|
Diplotaxodon Argenteus
''Diplotaxodon argenteus'' is a species of haplochromine cichlid fish in the family Cichlidae. It is endemic to Lake Malawi. It occurs throughout the lake and therefore is found in Malawi, Mozambique, and Tanzania. References argenteus The ''argenteus'' ( ''argentei'', 'of silver') was a silver coin produced by the Roman Empire from the time of Diocletian's coinage reform in AD 294 to ca. AD 310. It was of similar weight and fineness to the denarius of the time of Nero. The co ... Taxa named by Ethelwynn Trewavas Fish described in 1935 Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Cichlidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethelwynn Trewavas
Ethelwynn Trewavas (5 November 1900 – 16 August 1993) was an ichthyologist at the British Museum of Natural History. She was known for her work on the families Cichlidae and Sciaenidae. She worked with Charles Tate Regan, another ichthyologist and taxonomist. Academic studies and career She received her bachelor's degree and Board of Education Certificate in Teaching in 1921 from Reading University, and then worked as a teacher before being employed by the King's College of Household and Social Science as a part-time demonstrator, spending most of her time on research. She was taught by Dr. Nellie B. Eales when associated with the Freshwater Biological Association. She met Charles Regan and was employed by him as his assistant until hired by the British Museum (Natural History) as Assistant Keeper in 1935. She was appointed Deputy Keeper of Zoology in 1958, and retired in 1961. She served as the senior scientist in the Fish Section of the British Museum (Natural Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplochromine
__NOTOC__ The haplochromine cichlids are a tribe of cichlids in subfamily Pseudocrenilabrinae called Haplochromini. This group includes the type genus (''Haplochromis'') plus a number of closely related genera such as '' Aulonocara'', '' Astatotilapia'', and '' Chilotilapia''. They are endemic to eastern, southern and northern Africa, except for ''Astatotilapia flaviijosephi'' in the ''Middle East''. A common name in a scientific context is East African cichlids – while they are not restricted to that region, they are the dominant Cichlidae there. This tribe was extensively studied by Ethelwynn Trewavas, who made major reviews in 1935 and 1989, at the beginning and at the end of her career in ichthyology. Even today, numerous new species are being described each year. The haplochromines were in older times treated as subfamily Haplochrominae, However, the great African radiation of pseudocrenilabrine cichlids is certainly not monophyletic without them, and thus they are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
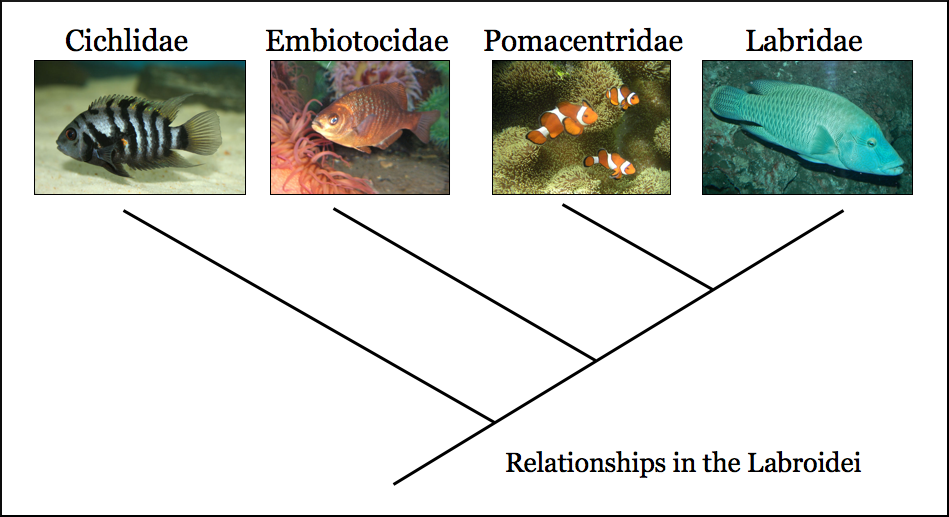
Cichlidae
Cichlids are fish from the family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes. Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses ( Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have contradicted this grouping. The closest living relative of cichlids is probably the convict blenny, and both families are classified in the 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' as the two families in the Cichliformes, part of the subseries Ovalentaria. This family is both large and diverse. At least 1,650 species have been scientifically described, making it one of the largest vertebrate families. New species are discovered annually, and many species remain undescribed. The actual number of species is therefore unknown, with estimates varying between 2,000 and 3,000. Many cichlids, particularly tilapia, are important food fishes, while others, such as the ''Cichla'' species, are valued game fish. The family also includes many popular freshwater aquar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, is an African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania. It is the fifth largest fresh water lake in the world by volume, the ninth largest lake in the world by area—and the third largest and second deepest lake in Africa. Lake Malawi is home to more species of fish than any other lake in the world, including at least 700 species of cichlids.Turner, Seehausen, Knight, Allender, and Robinson (2001). "How many species of cichlid fishes are there in African lakes?" ''Molecular Ecology'' 10: 793–806. The Mozambique portion of the lake was officially declared a reserve by the Government of Mozambique on June 10, 2011,WWF (10 June 2011)"Mozambique’s Lake Niassa declared reserve and Ramsar site"Retrieved 17 July 2014. while in Malawi a portion of the lake is included in Lake Malawi National Park. Lake Malawi is a meromic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplotaxodon
''Diplotaxodon'' is a small genus of seven formally described, as well as a number of undescribed, deep-water species of cichlid fish endemic to Lake Malawi in east Africa. These fishes represent a remarkable adaptive radiation of offshore and deep-water adapted fish descended from ancestral shallow water forms. They include the dominant zooplankton-feeding fish of the offshore and deep-water regions of the lake, as well as a number of larger species that appear to feed on small pelagic fishes. Adult sizes range from 10 to 30 cm in total length, depending on species. Reproductive biology Females and immature fish are silvery, like typical pelagic fish, but mature males develop stronger breeding colours, typically contrasting patterns of black, white and yellow. Females of several species have been found carrying eggs and young in their mouths and it is likely that all species are maternal mouthbrooders, like all other known haplochromine cichlids. Males in breeding dres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Ethelwynn Trewavas
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1935
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a vertebrate, true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed placodermi, external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


