|
Dioxalin
Dioxalin is a reaction product of glycerol with oxalic acid at 533 K. Its IUPAC name is 5-(hydroxymethyl)-1,4-dioxane-2,3-dione. Dioxalin readily loses two molecules of carbon dioxide at this high temperature to form allyl alcohol Allyl alcohol ( IUPAC name: prop-2-en-1-ol) is an organic compound with the structural formula . Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a raw material ... and therefore offers a method for conversion of glycerol to allyl alcohol. References {{reflist Primary alcohols Lactones Dioxanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. Because it has antimicrobial and antiviral properties, it is widely used in wound and burn treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Conversely, it is also used as a bacterial culture medium. It can be used as an effective marker to measure liver disease. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature. Structure Although achiral, glycerol is prochiral with respect to reactions of one of the two primary alcohols. Thus, in substituted derivatives, the stereospecific numbering labels the molecule with a "sn-" prefix before the stem name of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Alcohol
Allyl alcohol (IUPAC name: prop-2-en-1-ol) is an organic compound with the structural formula . Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a raw material for the production of glycerol, but is also used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers. Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols. Production Allyl alcohol can be obtained by many methods. It was first prepared in 1856 by Auguste Cahours and August Hofmann by hydrolysis of allyl iodide. Today allyl alcohol is produced commercially by the Olin and Shell corporations through the hydrolysis of allyl chloride: :CH2=CHCH2Cl + NaOH -> CH2=CHCH2OH + NaCl Allyl alcohol can also be made by the rearrangement of propylene oxide, a reaction that is catalyzed by potassium alum at high temperature. The advantage of this method relative to the allyl chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid is an organic acid with the systematic name ethanedioic acid and formula . It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. Its name comes from the fact that early investigators isolated oxalic acid from flowering plants of the genus ''Oxalis'', commonly known as wood-sorrels. It occurs naturally in many foods. Excessive ingestion of oxalic acid or prolonged skin contact can be dangerous. Oxalic acid has much greater acid strength than acetic acid. It is a reducing agent and its conjugate base, known as oxalate (), is a chelating agent for metal cations. Typically, oxalic acid occurs as the dihydrate with the formula . History The preparation of salts of oxalic acid (crab acid) from plants had been known, at least since 1745, when the Dutch botanist and physician Herman Boerhaave isolated a salt from wood sorrel. By 1773, François Pierre Savary of Fribourg, Switzerland had isolated oxalic acid from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meaning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC Nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). The IUPAC's rules for naming organic and inorganic compounds are contained in two publications, known as the ''Blue Book''. . and the '' Red Book'',. respectively. A third publication, known as the '' Green Book'',. recommends the use of symbols for physical quantities (in association with the IUPAP), while a fourth, the ''Gold Book'',''Compendium of Chemical Terminology, IMPACT Recommendations (2nd Ed.)'', Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications. (1997) defines many technical terms used in chemistry. Similar compendia exist for biochemistry''Biochemical Nomenclature and Related Documents'', London: Portland Press, 1992. (the ''White Book'', in association with the IUBMB), analytical chemistry (the '' Orange Book''), macromolecular chemistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Alcohols
A primary alcohol is an alcohol in which the hydroxy group In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ... is bonded to a primary carbon atom. It can also be defined as a molecule containing a “–CH2OH” group. In contrast, a secondary alcohol has a formula “–CHROH” and a tertiary alcohol has a formula “–CR2OH”, where “R” indicates a carbon-containing group. Examples of primary alcohols include ethanol and n-Butanol, 1-butanol. Methanol is also generally regarded as a primary alcohol, including the 1911 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica,. See also * Alcohol (chemistry), Alcohol (especially Nomenclature section for discussion on Secondary and Tertiary alcohols.) * Oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids References Primary alcohols, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
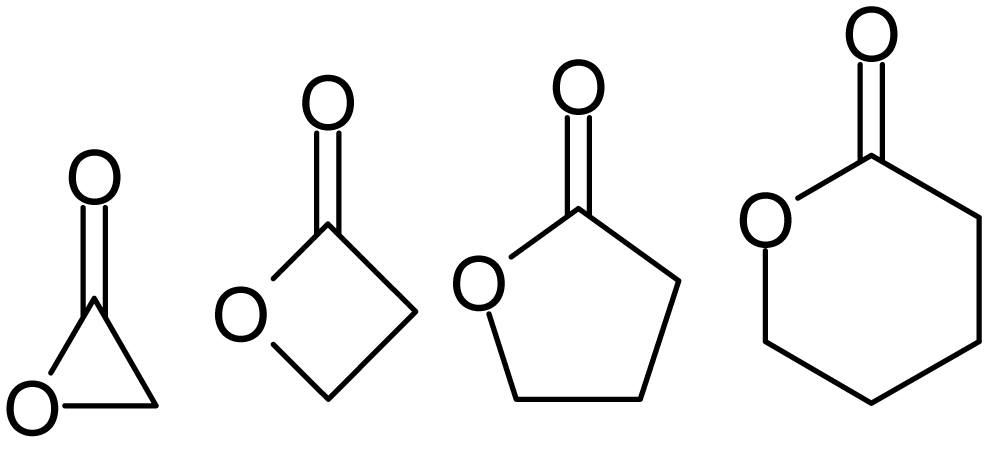
Lactones
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |