|
Donald Wills Douglas, Sr.
Donald Wills Douglas Sr. (April 6, 1892 – February 1, 1981) was an American aircraft industrialist and engineer. An aviation pioneer, he designed and built the Douglas Cloudster. Though it failed in its intended purpose—being the first to fly non-stop across the United States—it became the first airplane with a payload greater than its own weight. He founded the Douglas Aircraft Company in 1921 (the company later merged with McDonnell Aircraft to form McDonnell Douglas Corporation, which merged with Boeing in 1997). Under his leadership, the company became one of the leaders of the commercial aircraft industry, engaging in a decades-long struggle for supremacy with arch-rival William Boeing and his eponymous enterprise. Douglas gained the upper hand, particularly with his revolutionary and highly successful Douglas DC-3 airliner and its equally popular World War II military transport version, the C-47; at the start of the war, his airplanes made up 80% of all commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklyn
Brooklyn is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City located at the westernmost end of Long Island in the New York (state), State of New York. Formerly an independent city, the borough is coextensive with Kings County, one of twelve original counties established under English rule in 1683 in what was then the Province of New York. As of the 2020 United States census, the population stood at 2,736,074, making it the most populous of the five boroughs of New York City, and the most populous Administrative divisions of New York (state)#County, county in the state.Table 2: Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State - 2020 New York State Department of Health. Accessed January 2, 2024. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish American
Scottish Americans or Scots Americans (; ) are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Scotland. Scottish Americans are closely related to Scotch-Irish Americans, descendants of Ulster Scots, and communities emphasize and celebrate a common heritage.Celeste Ray, 'Introduction', p. 6, id., 'Scottish Immigration and Ethnic Organization in the United States', pp. 48-9, 62, 81, in id. (ed.), ''The Transatlantic Scots'' (Tuscaloosa, AL:University of Alabama Press, 2005). The majority of Scotch-Irish Americans originally came from Lowland Scotland and Northern England before migrating to the province of Ulster in Ireland (see ''Plantation of Ulster'') and thence, beginning about five generations later, to North America in large numbers during the eighteenth century. The number of Scottish Americans is believed to be around 25 million, and celebrations of Scottish identity can be seen through Tartan Day parades, Burns Night celebrations, and Tartan Kirking cere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DN-1 (airship)
The DN-1 was the United States Navy's first airship. Development Captain Mark L. Bristol, the second Director of Naval Aviation, supported the development of the dirigible in the anti-submarine role.Grossnik, Roy A. 1986 ''Kite Balloons to Airships . . . the Navy's Lighter-than-Air Experience'', Washington D.C.: Deputy Chief of Naval Operations (Air Warfare) and the Commander, Naval Air Systems Command, p. 3. Victor Herbster, Holden Richardson and LCDR Frank McCrary drew up the specifications for the DN-1. The contract was awarded on 1 June 1915 to the Connecticut Aircraft Company of New Haven, CT.Clark, Basil, ''The History of Airships'', New York: St Martin's Press, 1961, Library of Congress 64-12336, p. 146. The U.S. Navy had no experience with airships and it seems neither had any of the principals of Connecticut Aircraft Company. They were a lawyer who was the financial backer, an amusement park owner who acted as manager; the technical staff was an Austrian, Hans Otto S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikorsky Aircraft
Sikorsky Aircraft is an American aircraft manufacturer based in Stratford, Connecticut. It was established by the Russian-American aviation pioneer Igor Sikorsky in 1923, and was among the first companies to manufacture helicopters for civilian and military use. It also produced seaplanes for passenger transport and surface vehicles such as trains and boats. Sikorsky was owned by United Technologies Corporation until November 2015, when it was sold to Lockheed Martin. History On March 5, 1923, the Sikorsky Aero Engineering Corporation was founded near Roosevelt Field (airport), Roosevelt Field, New York, by Igor Sikorsky, an immigrant to the United States who was born in Kyiv, Kiev, in the Russian Empire (today in Ukraine). In 1925, the company name was changed to Sikorsky Manufacturing Company. After the success of the Sikorsky S-38, S-38, the company was reorganized as the Sikorsky Aviation Corporation with capital of $5,000,000, allowing the purchase of land and the buildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald W
Donald is a Scottish masculine given name. It is derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers. A short form of Donald is Don, and pet forms of Donald include Donnie and Donny. The feminine given name Donella is derived from Donald. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh '' Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name '' Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations Kings and noblemen Domnall or Domhnall is the name of many ancient and medieval Gaelic kings and noblemen: * Dyfnwal Moelmud (Dunvallo Molmutius), legendary kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerome Hunsaker
Jerome Clarke Hunsaker (August 26, 1886 – September 10, 1984) was an American naval officer and aeronautical engineer, born in Creston, Iowa, and educated at the U.S. Naval Academy and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. His work with Gustav Eiffel outside Paris led to the first wind tunnel in the US at MIT. He was instrumental in developing a weather reporting and airway navigation. Hunsaker was also pivotal in establishing the theoretical and scientific study of aerodynamics in the United States. And he was primarily responsible for the design and construction of the Navy-Curtiss airplane (NC-4) that accomplished the first transatlantic flight (May 1919), and the first successful shipboard fighter. Later he championed lighter-than-air flight but the loss of the Navy airship he designed, the USS Akron, led to the withdrawal of federal support. His WW2 chairmanship of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was notable for favouring the development of exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronautical Engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is similar, but deals with the electronics side of aerospace engineering. "Aeronautical engineering" was the original term for the field. As flight technology advanced to include vehicles operating in outer space, the broader term "aerospace engineering" has come into use. Aerospace engineering, particularly the astronautics branch, is often colloquially referred to as "rocket science". Overview Flight vehicles are subjected to demanding conditions such as those caused by changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature, with structural loads applied upon vehicle components. Consequently, they are usually the products of various technological and engineering disciplines including aerodynamics, air propulsion, avionics, materials science, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, B.S., B.Sc., SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree that is awarded for programs that generally last three to five years. The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of London in 1860. In the United States, the Lawrence Scientific School first conferred the degree in 1851, followed by the University of Michigan in 1855. Nathaniel Shaler, who was Harvard's Dean of Sciences, wrote in a private letter that "the degree of Bachelor of Science came to be introduced into our system through the influence of Louis Agassiz, who had much to do in shaping the plans of this School." Whether Bachelor of Science or Bachelor of Arts degrees are awarded in particular subjects varies between universities. For example, an economics student may graduate as a Bachelor of Arts in one university but as a Bachelor of Science in another, and occasionally, both options are offered. Some universities follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn Curtiss
Glenn Hammond Curtiss (May 21, 1878 – July 23, 1930) was an American aviation and motorcycling pioneer, and a founder of the U.S. aircraft industry. He began his career as a bicycle racer and builder before moving on to motorcycles. As early as 1904, he began to manufacture engines for airships. In 1908, Curtiss joined the Aerial Experiment Association, a pioneering research group, founded by Alexander Graham Bell at Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia, to build flying machines. Curtiss won a race at the world's first international air meet in France and made the first long-distance flight in the U.S. His contributions in designing and building aircraft led to the formation of the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company, which later merged into the Curtiss-Wright Corporation. His company built aircraft for the U.S. Army and Navy, and, during the years leading up to World War I, his experiments with seaplanes led to advances in naval aviation. Curtiss civil and military aircraft were some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grover Loening
Grover Cleveland Loening (September 12, 1888 – February 29, 1976) was an American aircraft manufacturer. Biography Loening was born in Bremen (city), Bremen, in what was then Imperial Germany, on September 12, 1888, while his American-born father was stationed there as U.S. Consul. He graduated from Columbia University in New York City, where he was awarded the first-ever degree in Aeronautical Engineering. Following graduation, he joined the Queen Aeroplane Company in New York, managed the Wright Company factory in Dayton, Ohio for Orville Wright in 1913 and 1914, published a book, ''Military Airplanes'', and became Vice President of the Sturtevant Aeroplane Company and Chief engineer for the Army in San Diego. In 1917 he formed the Loening Aircraft Engineering, Loening Aeronautical Engineering Corporation; after it merged with Keystone Aircraft in 1928, he formed the Grover Loening Aircraft Company. His work on the Loening S-1 Flying Yacht, Loening Flying Yacht won the 1921 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
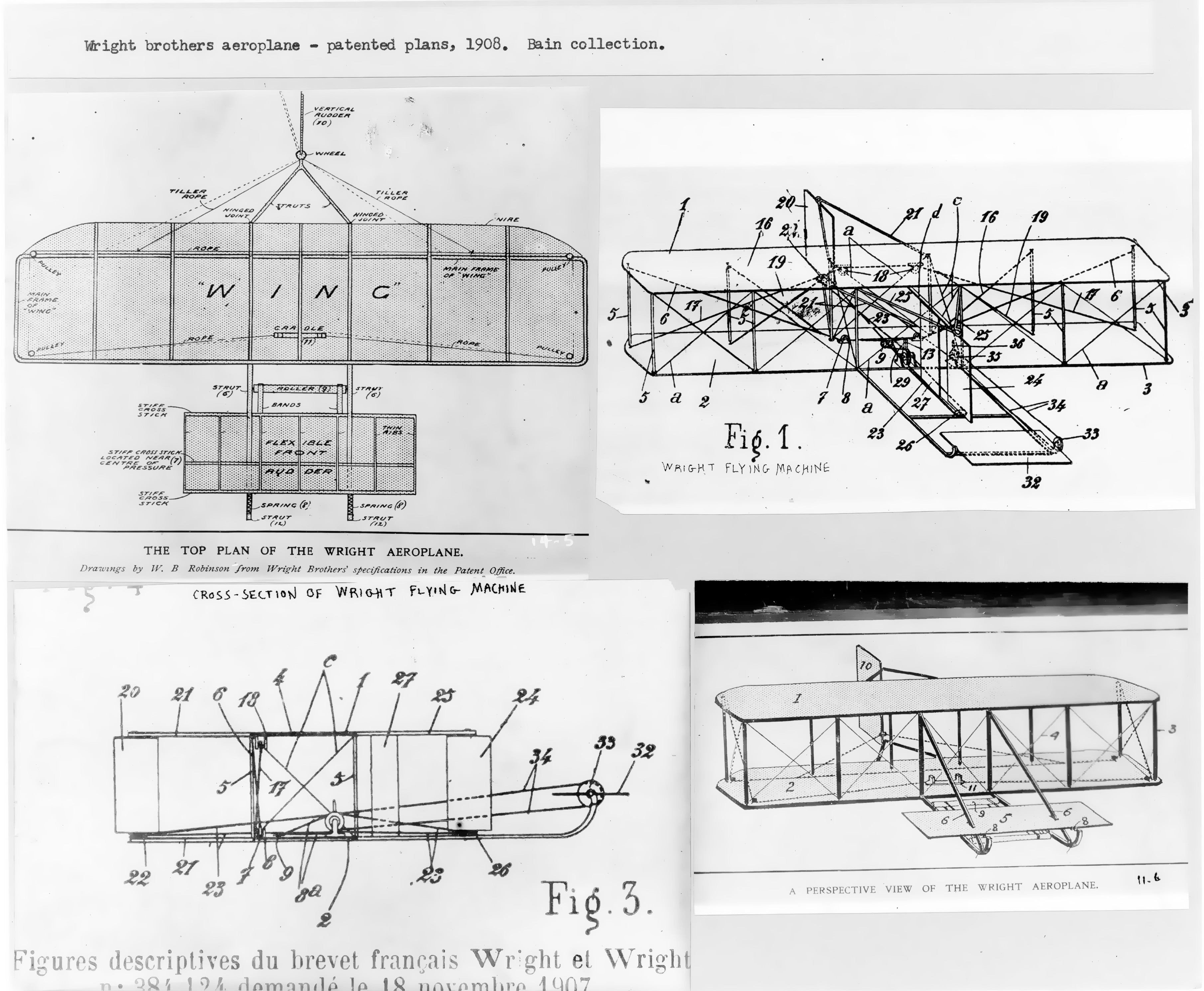
Wright Flyer
The ''Wright Flyer'' (also known as the ''Kitty Hawk'', ''Flyer'' I or the 1903 ''Flyer'') made the first sustained flight by a manned heavier-than-air powered and controlled aircraft on December 17, 1903. Invented and flown by brothers Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur Wright, it marked the beginning of the Aviation in the pioneer era, pioneer era of aviation. The aircraft is a single-place biplane design with Dihedral (aeronautics)#Anhedral and polyhedral, anhedral (drooping) wings, front double Elevator (aeronautics), elevator (a canard (aeronautics), canard) and rear double rudder. It used a gasoline engine powering two pusher propellers. Employing "wing warping", it was relatively unstable and very difficult to fly. The Wright brothers flew it four times in a location now part of the town of Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, Kill Devil Hills, about south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. The airplane flew on its fourth and final flight, but was damaged on landing, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
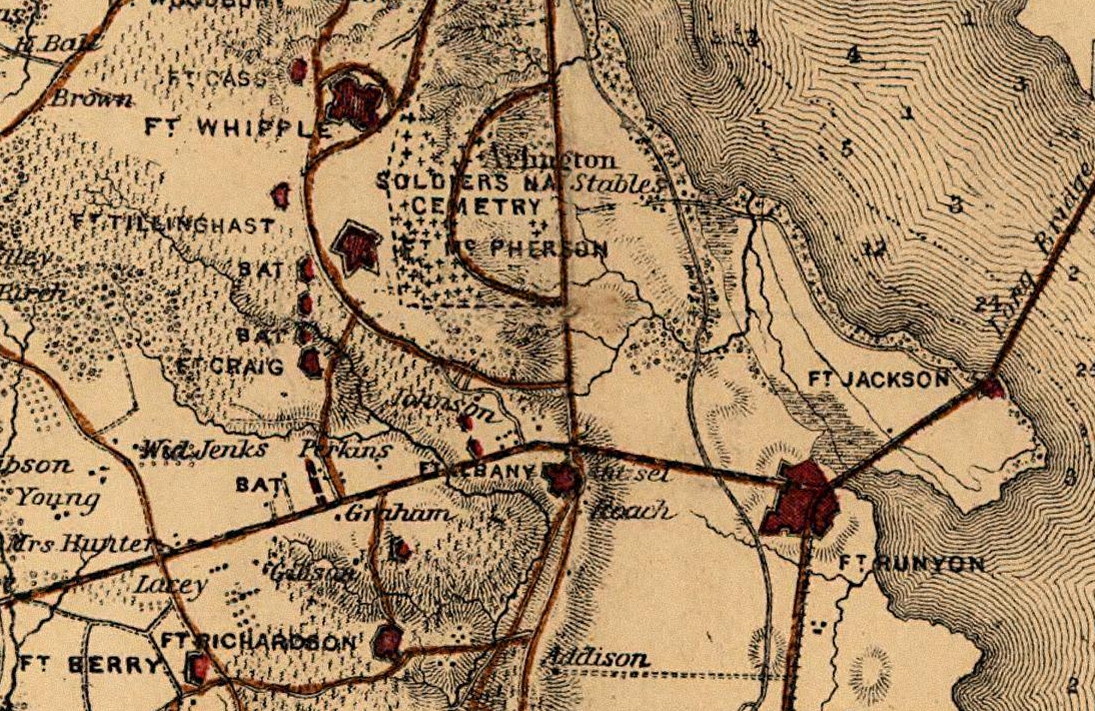
Fort Myer
Fort Myer is the previous name used for a U.S. Army Military base, post next to Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, and across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. Founded during the American Civil War as Fort Cass and Fort Whipple, the post merged in 2005 with the neighboring United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps installation, Henderson Hall, and is today named Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall. History In 1861, the land that Fort Myer would eventually occupy was part of the Arlington estate, which Mary Anna Custis Lee, the wife of Robert E. Lee, owned and at which Lee resided when not stationed elsewhere (see Arlington House, The Robert E. Lee Memorial). When the American Civil War, Civil War began, the Virginia, Commonwealth of Virginia seceded from the United States, Lee resigned his commission, and he and his wife left the estate. The United States Government then confiscated the estate and began to use it as a burial ground for Union Army dead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |