|
Dinosaur Isle
Dinosaur Isle is a purpose-built dinosaur museum located in Sandown on the Isle of Wight in southern England. The museum was designed by Isle of Wight architect Rainey Petrie Johns in the shape of a giant pterosaur. It claims to be the first custom-built dinosaur museum in Europe. History Throughout the 19th century, many collectors such as the Reverend William Fox (1813-1881) excavated the types of new dinosaur genera, including ''Aristosuchus'', ''Hypsilophodon foxii'', and ''Polacanthus''. Most of the discoveries were then transferred to the mainland for study and exhibition, which after some time prompted the Isle of Wight Council to begin its own collection. In 1923 the Isle of Wight's first geological museum opened in Sandown, under the name of the "Museum of Isle of Wight Geology". The £2.7 million cost of Dinosaur Isle, the new museum, was provided by Isle of Wight Council and the National Lottery Millennium Commission. Dinosaur Isle opened to visitors on 10 Augu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandown
Sandown is a seaside resort and civil parishes in England, civil parish on the south-east coast of the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom with the resort of Shanklin to the south and the settlement of Lake, Isle of Wight, Lake in between. Together with Shanklin, Sandown forms a built-up area of 21,374 inhabitants. The northernmost town of Sandown Bay, Sandown has an easily accessible, sandy shoreline with beaches that run continuously from the cliffs at Battery Gardens in the south to Yaverland in the north. Geography The town grew as a Victorian era, Victorian resort surrounded by a wealth of natural features. The coastal and inland areas of Sandown are part of the Isle of Wight Biosphere Reserve designated by UNESCO's Man and the Biosphere Programme in June 2019, and Sandown's sea front and clifftops form part of the Isle of Wight Coastal Path. The Bay that gives Sandown its name is an excellent example of a concordant coastline with five miles of well-developed tidal be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walking With Dinosaurs
''Walking with Dinosaurs'' is a 1999 six-part nature documentary television miniseries created by Tim Haines and produced by the BBC Science Unit the Discovery Channel and BBC Worldwide, in association with TV Asahi, ProSieben and France 3. Envisioned as the first "Natural History of Dinosaurs", ''Walking with Dinosaurs'' depicts dinosaurs and other Mesozoic animals as living animals in the style of a traditional nature documentary. The series first aired on the BBC in the United Kingdom in 1999 with narration by Kenneth Branagh. The series was subsequently aired in North America on the Discovery Channel in 2000, with Avery Brooks replacing Branagh. ''Walking with Dinosaurs'' recreated extinct species through the combined use of computer-generated imagery and animatronics that were incorporated with live action footage shot at various locations, the techniques being inspired by the film ''Jurassic Park (film), Jurassic Park'' (1993). At a cost of £6.1 million ($9.9 million), ''W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History Museums In England
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums Established In 2001
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public. There are many types of museums, including art museums, natural history museums, science museums, war museums, and children's museums. According to the International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are more than 55,000 museums in 202 cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Museums
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museums On The Isle Of Wight
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make these items available for public viewing through exhibits that may be permanent or temporary. The largest museums are located in major cities throughout the world, while thousands of local museums exist in smaller cities, towns, and rural areas. Museums have varying aims, ranging from the conservation and documentation of their collection, serving researchers and specialists, to catering to the general public. The goal of serving researchers is not only scientific, but intended to serve the general public. There are many types of museums, including art museums, natural history museums, science museums, war museums, and children's museums. According to the International Council of Museums (ICOM), there are more than 55,000 museums in 202 countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaurs Of The Isle Of Wight
The Isle of Wight is one of the richest dinosaur localities in Europe, with over 20 species of dinosaur having been recognised from the early Cretaceous Period (in particular between 132 and 110 million years ago), some of which were first identified on the island, as well as the contemporary non-dinosaurian species of crocodile, turtle and pterosaur. Compton Bay, near Freshwater features dinosaur footprints which are visible at low tide. Geological strata The Isle of Wight has layers of the Vectis and Wealden fossil-bearing beds exposed on the southern half of the island. These are revealed in the cliffs of Yaverland, close to Sandown, and at Hanover Point and Whale Chine, along the southwestern coast. The Cretaceous habitat The island's dinosaurs come from the Wessex Formation, which dates from between 125 and 110 million years ago ( mya). During this time the Isle of Wight, then located on a latitude at which North Africa resides today, had a subtropical environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
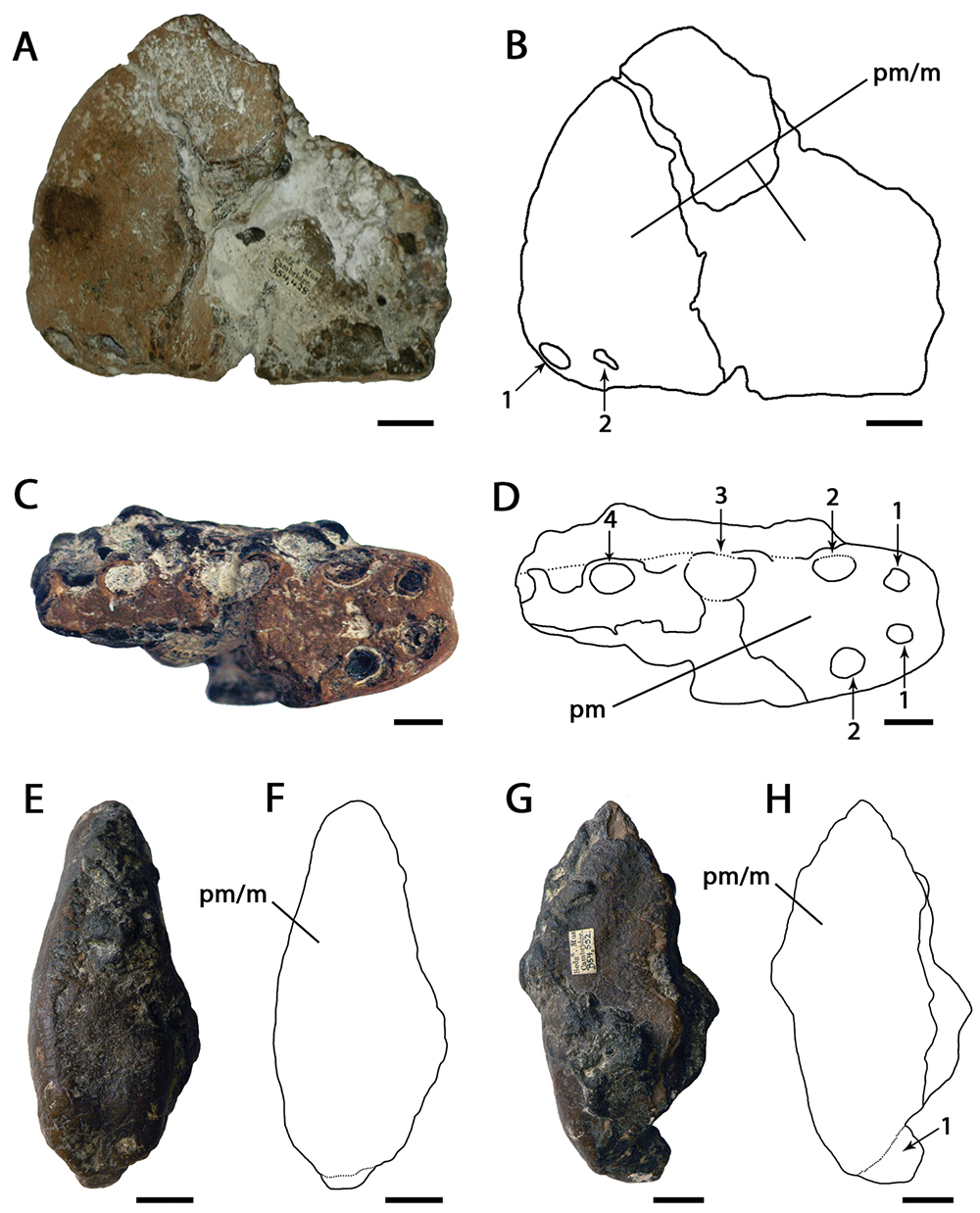
Caulkicephalus
''Caulkicephalus'' is a genus of anhanguerid pterosaur from the Isle of Wight off the coast of England. It lived during the Early Cretaceous period, about 130 million years ago. Discovery and naming Between 1995 and 2003, bone fragments of an unknown pterosaur were found at the Yaverland locality near Sandown. The discoveries were made in or from a brown clay layer from the Wessex Formation of the Wealden Group, stemming from the Early Cretaceous (Barremian age, about 130 million years ago). In 2005 a new genus was named and described by Lorna Steel, David Martill, David Unwin and John Winch. The type species is ''Caulkicephalus trimicrodon''. The genus name is a translation of "Caulkhead", a traditional nickname for Isle of Wight residents, partially derived from Greek ''kephale'', "head". The specific name, ''trimicrodon'', means "three small teeth", in reference to the dentition. Description The holotype is IWCMS 2002.189.1, 2, 4: three pieces, more or less contiguou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithocheirid
Ornithocheiridae (or ornithocheirids, meaning "bird hands") is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. These pterosaurs were among the last to possess teeth. Members that belong to this group lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods (Valanginian to Turonian stages), around 140 to 90 million years ago. Ornithocheirids are generally infamous for having an enormously controversial and very confusing taxonomy. Although agreements that these animals were related, and therefore similar to istiodactylids and pteranodontians, there is still no virtual consensus over the exact content and interrelationships of this group. Ornithocheirids were the most successful pterosaurs during their reign, they were also the largest pterosaurs before the appearance of the azhdarchids such as '' Quetzalcoatlus''. Ornithocheirids were excellent fish hunters, they used various flight techniques to catch their prey, and they are also capable of flying great distances without f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koumpiodontosuchus
''Koumpiodontosuchus'' is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived in the Early Cretaceous. The only species is ''K. aprosdokiti'', named in 2015. Discovery The first fossilised fragment of a skull was discovered by Diane Trevarthen on a beach near Sandown in the Isle of Wight in March 2011. Three months later, the second fragment of the skull was found by Austin and Finley Nathan. The two fragments were donated to Dinosaur Isle. Megan Jacobs also discovered an isolated tooth belonging to the same genus that were twice the size of those from the holotype. The species that the fragments belonged to was named ''Koumpiodontosuchus aprosdokiti'', meaning "unexpected button-toothed crocodile". When the fragments were first seen by Steve Sweetman, a palaeontologist with the University of Portsmouth, he thought that they belonged to the ''Bernissartia fagesii'' species because of its small size and button-shaped teeth. Sweetman published a paper on the discovery of the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic period (Bathonian stage, 166 million years ago) of Southern England. Although fossils from other areas have been assigned to the genus, the only certain remains of ''Megalosaurus'' come from Oxfordshire and date to the late Middle Jurassic. ''Megalosaurus'' was, in 1824, the first genus of non-avian dinosaur to be validly named. The type species is ''Megalosaurus bucklandii'', named in 1827. In 1842, ''Megalosaurus'' was one of three genera on which Richard Owen based his Dinosauria. On Owen's directions a model was made as one of the Crystal Palace Dinosaurs, which greatly increased the public interest for prehistoric reptiles. Over fifty other species would eventually be classified under the genus; at first, this was because so few types of dinosaur had been identified, but the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neovenator
''Neovenator'' (nee-o-ven-a-tor meaning "new hunter") is a genus of carcharodontosaurian theropod dinosaur. It is known from several skeletons found in the Early Cretaceous (Barremian~130-125 million years ago) Wessex Formation on the south coast of the Isle of Wight, southern England. It is one of the best known theropod dinosaurs from the Early Cretaceous of Europe. Discovery and species The first bones of ''Neovenator'' were discovered in the summer of 1978, when a storm made part of the Grange Chine collapse. Rocks containing fossils fell to the beach of Brighstone Bay on the southwestern coast of the Isle of Wight. The rocks consisted of plant debris bed L9 within the variegated clays and marls of the Wessex Formation dating from the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous, about 125 million years ago. They were first collected by the Henwood family and shortly afterwards by geology student David Richards. Richards sent the remains to the Museum of Isle of Wight (no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)