|
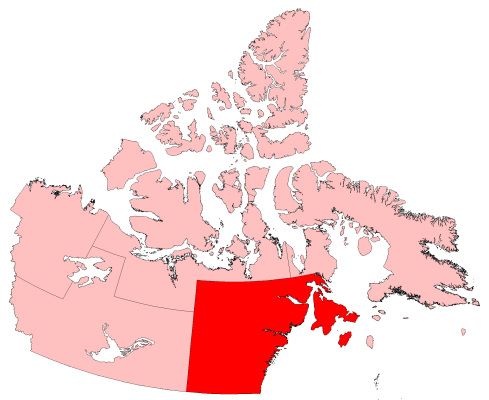
District Of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories. It was created in 1876 by the ''Keewatin Act'', and originally it covered a large area west of Hudson Bay. In 1905, it became a part of the Northwest Territories and in 1912, its southern parts were adjoined to the provinces of Manitoba and Ontario, leaving the remainder, now called the Keewatin Region, with a population of a few thousand people. On April 1, 1999, the Keewatin Region was formally dissolved, as Nunavut was created from eastern parts of the Northwest Territories, including all of Keewatin. The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either in Cree or in Ojibwe—both of which mean ''north wind'' in their respective languages. In Inuktitut, it was called —a name which persists as the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut. History as a territory, 1876–1905 The District of Keewatin was created by the passage of the ''Keewatin Act'' on October 7, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keewatin Region, Northwest Territories
:''The Keewatin Region was a distinct entity from the District of Keewatin, although much of their territory overlapped.'' The Keewatin Region was a region of the Northwest Territories, in use as an administrative and statistical division until the creation of Nunavut in 1999. The majority of Keewatin Region fell on the Nunavut side of the boundary and was reconstituted as Kivalliq Region within the new territory, while a strip on the region's west side remaining in the NWT was transferred to Fort Smith Region. Kivalliq continues to be referred to as "''Keewatin Region, Nunavut''" in some circumstances, such as by Statistics Canada. The regional seat of the Keewatin Region was Rankin Inlet Rankin Inlet ( iu, Kangiqliniq; Inuktitut syllabics: ᑲᖏᕿᓂᖅ or ''Kangirliniq'', ᑲᖏᖅᖠᓂᖅ, or ''Kangir&iniq'' meaning ''deep bay/inlet'') is an Inuit hamlet on Kudlulik Peninsula in Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest hamlet and .... Further reading * Anawak, Caroline, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James McKay (fur Trader)
James McKay (1828 – December 2, 1879) was a fur trader, pioneer, and pre-Canadian confederation politician and interpreter. Early life James McKay was born in 1828 at the Hudson's Bay Company's Edmonton House, the son of James Charles (b. 1797, Scotland) and Marguerite Gladu (b. 1809, Métis, Cumberland House). He was a brother to Angus McKay. McKay was educated at the Red River Colony and began work with the HBC in 1853 as a fur-trader and guide/interpreter. Many distinguished visitors sought him out as a guide; he often met the HBC governor, George Simpson in Crow Wing, Minnesota, and escorted him to Upper Fort Garry. In 1857, while at Fort Ellice, he was engaged to guide the John Palliser party from Fort Ellice ( St Lazare, MB) through the Saskatchewan plains to its winter quarters at Fort Carlton, Saskatchewan. McKay married in 1859 and left the HBC in 1860, going into business for himself. He established his home west of the Forks in present-day Manitoba and qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Of Franklin
The District of Franklin was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories. The district consisted of the Canadian high Arctic Islands, notably Ellesmere Island, Baffin Island, and Victoria Island. The district also contained the mainland Melville Peninsula and Boothia Peninsula. English navigators Martin Frobisher and Henry Hudson were the first Europeans known to have visited the area (although Viking sailors, coming from Greenland, may have made occasional landings and hunting treks on Baffin Island in the 11th and 12th centuries). The area was transferred from British colonial authority to the Dominion of Canada in 1894 and named after Sir John Franklin in the following year; however, the northernmost islands were claimed by Norway Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arcti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Of Mackenzie
The District of Mackenzie was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories. The district consisted of the portion of the Northwest Territories directly north of British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan on Canada's mainland. Along with the District of Keewatin and the District of Franklin, it was one of the last remaining districts of the old Northwest Territories before the formation of Nunavut in 1999, at which point it ceased to exist. As an administrative district of the NWT it had ceased to function several years prior to division. Today the area that formerly comprised the District of Mackenzie is mostly included in the Northwest Territories (which is no longer subdivided into districts). The remainder, along with all of Keewatin and most of Franklin, is in Nunavut. See also * Territorial evolution of Canada The history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
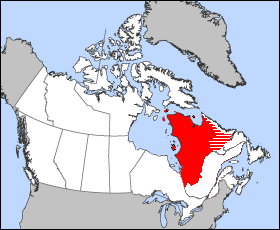
District Of Ungava
The District of Ungava was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories from 1895 to 1920, although it effectively ceased operation in 1912. It covered the northern portion of what is today Quebec, the interior of Labrador, and the offshore islands to the west and north of Quebec, which are now part of Nunavut. The name "Ungava" is of Inuktitut origin, meaning "towards the open water". It is believed to be in reference to the lands inhabited by the Ungava Inuit, who lived at the mouth of the Arnaud River which flows into Ungava Bay. Political history When created in 1895, the District of Ungava covered all of modern-day northern Quebec, the interior of modern-day Labrador, and all the islands in James Bay, the Hudson Strait, Ungava Bay, and the eastern side of Hudson Bay. Ungava's southern continental boundaries initially ranged as far south as Lake Timiskaming, well below James Bay on the modern Ontario/Quebec border. Note, however, that a dispute over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library And Archives Canada
Library and Archives Canada (LAC; french: Bibliothèque et Archives Canada) is the federal institution, tasked with acquiring, preserving, and providing accessibility to the documentary heritage of Canada. The national archive and library is the fifth largest library in the world. The LAC reports to the Parliament of Canada through the Minister of Canadian Heritage. The LAC traces its origins to the Dominion Archives, formed in 1872, and the National Library of Canada, formed in 1953. The former was later renamed as the Public Archives of Canada in 1912, and the National Archives of Canada in 1987. In 2004, the National Archives of Canada and the National Library of Canada were merged to form Library and Archives Canada. History Predecessors The Dominion Archives was founded in 1872 as a division within the Department of Agriculture tasked with acquiring and transcribing documents related to Canadian history. In 1912, the division was transformed into an autonomous organiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
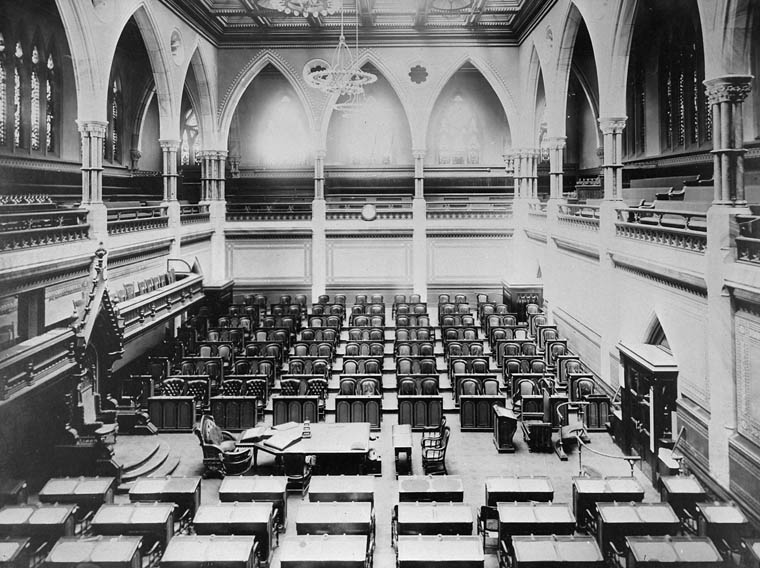
Legislative Assembly Of The Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories Legislative Assembly, or Legislative Council of the Northwest Territories (with Northwest hyphenated as North-West until 1906), is the legislature and the seat of government of Northwest Territories in Canada. It is a unicameral elected body that creates and amends law in the Northwest Territories. Permanently located in Yellowknife since 1993, the assembly was founded in 1870 and became active in 1872 with the first appointments from the Government of Canada. Until 2014, the assembly was officially defined under federal law as "Legislative Council". However, under Northwest Territories territorial law, it was defined as "Legislative Assembly". The federal name was changed when the Northwest Territories Act was rewritten in 2014. Under different periods of its history it has alternated names. Members of the Legislative Assembly are sworn in by the Commissioner of the Northwest Territories. Early history The Legislative Assembly was first known as the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
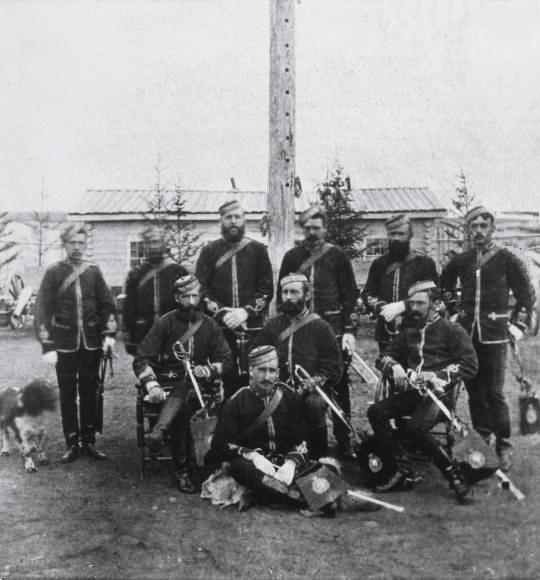
North-West Mounted Police
The North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) was a Canadian para-military police force, established in 1873, to maintain order in the new Canadian North-West Territories (NWT) following the 1870 transfer of Rupert’s Land and North-Western Territory to Canada from the Hudson’s Bay Company, the Red River Rebellion and in response to lawlessness, demonstrated by the subsequent Cypress Hills Massacre and fears of United States military intervention. The NWMP combined military, police and judicial functions along similar lines to the Royal Irish Constabulary. A small, mobile police force was chosen to reduce potential for tensions with the United States and First Nations in Canada, First Nations. The NWMP uniforms included red coats deliberately reminiscent of British and Canadian military uniforms. The NWMP was established by the Canadian government during the ministry of Prime Minister of Canada, Prime Minister Sir John A. Macdonald, John Macdonald who defined its purpose as "the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of Canada
The Senate of Canada (french: region=CA, Sénat du Canada) is the upper house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the House of Commons, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada. The Senate is modelled after the British House of Lords with members appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister. The explicit basis on which appointment is made and the chamber's size is set, at 105 members, is by province or territory assigned to 'divisions'. The Constitution divides provinces of Canada geographically among four regions, which are represented equally. Senatorial appointments were originally for life; since 1965, they have been subject to a mandatory retirement age of 75. While the Senate is the upper house of parliament and the House of Commons is the lower house, this does not imply the former is more powerful than the latter. It merely entails that its members and officers outrank the members and officers of the Commons in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Commons Of Canada The House of Commons of Canada (french: Chambre des communes du Canada) is the lower house of the Parliament of Canada. Together with the Crown and the Senate of Canada, they comprise the bicameral legislature of Canada. The House of Commons is a democratically elected body whose members are known as members of Parliament (MPs). There have been 338 MPs since the most recent electoral district redistribution for the 2015 federal election, which saw the addition of 30 seats. Members are elected by simple plurality ("first-past-the-post" system) in each of the country's electoral districts, which are colloquially known as ''ridings''. MPs may hold office until Parliament is dissolved and serve for constitutionally limited terms of up to five years after an election. Historically, however, terms have ended before their expiry and the sitting government has typically dissolved parliament within four years of an election according to a long-standing convention. In any case, an ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] |