|
Dillwynia Acerosa
''Dillwynia acerosa'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to Western Australia. It is an erect spindly shrub with hairy, needle-shaped leaves and yellow flowers. Description ''Dillwynia acerosa'' is an erect, spindly shrub that typically grows to a height of up to with hairy stems that are round in cross-section. The leaves or phylloclades are arranged alternately, needle-shaped, long and wide. The flowers are arranged on the ends of branchlets, each flower on a hairy pedicel long with hairy sepals long. The standard petal is long, the wings long and the keel long. There are ten stamens, the style is hairy and long. Flowering occurs in September and the fruit is a follicle that is not constricted between the seeds. Taxonomy and naming ''Dillwynia acerosa'' was first formally described in 1899 by Spencer Le Marchant Moore in ''Journal of the Linnean Society, Botany''. The specific epithet (''acerosa'') means "needle-shaped", referring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabaceae
The Fabaceae or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants. Article 18.5 states: "The following names, of long usage, are treated as validly published: ....Leguminosae (nom. alt.: Fabaceae; type: Faba Mill. Vicia L.; ... When the Papilionaceae are regarded as a family distinct from the remainder of the Leguminosae, the name Papilionaceae is conserved against Leguminosae." English pronunciations are as follows: , and . commonly known as the legume, pea, or bean family, are a large and agriculturally important of |
Esperance Plains
Esperance Plains, also known as Eyre Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia on the south coast between the Avon Wheatbelt and Hampton bioregions, and bordered to the north by the Mallee region. It is a plain punctuated by granite and quartz outcrops and ranges, with a semi-arid Mediterranean climate and vegetation consisting mostly of mallee-heath and proteaceous scrub. About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a bioregion under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Esperance Plains may be roughly approximated as the land within of the coast between Albany and Point Culver on the south coast of Western Australia. It has an area of about , making it about 9% of the South West Province, 1% of the state, and 0.3% of Australia. It is bounded to the north by the Mallee region, and to the west by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Spencer Le Marchant Moore
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular Taxonomic rank, ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's Linnaean taxonomy, system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard de Jussieu, Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudicots Of Western Australia
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination. The term derives from Dicotyledons. Traditionally they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicots by previous authors. The botanical terms were introduced in 1991 by evolutionary botanist James A. Doyle and paleobotanist Carol L. Hotton to emphasize the later evolutionary divergence of tricolpate dicots from earlier, less specialized, dicots. Numerous familiar plants are eudicots, including many common food plants, trees, and ornamentals. Some common and familiar eudicots include sunflower, dandelion, forget-me-not, cabbage, apple, buttercup, maple, and macadamia. Most leafy trees of midlatitudes also belong to eudicots, with notable exceptions being magnolias and tulip trees which belong to magnoliids, and ''Ginkgo biloba'', which is not an angiosperm. Description The close relationships among flowering plants with tricolpate po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dillwynia
''Dillwynia'' is a genus of about 20 species of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, and is endemic to Australia. Plants in this genus are shrubs with simple leaves and yellow or red and yellow flowers similar to others in the family. Description Plants in the genus ''Dillwynia'' are shrubs with simple leaves that are linear, needle-shaped leaves with a groove along the upper surface or triangular in cross-section. The flowers are yellow or red and yellow and usually arranged singly or in small groups in leaf axils or on the ends of branchlets. The upper two of five sepal lobes are joined in a single "lip", the Papilionaceous flower#Corolla, standard petal is broader than long, and the Papilionaceous flower#Corolla, keel is no longer than the Papilionaceous flower#Corolla, wings. The stamens are free from each other, the Ovary (botany), ovary is on a short stalk and the fruit is a more or less Sessility (botany), sessile Pod (botany), pod. Taxonomy The genus ''Dillwynia'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Parks And Wildlife (Western Australia)
The Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) was the department of the Government of Western Australia responsible for managing lands described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'' and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The minister responsible for the department was the Minister for the Environment. History The Department of Environment and Conservation (DEC) was separated on 30 June 2013, forming the Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW) and the Department of Environment Regulation (DER), both of which commenced operations on 1 July 2013. DPaW focused on managing multiple use state forests, national parks, marine parks and reserves. DER focused on environmental regulation, approvals and appeals processes, and pollution prevention. It was announced on 28 April 2017 that the Department of Parks and Wildlife would merge with the Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority, the Zoological Parks Authority and the Rott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBRA
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 419 subregions. Each region is a land area made up of a group of interacting ecosystems that are repeated in similar form across the landscape. IBRA is updated periodically based on new data, mapping improvements, and review of the existing scheme. The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nullarbor Plain
The Nullarbor Plain ( ; Latin: feminine of , 'no', and , 'tree') is part of the area of flat, almost treeless, arid or semi-arid country of southern Australia, located on the Great Australian Bight coast with the Great Victoria Desert to its north. It is the world's largest single exposure of limestone bedrock, and occupies an area of about . At its widest point, it stretches about from east to west across the border between South Australia and Western Australia. History Historically, the Nullarbor was seasonally occupied by Indigenous Australian people, the Mirning clans and Yinyila people. Traditionally, the area was called ''Oondiri'', which is said to mean "the waterless". The first Europeans known to have sighted and mapped the Nullarbor coast were Captain François Thijssen and Councillor of the Indies, Pieter Nuyts, on the Dutch East Indiaman '''t Gulden Zeepaert'' (the Golden Seahorse). In 1626–1627, they charted a stretch of the southern Australian coast eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murchison (biogeographic Region)
The Murchison is an interim Australian bioregion located within the Mid West of Western Australia. The bioregion is loosely related to the catchment area of the Murchison River and has an area of . Traditionally the region is known as ''The Murchison''. Geography The landscape is characterised by low hills and mesas, separated by colluvium flats and alluvial plains. The western portion of the bioregion is drained by the upper Murchison and Wooramel rivers, which drain westwards towards the coast.Anthony Desmond, Mark Cowan and Alanna Chant (2001). "Murchison 2 (MUR2 – Western Murchison subregion)", in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. The Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001/ref> Together with Gascoyne bioregion, it constitutes the Western Australian mulga shrublands ecoregion. Population is scattered; the largest population centres are Meekatharra, Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallee (biogeographic Region)
Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie bioregions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive ''Eucalyptus'' mallee vegetation. It has an area of . About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Mallee region has a complex shape with tortuous boundaries, but may be roughly approximated as the triangular area south of a line from Bruce Rock to Eyre, but not within 40 kilometres (25 mi) of the south coast, except at its eastern limits. It has an area of about 79000 square kilometres (31000 mi²), making it about a quarter of the South West Botanic Province, 3% of the state, and 1% of Australia. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jarrah Forest
Jarrah forest is tall open forest in which the dominant overstory tree is ''Eucalyptus marginata'' (jarrah). The ecosystem occurs only in the Southwest Botanical Province of Western Australia. It is most common in the biogeographic region named in consequence Jarrah Forest. Most jarrah forest contains at least one other co-dominant overstory tree; association with ''Corymbia calophylla'' is especially common, and results in which is sometimes referred to as jarrah-marri forest. Considerable amount of research delineates northern, central and southern jarrah forestStrelein, G. J. (1988) ''Site classification in the Southern jarrah forest of Western Australia'' Como, W.A. Dept. of Conservation and Land Management, Western Australia. Research bulletin 0816-9675 ; 2. (not printed in book) which relates to rainfall, geology and ecosystem variance. See also *Darling Scarp The Darling Scarp, also referred to as the Darling Range or Darling Ranges, is a low escarpment running nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
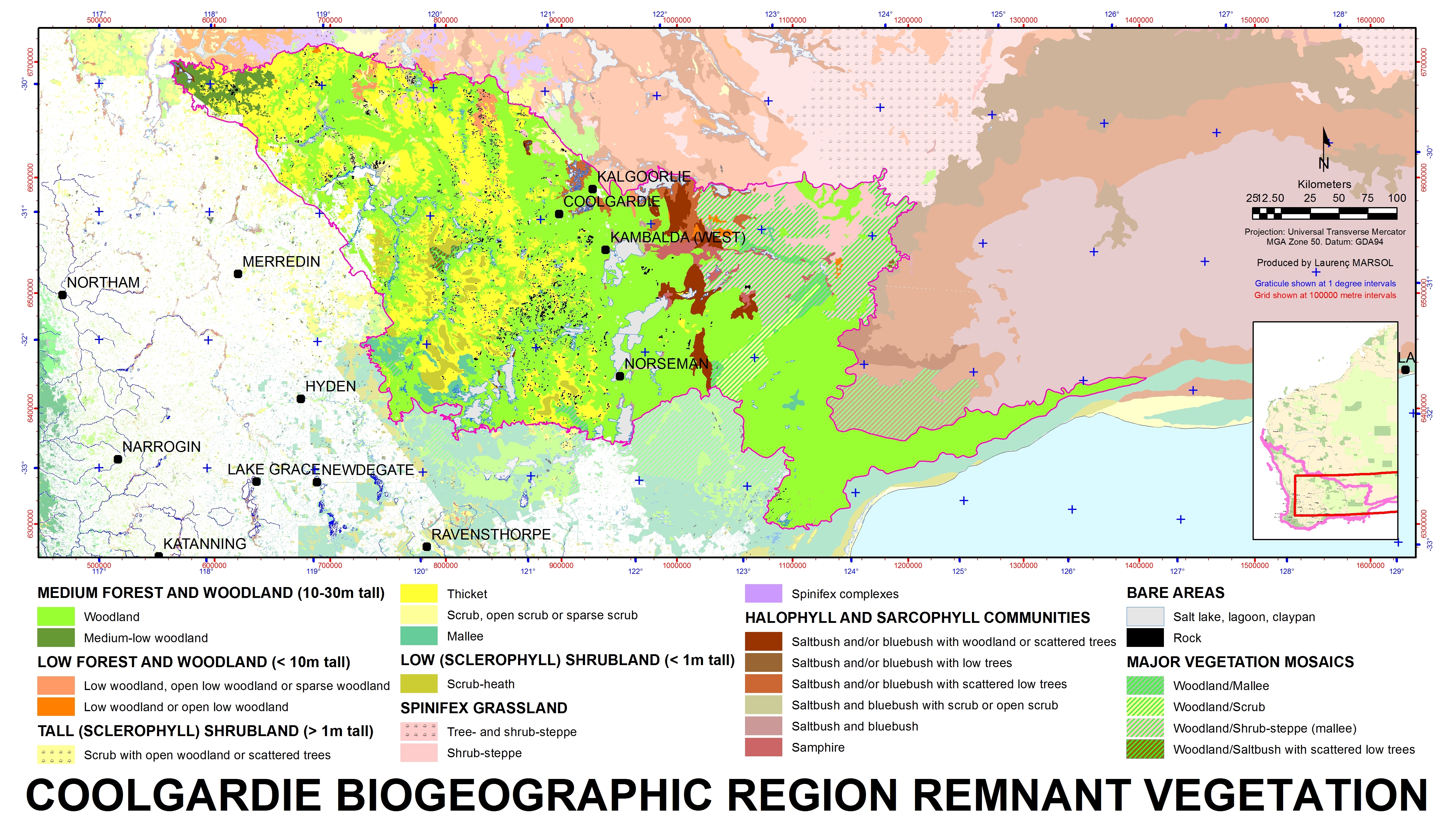
Coolgardie (biogeographic Region)
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |