|
Dewclaws
A dewclaw is a digit – vestigial in some animals – on the foot of many mammals, birds, and reptiles (including some extinct orders, like certain theropods). It commonly grows higher on the leg than the rest of the foot, such that in digitigrade or unguligrade species it does not make contact with the ground when the animal is standing. The name refers to the dewclaw's alleged tendency to brush dew away from the grass.Danziger, D., & McCrum, M. (2008). ''The Thingummy: A book about those everyday objects you just can't name''. London: Doubleday. On dogs and cats the dewclaws are on the inside of the front legs, similarly to a human's thumb, which shares evolutionary homology. Although many animals have dewclaws, other similar species do not, such as horses, giraffes and the African wild dog. Dogs Dogs almost always have dewclaws on the inside of the front legs and occasionally also on the hind legs. Unlike front dewclaws, rear dewclaws tend to have little bone or mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beauceron
The Beauceron is a herding dog breed originating from the plains of Central France. The Beauceron is also known as Berger de Beauce (sheepdog from Beauce) or Bas Rouge (red-stockings). History A French herding breed known for centuries in western Europe, the Beauceron is noted as one of the breeds used to create the Doberman Pinscher. Although quite different in appearance, the Beauceron and the long-haired sheep dog, the Briard, stem from similar ancestral stock, sharing the trait of double dewclaws on the hind legs. Both were used to herd sheep and cattle. Like the Beauceron, the Briard is found throughout northern France, and despite implications from its name, also did not come exclusively from the Brie region. In 1809, Abbé Rozier wrote an article on these French herding dogs, in which he described the differences in type and used the terms Berger de Brie and Berger de Beauce. In 1893, the veterinarian Paul Megnin differentiated between the long-haired Berger de la Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unguligrade
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized gut bacteria to allow them to digest cellulose. Some modern species, such as pigs, are omnivoro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
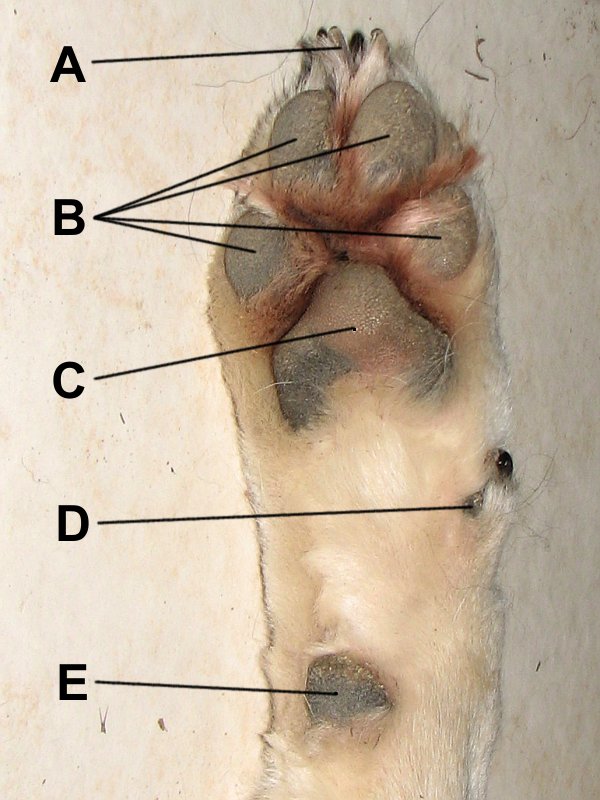
Paw And Pads
A paw is the soft foot-like part of a mammal, generally a quadruped, that has claws. Common characteristics The paw is characterised by thin, pigmented, keratinised, hairless epidermis covering subcutaneous collagenous and adipose tissue, which make up the pads. These pads act as a cushion for the load-bearing limbs of the animal. The paw consists of the large, heart-shaped metacarpal or palmar pad (forelimb) or metatarsal or plantar pad (rear limb), and generally four load-bearing digital pads, although there can be five or six toes in the case of domestic cats and bears (including giant panda). A carpal pad is also found on the forelimb which is used for additional traction when stopping or descending a slope in digitigrade species. Additional dewclaws can also be present. The paw also includes a horn-like, beak shaped claw on each digit. Though usually hairless, certain animals do have fur on the soles of their paws. An example is the red panda, whose furry soles help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Wild Dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called the painted dog or Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine which is a native species to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lycaon'', which is distinguished from '' Canis'' by dentition highly specialised for a hypercarnivorous diet, and by a lack of dewclaws. It is estimated that about 6,600 adults (including 1,400 mature individuals) live in 39 subpopulations that are all threatened by habitat fragmentation, human persecution, and outbreaks of disease. As the largest subpopulation probably comprises fewer than 250 individuals, the African wild dog has been listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List since 1990. The species is a specialised diurnal hunter of antelopes, which it catches by chasing them to exhaustion. Its natural enemies are lions and spotted hyenas: the former will kill the dogs where possible, whilst hyenas are frequent kleptoparasites. Like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felidae
Felidae () is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a felid (). The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the domestic cat ('' Felis catus''). Felidae species exhibit the most diverse fur pattern of all terrestrial carnivores. Cats have retractile claws, slender muscular bodies and strong flexible forelimbs. Their teeth and facial muscles allow for a powerful bite. They are all obligate carnivores, and most are solitary predators ambushing or stalking their prey. Wild cats occur in Africa, Europe, Asia and the Americas. Some wild cat species are adapted to forest habitats, some to arid environments, and a few also to wetlands and mountainous terrain. Their activity patterns range from nocturnal and crepuscular to diurnal, depending on their preferred prey species. Reginald Innes Pocock divided the extant Felidae into three subfamilies: th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Water Dog
The Portuguese Water Dog originated from the Algarve region of Portugal. From there the breed expanded to all around Portugal's coast, where they were taught to herd fish into fishermen's nets, retrieve lost tackle or broken nets, and act as couriers from ship to ship, or ship to shore. Portuguese Water Dogs rode in fishing trawlers as they worked their way from the Atlantic waters of Portugal to the waters off the coast of Iceland Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ... fishing for cod. In Portuguese language, Portuguese, the breed is called (; literally 'dog of water'). In Portugal, the dog is also known as the Algarvian Water Dog (), or Portuguese Fishing Dog (). is the name given to the wavy-haired variety, and is the name for the curly-coated variety. The P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinarian
A veterinarian (vet), also known as a veterinary surgeon or veterinary physician, is a medical professional who practices veterinary medicine. They manage a wide range of health conditions and injuries in non-human animals. Along with this, vets also play a role in animal reproduction, animal health management, conservation, husbandry and breeding and preventive medicine like animal nutrition, vaccination and parasitic control as well as biosecurity and zoonotic disease surveillance and prevention. Description In many countries, the local nomenclature for a veterinarian is a regulated and protected term, meaning that members of the public without the prerequisite qualifications and/or licensure are not able to use the title. This title is selective in order to produce the most knowledgeable veterinarians that pass these qualifications. In many cases, the activities that may be undertaken by a veterinarian (such as treatment of illness or surgery in animals) are restricted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitterant
A bitterant (or bittering agent) is a chemical that is added to a product to make it smell or taste bitter. Bitterants are commonly used as aversive agents to discourage the inhalation or ingestion of toxic substances. Examples of use *The addition of a bitterant to ethanol denatures the product. *Bitterants are used in antifreeze to prevent pet and child poisonings. It is required by law in some places (France, Oregon, etc.). * Gas dusters often use a bitterant to discourage inhalant abuse, although this can cause problems for legitimate users. The bitterant not only leaves a bitter flavor in the air, but also leaves a bitter residue on objects, like screens and keyboards, that may transfer to hands and cause problems (such as when eating). * Game cartridges for the Nintendo Switch are coated with denatonium as a safety feature to deter small children from ingesting them. *Some button cell batteries manufactured by Duracell are coated with a bitterant to discourage accidenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabethan Collar
An Elizabethan collar, E collar or pet cone (sometimes humorously called a treat funnel, pet lamp-shade, pet radar dish, dog-saver, or cone of shame) is a protective medical device worn by an animal, usually a cat or dog. Shaped like a truncated cone, its purpose is to prevent the animal from biting or licking at its body or scratching at its head or neck while wounds or injuries heal. The collars are named from the ruffs worn in the Elizabethan era. A U.S. patent was filed by Frank L. Johnson in 1959. The device is generally attached to the pet's usual collar with strings or tabs passed through holes punched in the sides of the plastic. The neck of the collar should be short enough to let the animal eat and drink. Although most pets adjust to them quite well, others will not eat or drink with the collar in place and the collar is temporarily removed for meals. While purpose-made collars can be purchased from veterinarians or pet stores, they can also be made from plastic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx Bones
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMBR1
Limb region 1 protein homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LMBR1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the LMBR1-like membrane protein family. Another member of this protein family has been shown to be a lipocalin transmembrane receptor. A highly conserved, cis-acting regulatory module for the sonic hedgehog (protein) gene is located within an intron of this gene. Consequently, disruption of this genic region can alter sonic hedgehog expression and affect limb patterning, but if this gene functions directly in limb development is unknown. Mutations and chromosomal deletions and rearrangements in this genic region are associated with acheiropody and preaxial polydactyly Polydactyly or polydactylism (), also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly (fewer fingers or toes). Signs and symptoms In human ..., which likely result from altered sonic hedge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


