|
Dome Mountain Land
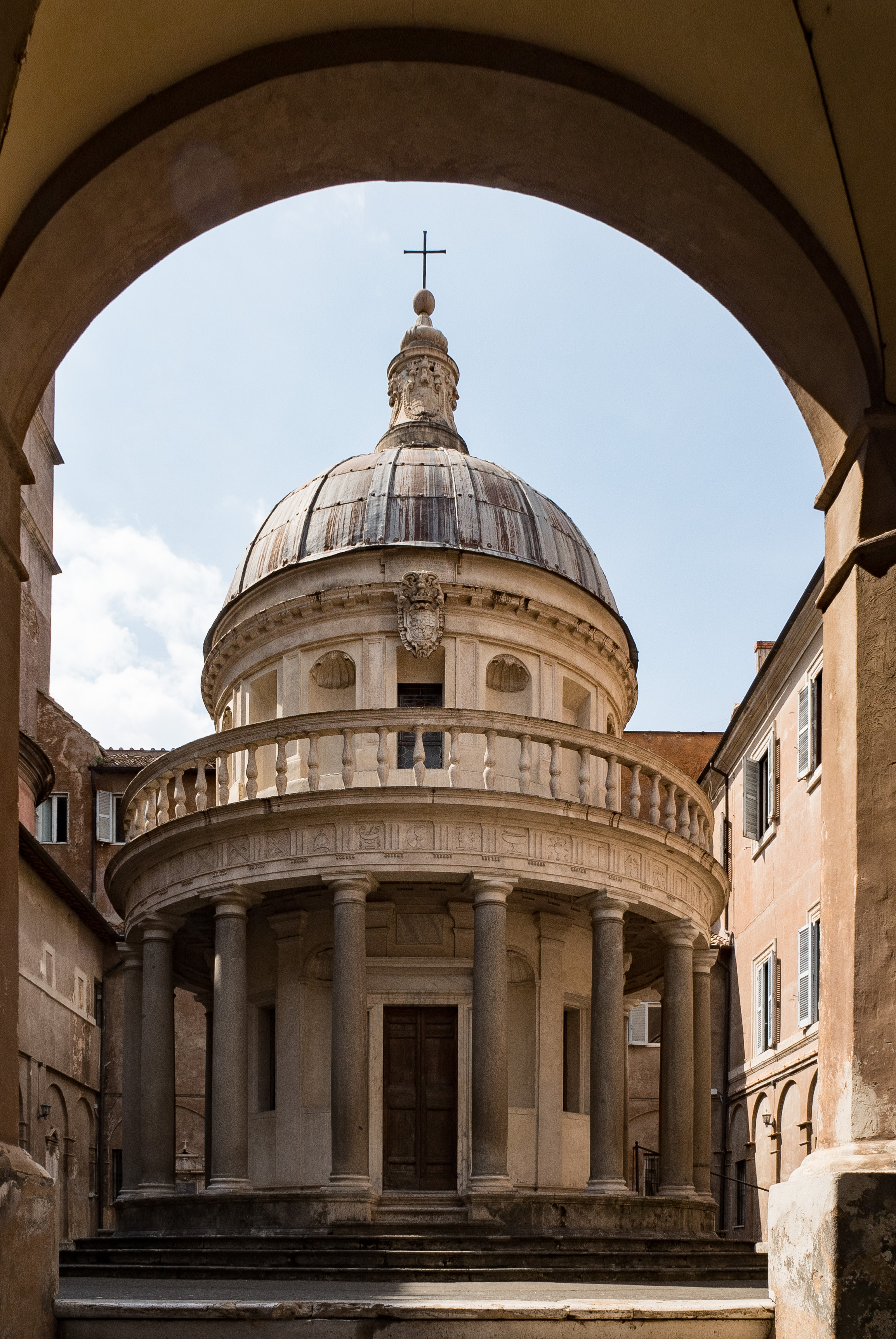
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a matter of controversy and there are a wide variety of forms and specialized terms to describe them. A dome can rest directly upon a rotunda wall, a drum, or a system of squinches or pendentives used to accommodate the transition in shape from a rectangular or square space to the round or polygonal base of the dome. The dome's apex may be closed or may be open in the form of an oculus, which may itself be covered with a roof lantern and cupola. Domes have a long architectural lineage that extends back into prehistory. Domes were built in ancient Mesopotamia, and they have been found in Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, and Chinese architecture in the ancient world, as well as among a number of indigenous building traditions throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre (geometry), centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. spherical Earth, The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in any direction, so mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
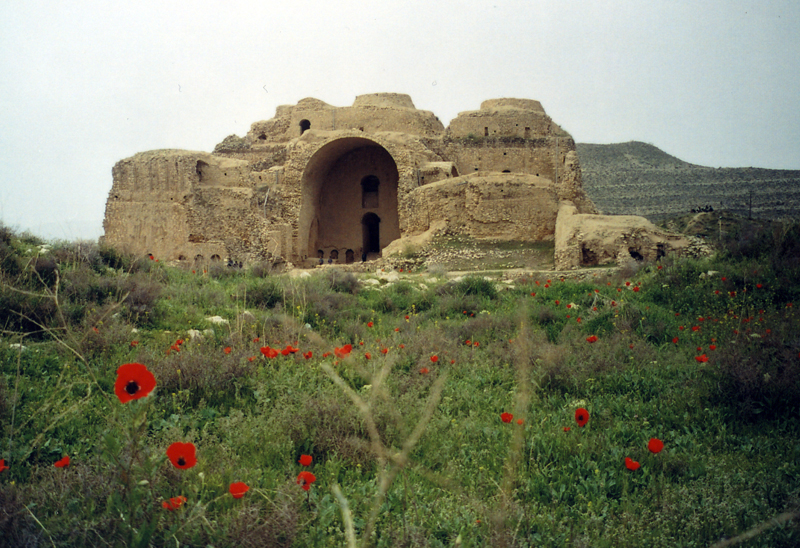
Sasanian Architecture
Sasanian architecture refers to the Persian architectural style that reached a peak in its development during the Sasanian era. In many ways the Sasanian Empire period (224–651 CE) witnessed the highest achievement of Iranian civilization, and constituted the last great pre-Islamic Persian Empire before the Muslim conquest. Much of Sasanian architecture was adopted by Muslims and became part of Islamic architecture. The Sasanian dynasty, like the Achaemenid Empire, originated in the province of Persis ( Fars). They saw themselves as successors to the Achaemenians, after the Hellenistic and Parthian dynasty interlude, and perceived it as their role to restore the greatness of Persia. Origins In reviving the glories of the Achaemenian past, the Sasanians were no mere imitators. The art of this period reveals an astonishing virility. In certain respects it anticipates features later developed during the Islamic period. The conquest of Persia by Alexander the Great had inaugura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corbel Arch
A corbel arch (or corbeled / corbelled arch) is an arch-like construction method that uses the architectural technique of corbeling to span a space or void in a structure, such as an entranceway in a wall or as the span of a bridge. A corbel vault uses this technique to support the superstructure of a building's roof. A corbel arch is constructed by offsetting successive horizontal courses of stone (or brick) beginning at the springline of the walls (the point at which the walls break off from verticality to form an arc toward the apex at the archway's center) so that they project towards the archway's center from each supporting side, until the courses meet at the apex of the archway (often, the last gap is bridged with a flat stone). For a corbeled vault covering, the technique is extended in three dimensions along the lengths of two opposing walls. Although an improvement in load-bearing efficiency over the post and lintel design, corbeled arches are not entirely self-suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Truefalserp
ARC may refer to: Business * Aircraft Radio Corporation, a major avionics manufacturer from the 1920s to the '50s * Airlines Reporting Corporation, an airline-owned company that provides ticket distribution, reporting, and settlement services * Airport Regions Conference, a European organization of major airports * Amalgamated Roadstone Corporation, a British stone quarrying company * American Record Company (1904–1908, re-activated 1979), one of two United States record labels by this name * American Record Corporation (1929–1938), a United States record label also known as American Record Company * ARC (American Recording Company) (1978-present), a vanity label for Earth, Wind & Fire * ARC Document Solutions, a company based in California, formerly American Reprographics Company * Amey Roadstone Construction, a former British construction company * Aqaba Railway Corporation, a freight railway in Jordan * ARC/Architectural Resources Cambridge, Inc., Cambridge, Massachuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent collapse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
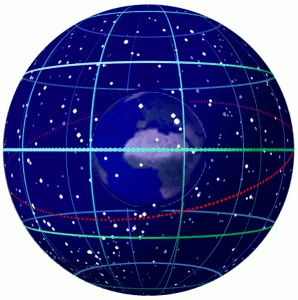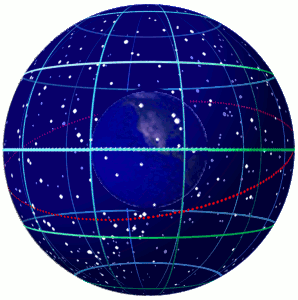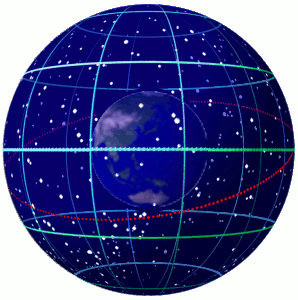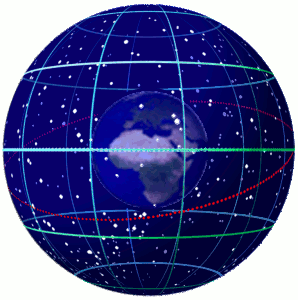
Celestial Sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Introduction Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westward o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Funerary Art
Funerary art is any work of art forming, or placed in, a repository for the remains of the dead. The term encompasses a wide variety of forms, including cenotaphs ("empty tombs"), tomb-like monuments which do not contain human remains, and communal memorials to the dead, such as war memorials, which may or may not contain remains, and a range of prehistoric megalithic constructs. Funerary art may serve many cultural functions. It can play a role in burial rites, serve as an article for use by the dead in the afterlife, and celebrate the life and accomplishments of the dead, whether as part of kinship-centred practices of ancestor veneration or as a publicly directed dynastic display. It can also function as a reminder of the mortality of humankind, as an expression of cultural values and roles, and help to propitiate the spirits of the dead, maintaining their benevolence and preventing their unwelcome intrusion into the lives of the living. The deposit of objects with an appar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia and the Spanish and Portuguese colonies in Latin America. About 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe. Baroque architects took the basic elements of Renaissance architecture, including domes and colonnades, and made them higher, grander, more decorated, and more dramatic. The interior effects were often achieved with the use of ''quadratura'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Architecture
Ottoman architecture is the architectural style that developed under the Ottoman Empire. It first emerged in northwestern Anatolia in the late 13th century and developed from earlier Seljuk architecture, Seljuk Turkish architecture, with influences from Byzantine architecture, Byzantine and Iranian architecture, Iranian architecture along with other architectural traditions in the Middle East.: "The grand tradition of Ottoman architecture, established in the 16th century, differed markedly from that of the earlier Moors. It was derived from both the Byzantine Christian tradition, outlined above, and native Middle Eastern forms used by the Islamic Seljuk Turks, who preceded the Ottomans. The Byzantine tradition, particularly as embodied in Hagia Sophia, was perhaps the major source of inspiration." "The mosques of the classical period are more elaborate than those of earlier times. They derive from a fusion of a native Turkish tradition with certain elements of the plan of Haghia S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to Spain, France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact. Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion (architecture), proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts, as demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)

.jpg)
