|
Display Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio of a display device is the proportional relationship between the width and the height of the display. It is expressed as two numbers separated by a colon (''x'':''y''), where ''x'' corresponds to the width and ''y'' to the height. Common aspect ratios for displays, past and present, include 5:4, 4:3, 16:10 and 16:9. Computer displays As of 2016, most computer monitors use widescreen displays with an aspect ratio of 16:9, although some portable PCs use narrower aspect ratios like 3:2 and 16:10 while some high-end desktop monitors have adopted ultrawide displays. The following table summarises the different aspect ratios that have been used in computer displays: † The resolution doesn't match the aspect ratio exactly, but is commonly marketed or described as such. History 4:3, 5:4 and 16:10 Until about 2003, most computer monitors used an aspect ratio of 4:3, and in some cases 5:4. For cathode ray tubes (CRT)s 4:3 was most common even in resolutions w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspect Ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height, and is expressed with two numbers separated by a colon, such as ''16:9'', sixteen-to-nine. For the ''x'':''y'' aspect ratio, the image is ''x'' units wide and ''y'' units high. Common aspect ratios are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1 in cinematography, 4:3 and 16:9 in television photography, and 3:2 in still photography. Some common examples The common film aspect ratios used in cinemas are 1.85:1 and 2.39:1.The 2.39:1 ratio is commonly labeled 2.40:1, e.g., in the American Society of Cinematographers' ''American Cinematographer Manual'' (Many widescreen films before the 1970 SMPTE revision used 2.35:1). Two common videographic aspect ratios are 4:3 (1.:1), the universal video format of the 20th century, and 16:9 (1.:1), universal for high-definition television and European digital television. Other cinema and video aspect ratios exist, but are used infrequently. In still camera photography, the most common aspec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letter (paper Size)
Letter or ANSI Letter is a paper size standard defined by the American National Standards Institute, commonly used as home or office stationery in the United States, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Mexico, Panama, Guatemala, the Dominican Republic and the Philippines. It measures and is similar in use to the A4 paper standard used by most other countries, defined in ISO 216 by the International Organization for Standardization. Details The Reagan administration made Letter-size paper the norm for US federal forms in the early 1980s; previously, the smaller "official" ''Government Letter'' size, (aspect ratio: 1.3125), was used in government, while paper was standard in most other offices. The aspect ratio is ≈ 1.294 and the diagonal is () in length. In the US, paper density is usually measured in "pound per reams" (of 500 sheets). Typical Letter paper has a basis weight of paper of – the weight of 500 sheets (a ream) of paper at and at 50% humidity. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
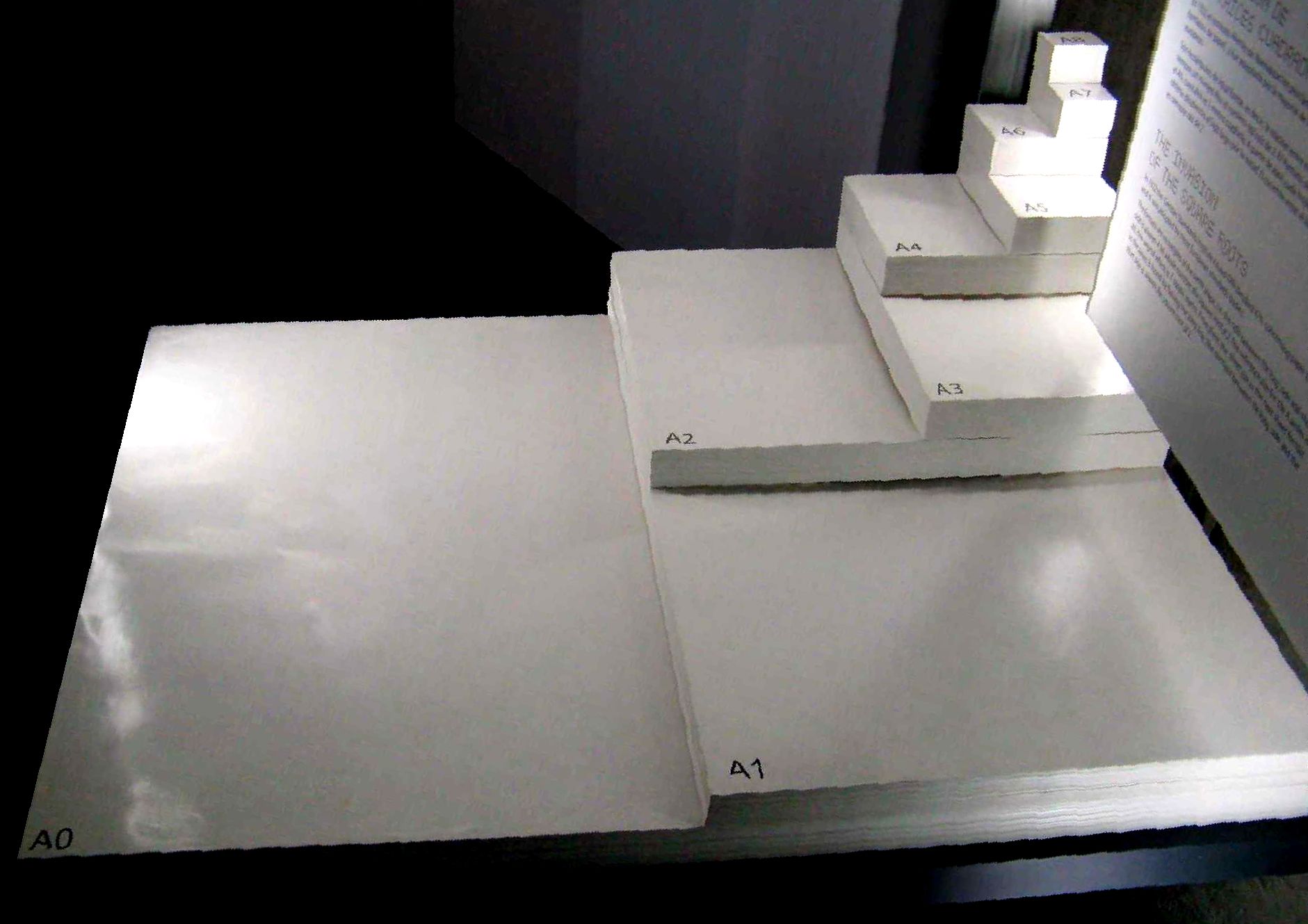
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 8
Windows 8 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on August 1, 2012; it was subsequently made available for download via MSDN and TechNet on August 15, 2012, and later to retail on October 26, 2012. Windows 8 introduced major changes to the operating system's platform and user interface intended to improve its user experience on tablets, where Windows was now competing with mobile operating systems, including Android and iOS. In particular, these changes included a touch-optimized Windows shell based on Microsoft's Metro design language and the Start screen, a new platform for developing apps with an emphasis on touchscreen input, integration with online services, and Windows Store, an online distribution for downloading and purchasing new software, and a new keyboard shortcut for screenshots. Many of these features were adopted from Windows Phone. Windows 8 added support for USB 3.0, Advanced Form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tablet Computer
A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being computers, do what other personal computers do, but lack some input/output (I/O) abilities that others have. Modern tablets largely resemble modern smartphones, the only differences being that tablets are relatively larger than smartphones, with screens or larger, measured diagonally, and may not support access to a cellular network. Unlike laptops which have traditionally run off operating systems usually designed for desktops, tablets usually run mobile operating systems, alongside smartphones. The touchscreen display is operated by Gesture recognition, gestures executed by finger or digital pen (stylus), instead of the Computer mouse, mouse, touchpad, and Keyboard (computing), keyboard of larger computers. Portable computers can be classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Of View In Video Games
In first person video games, the field of view or field of vision (abbreviated FOV) is the extent of the observable game world that is seen on the display at any given moment. It is typically measured as an angle, although whether this angle is the horizontal, vertical, or diagonal component of the field of view varies from game to game. The FOV in a video game may change depending on the aspect ratio of the rendering resolution. In computer games and modern game consoles the FOV normally increases with a wider aspect ratio of the rendering resolution.Master Games List http://www.wsgf.org/mgl Field of view calculations The field of view is usually given as an angle for the horizontal or vertical component of the FOV. A larger angle indicates a larger field of view. However, depending on the FOV scaling method used by the game, it may only affect the horizontal or the vertical component of the field of view. The horizontal and vertical FOV are calculated from the following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedback mostly commonly is shown on a video display device, such as a TV set, computer monitor, monitor, touchscreen, or virtual reality headset. Some computer games do not always depend on a graphics display, for example List of text-based computer games, text adventure games and computer chess can be played through teletype printers. Video games are often augmented with audio feedback delivered through loudspeaker, speakers or headphones, and sometimes with other types of feedback, including haptic technology. Video games are defined based on their computing platform, platform, which include arcade video games, console games, and PC game, personal computer (PC) games. More recently, the industry has expanded on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC Perspective
PC Perspective (often shortened to PCPer) is a web site dedicated to news and reviews of personal computing and gaming hardware. PCPer's "About Us" page. March 22, 2018. PC Perspective specializes in hardware that is most relevant to home users and enthusiasts. The site also has an active online community, a weekly podcast, and founder Ryan Shrout was the co-host of TWiT.tv's This Week in Computer Hardware. History PCPer was founded by Ryan Shrout in 2004. Shrout previously ran the AMD centric Amdmb.com, Athlonmb.com, and ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PR Newswire
PR Newswire is a distributor of press releases headquartered in Chicago. The service was created in 1954 to allow companies to electronically send press releases to news organizations, using teleprinters at first. The founder, Herbert Muschel, operated the service from his house in Manhattan for approximately 15 years. The business was eventually sold to Western Union and then United Newspapers of London. In December 2015, Cision Inc. announced it would acquire the company. On January 1, 2021, Cision formally merged PR Newswire into the company, ending its status as a legal entity after 66 years. Cision plans to continue utilizing the brand name for the foreseeable future in the United States, as well as in Europe and the Asia-Pacific regions. History PR Newswire was founded in March 1954 by Herbert Muschel, who ran the business from his town house in New York City for the first 15 years of its operation. The company used telecommunications lines and teleprinters owned by West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-in-1 PC
A 2-in-1 PC, also known as convertible laptop, 2-in-1 tablet, 2-in-1 laptop, 2-in-1 detachable, laplet, tabtop, laptop tablet, or simply 2-in-1, is a portable computer that has features of both tablets and laptops. Before the emergence of ''2-in-1s'' and their denomination as such, technology journalists used the words ''convertible'' and ''hybrid'' to denominate pre-2-in-1 portable computers: ''Convertible'' typically denominated those that featured a mechanism to conceal the physical keyboard by sliding or rotating it behind the chassis, and ''hybrid'' those that featured a hot-pluggable, complementary, physical keyboard. Both pre-2-in-1 convertibles and hybrids were crossover devices that combined features of both tablets and laptops. The later 2-in-1 PCs comprise a category that is a sibling to both the pre-2-in-1 convertibles and hybrids. Models of 2-in-1 PC were each similarly denominated either a ''2-in-1 convertible'' or ''2-in-1 detachable'', respectively, and despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromebook Pixel
The Chromebook Pixel is a 2013 laptop at the high end of Google's Chromebook family of machines, which all come preinstalled with ChromeOS operating system.Google takes Chromebook upmarket with touchy-feely Pixel theregister.com, 21 February 2013 The Chromebook Pixel is part of the series of consumer electronics. An updated model was released in 2015. Chromebook Pixel stopped receiving software and security updates in August 2018. History The Chromebook Pixel was launched on February 21, 2013, with shipments starting immediately.[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PowerBook G4
The PowerBook G4 is a series of notebook computers manufactured, marketed, and sold by Apple Computer between 2001 and 2006 as part of its PowerBook line of notebooks. The PowerBook G4 runs on the RISC-based PowerPC G4 processor, designed by the AIM (Apple/ IBM/Motorola) development alliance and initially produced by Motorola. It was built later by Freescale, after Motorola spun off its semiconductor business under that name in 2004. The PowerBook G4 has two different designs: one enclosed in a titanium body with a translucent black keyboard and a 15-inch screen; and another in an aluminum body with an aluminum-colored keyboard, in 12-inch, 15-inch, and 17-inch sizes. Between 2001 and 2003, Apple produced the titanium PowerBook G4; between 2003 and 2006, the aluminum models were produced. Both models were hailed for their modern design, long battery life, and processing power. When the aluminum PowerBook G4s were first released in January 2003, 12-inch and 17-inch models were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |