|
Dorylaion
Dorylaeum or Dorylaion ( el, Δορύλαιον; tr, Şarhöyük) was an ancient city in Anatolia. It is now an archaeological site located near the city of Eskişehir, Turkey. Its original location was about 10 km southwest of Eskişehir, at a place now known as Karaca Hisar; about the end of the fourth century B.C. it was moved to a location north of modern Eskişehir.''Catholic Encyclopedia'' History The city existed under the Phrygians but may have been much older. It was a Roman trading post. It also was probably a key city of the route the Apostle Paul took on his Second Missionary Voyage in 50 AD. It became a bishopric when part of the Late Roman province of Phrygia Salutaris. In the third century AD, it was threatened by Gothic raids. The Roman army that was based in Asia minor was spread thin, and the navy had moved west from the Northern city of Sinope, therefore the provincials were left exposed. These Goths came from the trans-danubian region on the black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Myriokephalon
The Battle of Myriokephalon (also known as the Battle of Myriocephalum, gr, Μάχη του Μυριοκέφαλου, tr, Miryokefalon Savaşı or ''Düzbel Muharebesi'') was a battle between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Turks in Phrygia in the vicinity of Lake Beyşehir in southwestern Turkey on 17 September 1176. The battle was a strategic reverse for the Byzantine forces, who were ambushed when moving through a mountain pass. It was to be the final, unsuccessful effort by the Byzantines to recover the interior of Anatolia from the Seljuk Turks. Background Between 1158 and 1161 a series of Byzantine campaigns against the Seljuk Turks of the Sultanate of Rûm resulted in a treaty favourable to the Empire, with the sultan recognising a form of subordination to the Byzantine emperor. Immediately after peace was negotiated the Seljuk sultan Kilij Arslan II visited Constantinople where he was treated by Emperor Manuel I Komnenos as both an honoured guest and an imperia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont, during which Pope Urban II supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. This call was met with an enthusiastic popular response across all social classes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
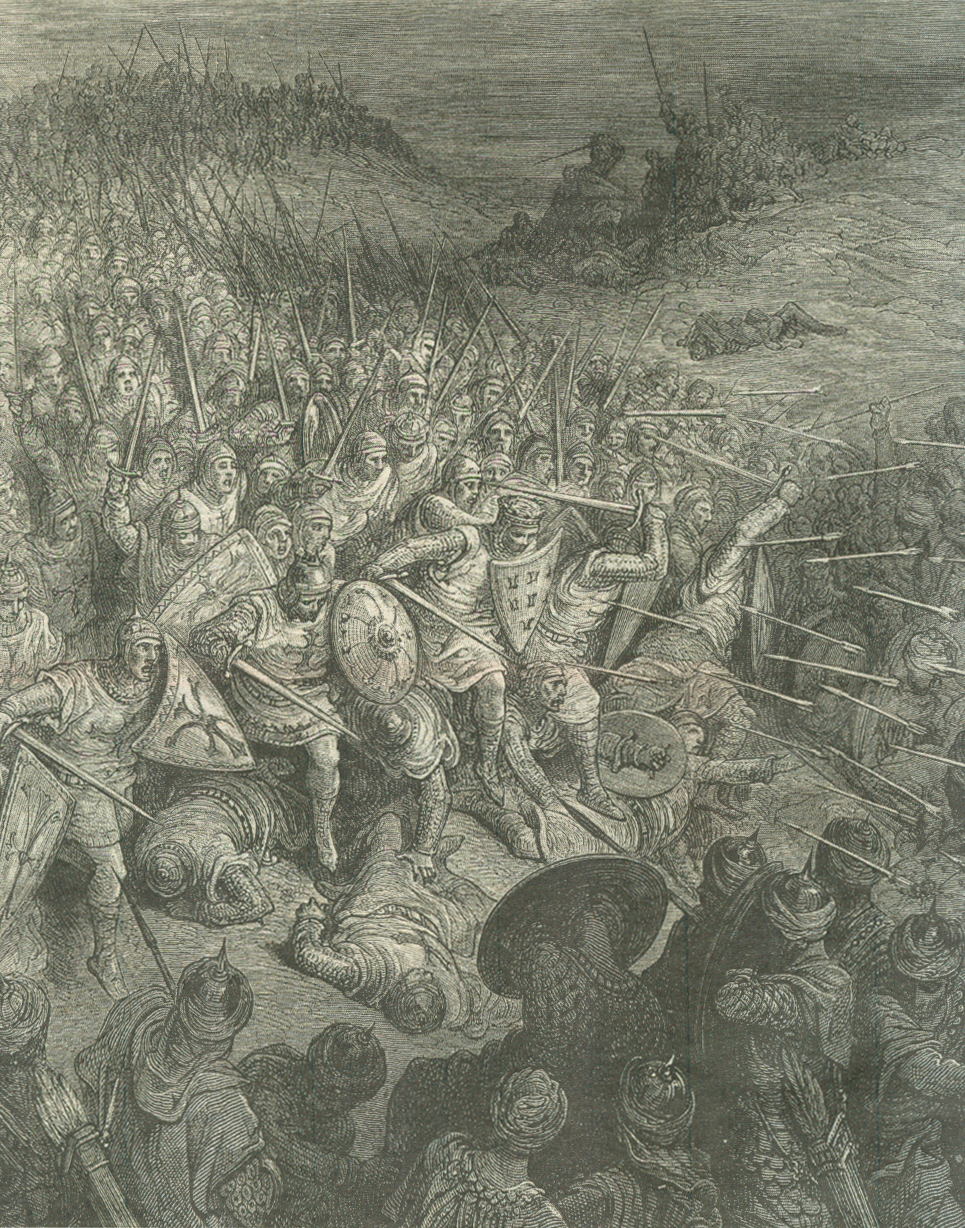
Battle Of Dorylaeum (1097)
The Battle of Dorylaeum took place during the First Crusade on 1 July 1097 between the crusader forces and the Seljuk Turks, near the city of Dorylaeum in Anatolia. Though the Turkish forces of Kilij Arslan nearly destroyed the Crusader contingent of Bohemond, other Crusaders arrived just in time to reverse the course of the battle. Background The crusaders had left Nicaea on 26 June 1097, with a deep distrust of the Byzantines, who had taken the city without their knowledge after the lengthy siege of Nicaea. In order to simplify the problem of supplies, the Crusader army had split into two groups; the weaker led by Bohemond of Taranto, his nephew Tancred, Robert Curthose, Robert of Flanders, and the Byzantine general Tatikios in the vanguard, and Godfrey of Bouillon, his brother Baldwin of Boulogne, Raymond IV of Toulouse, Stephen II of Blois, and Hugh of Vermandois in the rear. On 29 June, they learnt that the Turks were planning an ambush near Dorylaeum (Bohemond noticed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
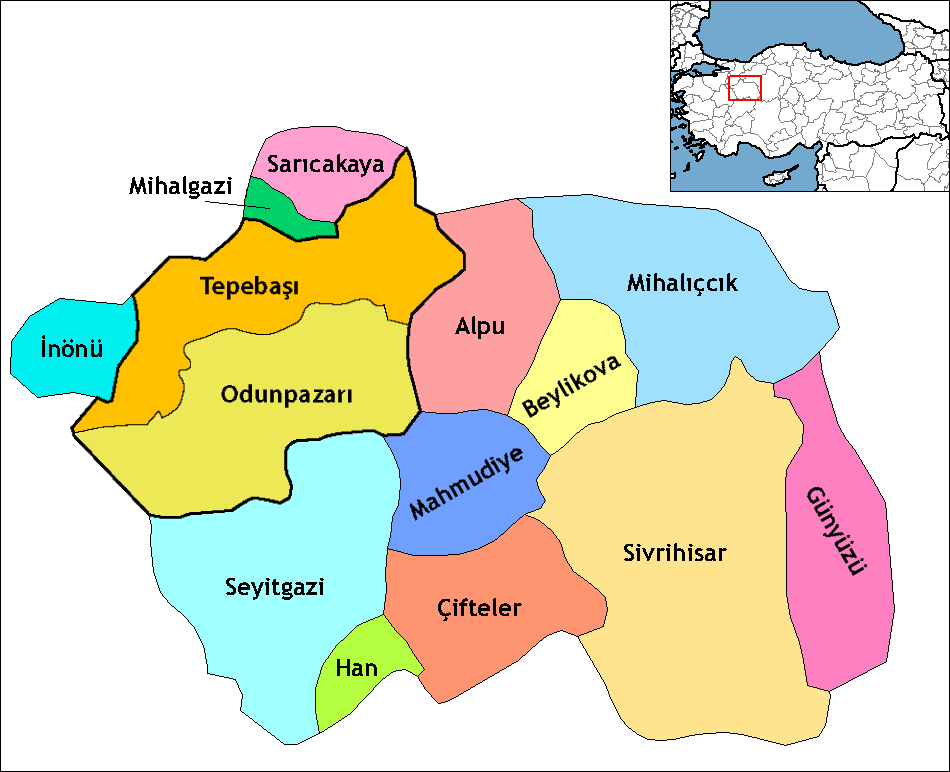
Eskişehir Province
Eskişehir Province ( tr, ) is a province in northwestern Turkey. Its adjacent provinces are Bilecik to the northwest, Kütahya to the west, Afyon to the southwest, Konya to the south, Ankara to the east, and Bolu to the north. The provincial capital is Eskişehir. Most of the province is laid down in Central Anatolia Region. Northern parts of Mihalıççık district and ones of Mihalgazi and Sarıcakaya are located in the Black Sea Region and one of them belong to the Aegean Region. Eskişehir is an old, culturally developed province of Turkey. It has a population of 844,842. Its urban population is 734,837. Eskişehir has 2 universities, Eskişehir Osmangazi University and Anadolu University, which is the largest university in Turkey and which has some branch offices in Europe. Districts Eskişehir province is divided into 14 districts, two of which are included in the greater municipality of Eskişehir (shown in boldface letters). *Odunpazarı * Tepebaşı *Alpu *Beyli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors (''symbasileis'') who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. It was under Constantine that the major characteristics of what is considered the Byzantine state emerged: a Roman polity centered at Constantinople and culturally dominated by the Greek East, with Christianity as the state religion. The Byzantine Empire was the direct le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synnada In Phrygia
Synnada ( gr, τὰ Σύνναδα) was an ancient town of Phrygia Salutaris in Asia Minor. Its site is now occupied by the modern Turkey, Turkish town of Şuhut, in Afyonkarahisar Province. Situation Synnada was situated in the south-eastern part of eastern Phrygia, or Parorea, thus named because it extended to the foot of the mountains of Pisidia, at the extremity of a plain about 60 stadia in length, and covered with opium plantations. Early history Synnada is said to have been founded by Acamas who went to Phrygia after the Trojan war and took some Macedonian colonists. It enters written history when the Ancient Rome, Roman consul Gnaeus Manlius Vulso (consul 189 BC), Gnaeus Manlius Vulso passed through that city on his expeditions against the Galatians (189 BCE). After having belonged to the kingdom of the Attalids, it became the capital of a district of the province of Asia, except on two occasions during the last century of the Roman Republic when it was temporarily atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffragan
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations. In the Anglican Communion, a suffragan bishop is a bishop who is subordinate to a metropolitan bishop or diocesan bishop (bishop ordinary) and so is not normally jurisdictional in their role. Suffragan bishops may be charged by a metropolitan to oversee a suffragan diocese and may be assigned to areas which do not have a cathedral of their own. In the Catholic Church, a suffragan Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop instead leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the Metropolitan bishop#Roman Catholic, metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led by the suffragan is called a suffragan diocese. Anglican Communion In the Anglican churches, the term applies to a bishop who is assigned responsibilities to support a diocesan bishop. For example, the Bishop of Jarrow is a suffragan to the diocesan Bishop of Durham. Suffragan bishops in the Anglican Communion are nearly id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circulation through faults to hot rock deep in the Earth's crust. In either case, the ultimate source of the heat is radioactive decay of naturally occurring radioactive elements in the Earth's mantle, the layer beneath the crust. Hot spring water often contains large amounts of dissolved minerals. The chemistry of hot springs ranges from acid sulfate springs with a pH as low as 0.8, to alkaline chloride springs saturated with silica, to bicarbonate springs saturated with carbon dioxide and carbonate minerals. Some springs also contain abundant dissolved iron. The minerals brought to the surface in hot springs often feed communities of extremophiles, microorganisms adapted to extreme conditions, and it is possible that life on Earth had its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)