|
Differentiation Therapy
Differentiation therapy is a method to treating advanced cancers in which malignant cells are encouraged to differentiate into more mature forms using pharmacological agents. The basis of the therapy stems from the tendency of malignant tumor cells to assume a less specialized, stem cell-like dedifferentiated state. Leukemia The approach was motivated by noticing that leukemia cells fail to differentiate and fully mature. By 2001 encouraging clinical results were seen. The first differentiation agent found to be successful was all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Other cancers The process of cancer spreading (metastasis) involves tumour cells undergoing an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to invade and spread, followed by a mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) at remote sites. Other agents investigated (pre-clinically) to encourage MET include cholera toxin (CTx) and forskolin Forskolin (coleonol) is a labdan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse. Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not self-limited in its growth, is capable of invading into adjacent tissues, and may be capable of spreading to distant tissues. A benign tumor has none of those properties. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis. Malignant tumors are also characterized by genome instability, so that cancers, as assessed by whole genome sequencing, frequently have between 10,000 and 100,000 mutations in their entire genomes. Cancers usually show tumour heterogeneity, containing multiple subclones. They also frequently have reduced expression of DNA repair enzymes due to epigenetic methylation of DNA repair genes or altered microRNAs that control DNA repair gene expression. Tumours can be detected through the visual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-trans-retinoic Acid
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth for up to three months. Topical tretinoin is also the most extensively investigated retinoid therapy for photoaging. Common side effects when used as a cream are limited to the skin and include skin redness, peeling, and sun sensitivity. When used by mouth, side effects include shortness of breath, headache, numbness, depression, skin dryness, itchiness, hair loss, vomiting, muscle pains, and vision changes. Other severe side effects include high white blood cell counts and blood clots. Use during pregnancy is contraindicated due to the risk of birth defects. It is in the retinoid family of medications. Tretinoin was patented in 1957, and approved for medical use in 1962. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML, APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a cancer of the white blood cells. In APL, there is an abnormal accumulation of immature granulocytes called promyelocytes. The disease is characterized by a chromosomal translocation involving the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) gene and is distinguished from other forms of AML by its responsiveness to all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA; also known as tretinoin) therapy. Acute promyelocytic leukemia was first characterized in 1957 by French and Norwegian physicians as a hyperacute fatal illness, with a median survival time of less than a week. Today, prognoses have drastically improved; 10-year survival rates are estimated to be approximately 80-90% according to one study. Signs and symptoms The symptoms tend to be similar to AML in general with the following being possible symptoms: * Anemia * Fatigue * Weakness * Chills * Depression * Difficulty breathing (dyspnea) * Low platelets (thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells known as circulating tumor cells acquire the ability to penetrate the walls of lymphatic or blood vessels, after which they are abl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
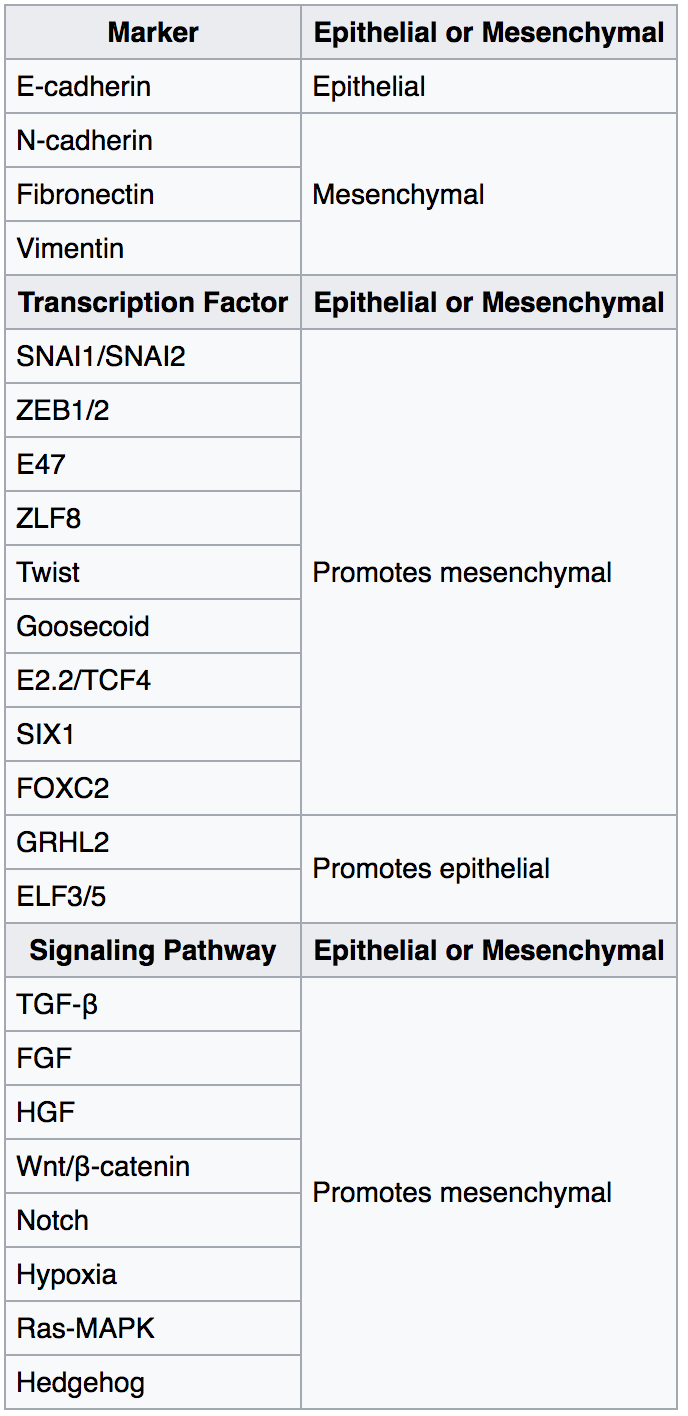
Epithelial–mesenchymal Transition
The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell–cell adhesion, and gain migratory and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells; these are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types. EMT is essential for numerous developmental processes including mesoderm formation and neural tube formation. EMT has also been shown to occur in wound healing, in organ fibrosis and in the initiation of metastasis in cancer progression. Introduction Epithelial–mesenchymal transition was first recognized as a feature of embryogenesis by Betty Hay in the 1980s. EMT, and its reverse process, MET ( mesenchymal-epithelial transition) are critical for development of many tissues and organs in the developing embryo, and numerous embryonic events such as gastrulation, neural crest formation, heart valve formation, secondary palate development, and myogenesis. Epithelial and mesenchyma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchymal–epithelial Transition
A mesenchymal–epithelial transition (MET) is a reversible biological process that involves the transition from motile, multipolar or spindle-shaped mesenchymal cells to planar arrays of polarized cells called epithelia. MET is the reverse process of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and it has been shown to occur in normal development, induced pluripotent stem cell reprogramming, cancer metastasis and wound healing. __TOC__ Introduction Unlike epithelial cells – which are stationary and characterized by an apico-basal polarity with binding by a basal lamina, tight junctions, gap junctions, adherent junctions and expression of cell-cell adhesion markers such as E-cadherin, mesenchymal cells do not make mature cell-cell contacts, can invade through the extracellular matrix, and express markers such as vimentin, fibronectin, N-cadherin, Twist, and Snail. MET plays also a critical role in metabolic switching and epigenetic modifications. In general epithelium-associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholera Toxin
Cholera toxin (also known as choleragen and sometimes abbreviated to CTX, Ctx or CT) is AB5 multimeric protein complex secreted by the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. CTX is responsible for the massive, watery diarrhea characteristic of cholera infection. It is a member of the Heat-labile enterotoxin family. History Cholera toxin was discovered in 1959 by Indian microbiologist Sambhu Nath De. Structure The complete toxin is a hexamer made up of a single copy of the A subunit (part A, enzymatic, ), and five copies of the B subunit (part B, receptor binding, ), denoted as AB5. Subunit B binds while subunit A activates the G protein which activates adenylate cyclase. The three-dimensional structure of the toxin was determined using X-ray crystallography by Zhang ''et al.'' in 1995. The five B subunits—each weighing 11 kDa, form a five-membered ring. The A subunit which is 28 kDa, has two important segments. The A1 portion of the chain (CTA1) is a globular enzyme payload t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forskolin
Forskolin (coleonol) is a labdane diterpene produced by the plant ''Coleus barbatus'' (Blue Spur Flower). Other names include pashanabhedi, Indian coleus, makandi, HL-362, mao hou qiao rui hua. As with other members of the large diterpene class of plant metabolites, forskolin is derived from geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). Forskolin contains some unique functional elements, including the presence of a tetrahydropyran-derived heterocyclic ring. Forskolin is commonly used in laboratory research to increase levels of cyclic AMP by stimulation of adenylate cyclase. Mechanism of action Forskolin is commonly used in biochemistry to raise levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the study and research of cell physiology. Forskolin activates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase and increases intracellular levels of cAMP. cAMP is an important second messenger necessary for the proper biological response of cells to hormones and other extracellular signals. It is required for cell communication in the hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |