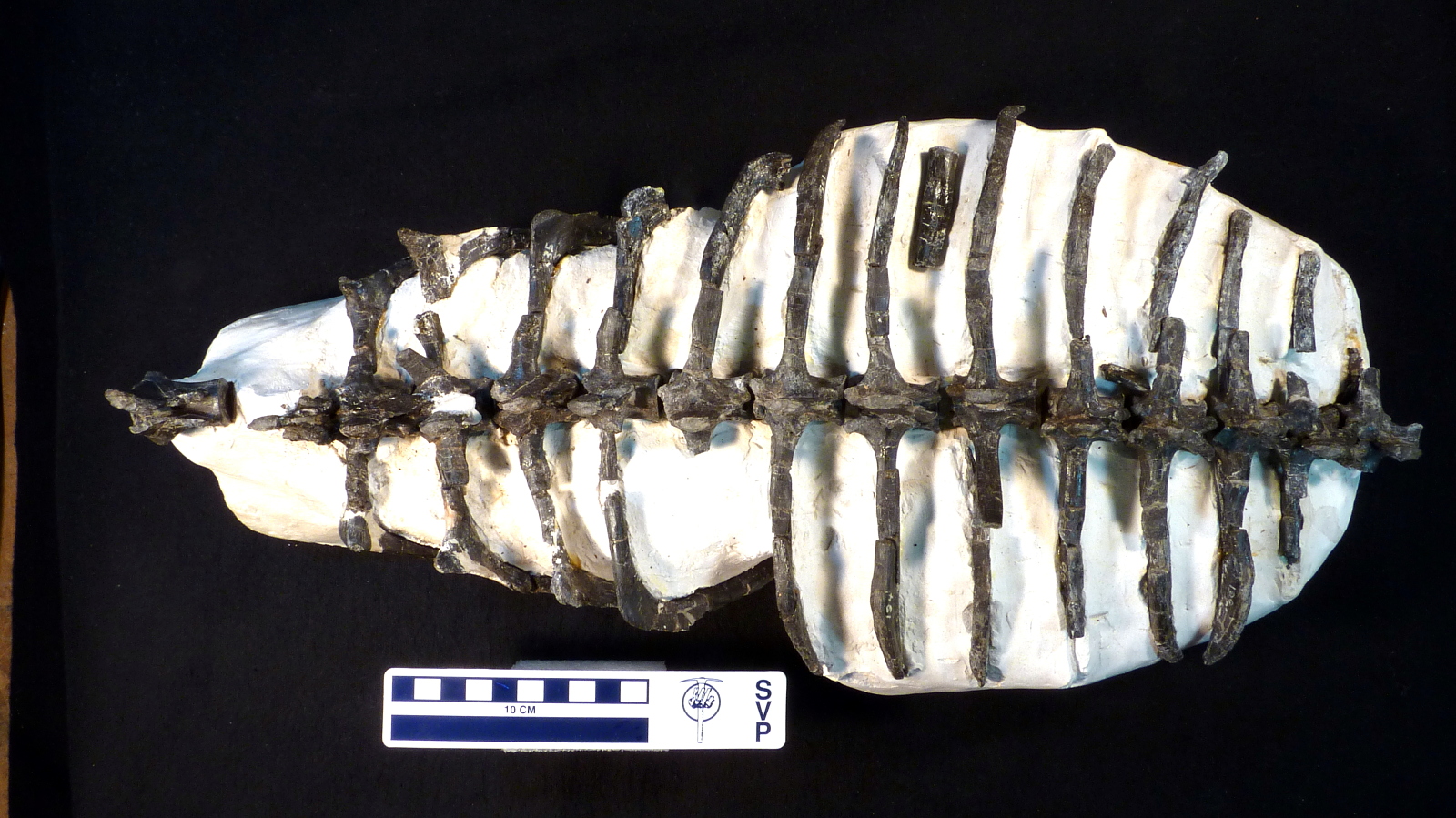
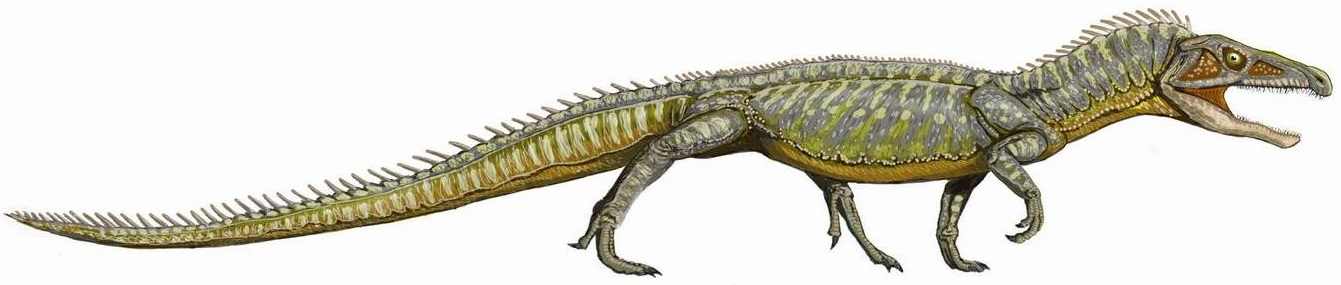
Doswellia Kaltenbachi
''Doswellia'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Late Triassic of North America. It is the most notable member of the family Doswelliidae, related to the proterochampsids. ''Doswellia'' was a low and heavily built carnivore which lived during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. It possesses many unusual features including a wide, flattened head with narrow jaws and a box-like rib cage surrounded by many rows of bony plates. The type species ''Doswellia kaltenbachi'' was named in 1980 from fossils found within the Vinita member of the Doswell Formation (formerly known as the Falling Creek Formation) in Virginia. The formation, which is found in the Taylorsville Basin, is part of the larger Newark Supergroup. ''Doswellia'' is named after Doswell, the town from which much of the taxon's remains have been found. A second species, ''D. sixmilensis,'' was described in 2012 from the Bluewater Creek Formation of the Chinle Group in New Mexico; however, this species was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doswellia
''Doswellia'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Late Triassic of North America. It is the most notable member of the family Doswelliidae, related to the proterochampsids. ''Doswellia'' was a low and heavily built carnivore which lived during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. It possesses many unusual features including a wide, flattened head with narrow jaws and a box-like rib cage surrounded by many rows of bony plates. The type species ''Doswellia kaltenbachi'' was named in 1980 from fossils found within the Vinita member of the Doswell Formation (formerly known as the Falling Creek Formation) in Virginia. The formation, which is found in the Taylorsville Basin, is part of the larger Newark Supergroup. ''Doswellia'' is named after Doswell, the town from which much of the taxon's remains have been found. A second species, ''D. sixmilensis,'' was described in 2012 from the Bluewater Creek Formation of the Chinle Group in New Mexico; however, this species was sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugarhynchos
''Rugarhynchos'' is an extinct genus of doswelliid archosauriform from the Late Triassic of New Mexico. The only known species is ''Rugarhynchos sixmilensis''. It was originally described as a species of ''Doswellia'' in 2012, before receiving its own genus in 2020. ''Rugarhynchos'' was a close relative of ''Doswellia'' and shared several features with it, such as the absence of an infratemporal fenestra and heavily textured skull bones. However, it could also be distinguished by many unique characteristics, such as a thick diagonal ridge on the side of the snout, blunt spikes on its osteoderms, and a complex suture between the quadratojugal, squamosal, and jugal. Non-metric multidimensional scaling and tooth morphology suggest that ''Rugarhynchos'' had a general skull anatomy convergent with some crocodyliforms, spinosaurids, and phytosaurs (particularly ''Smilosuchus''). However, its snout was somewhat less elongated than those other reptiles. Discovery The only known spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterochampsidae
Proterochampsidae is a family of proterochampsian archosauriforms. Proterochampsids may have filled an ecological niche similar to modern crocodiles, and had a general crocodile-like appearance. They lived in what is now South America in the Middle and Late Triassic. Description Proterochampsids have long, crocodile-like skulls. The posterior portion of the skull is wide while the snout is very narrow. Most proterochampsids also have downturned snouts. Like many early archosauriforms, they also have dermal armour. Proterochampsids have small holes called dorsal fenestrae at the top of their skulls. Unlike other early archosauromorphs, they do not have a parietal foramin, which in many reptiles holds a parietal eye. The postorbital bones behind the eye sockets have thick, jagged crests. As another diagnostic feature of the group, the holes that allow the passage of the internal carotid artery through the braincase open at the sides of a bony projection called the basipterygoid p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarjadia
''Tarjadia'' is an Extinction, extinct genus of Erpetosuchidae, erpetosuchid pseudosuchian, distantly related to modern crocodilians. It is known from a single species, ''T. ruthae'', first described in 1998 from the Middle Triassic Chañares Formation in Argentina. Partial remains have been found from deposits that are Anisian-Ladinian in age. Long known mostly from osteoderms, vertebrae, and fragments of the skull, specimens described in 2017 provided much more anatomical details and showed that it was a fairly large predator. ''Tarjadia'' predates known species of aetosaurs and phytosaurs, two Late Triassic groups of Crurotarsi, crurotarsans with heavy plating, making it one of the first heavily armored archosaurs. Prior to 2017, most studies placed it outside Archosauria as a member of Doswelliidae, a family of heavily armored and crocodile-like archosauriforms. The 2017 specimens instead show that it belonged to the Erpetosuchidae. Etymology The genus name ''Tarjadia'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erpetosuchidae
Erpetosuchidae is an extinct family of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Erpetosuchidae was named by D. M. S. Watson in 1917 to include ''Erpetosuchus''. It includes the type species '' Erpetosuchus granti'' from the Late Triassic of Scotland, ''Erpetosuchus'' sp. from the Late Triassic of eastern United States and '' Parringtonia gracilis'' from the middle Middle Triassic of Tanzania; the group might also include '' Dyoplax arenaceus'' from the Late Triassic of Germany, '' Archeopelta arborensis'' and '' Pagosvenator candelariensis'' from Brazil and '' Tarjadia ruthae'' from Argentina. Description General features Erpetosuchids were lithe but well-armored carnivorous pseudosuchians. Two rows of overlapping armored plates (osteoderms) extended from the neck to the tail, supplemented by an additional row on the back and tail and small oval-shaped osteoderms on the legs and possibly the arms as well. The osteoderms were unusually sculptured by deep pits and ranged in shape and thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria (the group that contains crocodiles, pterosaurs and dinosaurs bird.html"_;"title="ncluding_bird">ncluding_birds;_Phil_Senter.html" ;"title="bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter">bird">ncluding_birds.html" ;"title="bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds">bird.html" ;"title="ncluding bird">ncluding birds; Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing ''Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. These reptiles, which include members of the Family (biology), family Proterosuchidae and more advanced forms, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphodrosaurus
''Sphodrosaurus'' is an extinct genus of basal archosauriformn reptiles from the Late Triassic-aged New Oxford Formation (not the Brunswick Formation as initially suggested) of Pennsylvania. The type species is ''S. pennsylvanicus'', described by Edwin Colbert in 1960. Colbert, E. H. (1960). A New Triassic Procolophonid from Pennsylvania. ''American Museum Novitates'' 2022:1-19 The holotype ( NMN Franklin and Marshall College] 2321; the cast is listed under AMNH 7601) consists of a partial skeleton including the back of the skull, the vertebral column, all of the ribs, all of the hindlimbs and part of the upper forelimbs; ''Sphodrosaurus'' was originally believed to have been a member of the Procolophonidae while more recently ''Sphodrosaurus'' was believed to be a basal member of the Diapsida by most authors starting with Sues ''et al.'' (1993), or a member of the Rhynchosauria Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleromochlus
''Scleromochlus'' (from el, σκληρός , 'hard' and el, μοχλός , 'lever') is an extinct genus of small pterosauromorph archosaurs from the Late Triassic period. The genus contains the type and only species ''Scleromochlus taylori'', named by Arthur Smith Woodward in 1907. Discovery Its fossils have been found in the Carnian Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland. The holotype was discovered around 1900 and is listed as specimen BMNH R3556, a partial skeleton preserved as an impression in sandstone, with portions of the skull and tail missing. Description ''Scleromochlus taylori'' was about long, with long hind legs; it may have been capable of four-legged and two-legged locomotion. Studies about its gait suggest that it engaged in kangaroo- or springhare-like plantigrade hopping; however, a 2020 reassessment of ''Scleromochlus'' by Bennett suggested that it was a "sprawling quadrupedal hopper analogous to frogs." If ''Scleromochlus'' is indeed related to pterosaurs, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaxtasuchus
''Jaxtasuchus'' is an extinct genus of armored doswelliid archosauriform reptile known from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian stage) of the Erfurt Formation in Germany. The type species, ''Jaxtasuchus salomoni'', was named in 2013 on the basis of several incomplete skeletons and other isolated remains. Like other doswelliids, members of the genus were heavily armored, with four longitudinal rows of bony plates called osteoderms covering the body. ''Jaxtasuchus'' is the first doswelliid known from Europe and is most closely related to ''Doswellia'' from the Late Triassic of the eastern United States. However, it was not as specialized as ''Doswellia'', retaining several generalized archosauriform characteristics and having less armor. ''Jaxtasuchus'' fossils have been found in aquatic mudstones alongside fossils of temnospondyl amphibians, crustaceans, and mollusks, suggesting that ''Jaxtasuchus'' was semiaquatic like modern crocodilians. Discovery Fossils of ''Jaxtasuchus'' have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |