|
Discone Antenna
A discone antenna is a version of a biconical antenna in which one of the cones is replaced by a disc. It is usually mounted vertically, with the disc at the top and the cone beneath. Omnidirectional, vertically polarized and with gain similar to a dipole, it is exceptionally wideband, offering a frequency range ratio of up to approximately 10:1. The radiation pattern in the vertical plane is quite narrow, making its sensitivity highest in the direction of the horizon and rather less for signals coming from relatively close by. History On February 6, 1945, Armig G. Kandoian of New York City was awarded U.S. patent number (assignor to Federal Telephone and Radio Corporation, later merged with ITT Corporation), from an application made on May 15, 1943. Excerpt from the Kandoian patent: In keeping with progress made during the last few years in the development of ultra-high frequency radio technique, and applications thereof to aircraft communication, direction finding, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direction Finding
Direction finding (DF), or radio direction finding (RDF), isin accordance with International Telecommunication Union (ITU)defined as radio location that uses the reception of radio waves to determine the direction in which a radio station or an object is located. This can refer to radio or other forms of wireless communication, including radar signals detection and monitoring (ELINT/ESM). By combining the direction information from two or more suitably spaced receivers (or a single mobile receiver), the source of a transmission may be located via triangulation. Radio direction finding is used in the navigation of ships and aircraft, to locate emergency transmitters for search and rescue, for tracking wildlife, and to locate illegal or interfering transmitters. RDF was important in combating German threats during both the World War II Battle of Britain and the long running Battle of the Atlantic. In the former, the Air Ministry also used RDF to locate its own fighter gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clothes Hanger
A clothes hanger, coat hanger, or coathanger, is a hanging device in the shape/contour of: * Human shoulders designed to facilitate the hanging of a coat, jacket, sweater, shirt, blouse or dress in a manner that prevents wrinkles, with a lower bar for the hanging of trousers or skirts. * Clamp for the hanging of trousers, skirts, or kilts. Both types can be combined in a single hanger. The clothing hanger was originally designed to allow people quick access to their clothing as well as designate an area, in their home, to keep their clothing in. It was also used to keep clothing dry or without a wrinkle. There are three basic types of clothes hangers. The first is the wire hanger, which has a simple loop of wire, most often steel, in a flattened triangle shape that continues into a hook at the top. The second is the wooden hanger, which consists of a flat piece of wood cut into a boomerang-like shape with the edges sanded down to prevent damage to the clothing, and a hoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoke
A spoke is one of some number of rods radiating from the center of a wheel (the hub where the axle connects), connecting the hub with the round traction surface. The term originally referred to portions of a log that had been riven (split lengthwise) into four or six sections. The radial members of a wagon wheel were made by carving a spoke (from a log) into their finished shape. A spokeshave is a tool originally developed for this purpose. Eventually, the term spoke was more commonly applied to the finished product of the wheelwright's work, than to the materials they used. History The spoked wheel was invented to allow the construction of lighter and swifter vehicles. Earliest physical evidence for spoked wheels were found in Sintashta culture, dating to 2000 BC. Soon after this, horse cultures of the Caucasus region used horse-drawn spoked-wheel war chariots for the greater part of three centuries. They moved deep into the Greek peninsula where they joined with the exis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks in the world, used globally in home and small office networks to link desktop and laptop computers, tablet computers, smartphones, smart TVs, printers, and smart speakers together and to a wireless router to connect them to the Internet, and in wireless access points in public places like coffee shops, hotels, libraries and airports to provide visitors with Internet access for their mobile devices. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the non-profit Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term ''Wi-Fi Certified'' to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from around the world. over 3.05 billion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ) is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, with the two separated by a dielectric ( insulating material); many coaxial cables also have a protective outer sheath or jacket. The term ''coaxial'' refers to the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable is a type of transmission line, used to carry high-frequency electrical signals with low losses. It is used in such applications as telephone trunk lines, broadband internet networking cables, high-speed computer data busses, cable television signals, and connecting radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas. It differs from other shielded cables because the dimensions of the cable and connectors are controlled to give a precise, constant conductor spacing, which is needed for it to function efficiently as a transmission line. Coaxial cable was used in the first (1858) and followin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
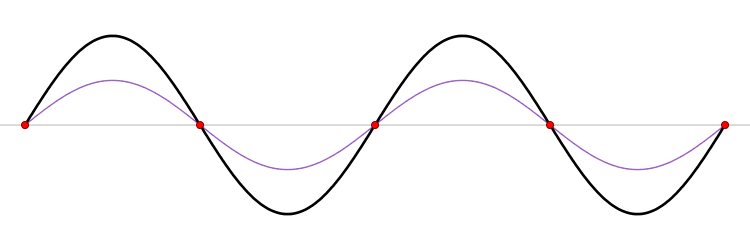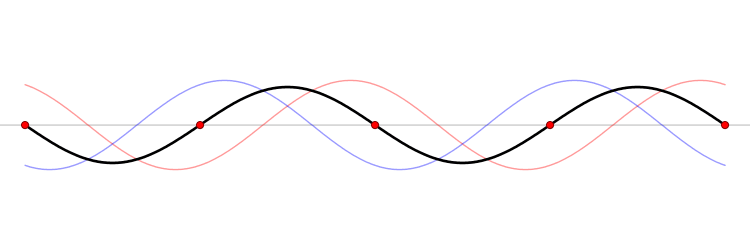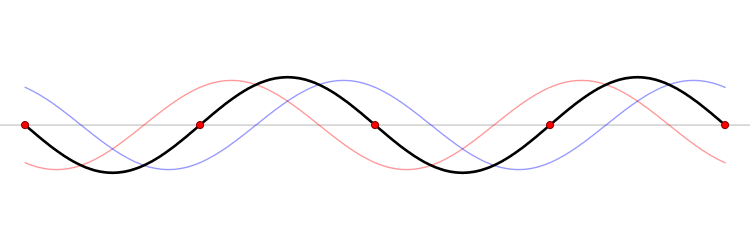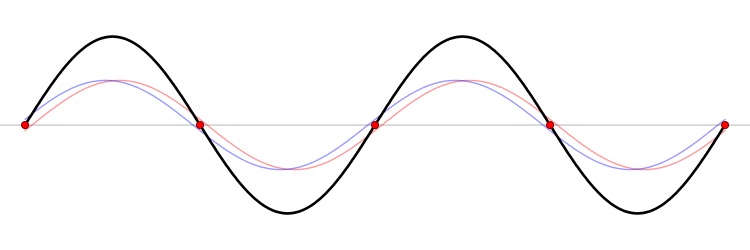
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter ''lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) that a wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Radio Relay League
The American Radio Relay League (ARRL) is the largest membership association of amateur radio enthusiasts in the United States. ARRL is a non-profit organization, and was co-founded on April 6, 1914, by Hiram Percy Maxim and Clarence D. Tuska of Hartford, Connecticut. The ARRL represents the interests of amateur radio operators before federal regulatory bodies, provides technical advice and assistance to amateur radio enthusiasts, supports a number of educational programs and sponsors emergency communications service throughout the country. The ARRL has approximately 161,000 members. In addition to members in the US, the organization claims over 7,000 members in other countries. The ARRL publishes many books and a monthly membership journal called ''QST''. The ARRL is the primary representative organization of amateur radio operators to the US government. It performs this function by lobbying the United States Congress, US Congress and the Federal Communications Commission. The AR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Wave Ratio
In radio engineering and telecommunications, standing wave ratio (SWR) is a measure of impedance matching of loads to the characteristic impedance of a transmission line or waveguide. Impedance mismatches result in standing waves along the transmission line, and SWR is defined as the ratio of the partial standing wave's amplitude at an antinode (maximum) to the amplitude at a node (minimum) along the line. The SWR is usually thought of in terms of the maximum and minimum AC voltages along the transmission line, thus called the voltage standing wave ratio or VSWR (sometimes pronounced "vizwar" ). For example, the VSWR value 1.2:1 means that an AC voltage, due to standing waves along the transmission line, will have a peak value 1.2 times that of the minimum AC voltage along that line, if the line is at least one half wavelength long. The SWR can be also defined as the ratio of the maximum amplitude to minimum amplitude of the transmission line's currents, electric field strength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |