|
Devinuwara Sri Vishnu Maha Devalaya In Sri Lanka
Dondra (, ) is a settlement on the extreme southernmost tip of Sri Lanka, in the Indian Ocean near Matara, Southern Province, Sri Lanka. The Dondra Head Lighthouse, ruins of several Hindu shrines of Tenavaram and a Vihara (Buddhist temple) are located in the vicinity. Etymology King Nissankamalla's (1187-1196 A.D.) Dambulla Vihara rock inscription is considered the oldest document that mentions the name Devi-nuwara which means the "City of Gods". The Pali form of the name, Deva-nagara appears for the first time in the Mahavamsa with reference to the reign of King Vijayabahu I (1058-1114 A.D.).The Buddhist Vishnu: Religious Transformation, Politics, and Culture By John C. Holt, pp. 5, 67-87, 97-100, 113, 257, 343, 413 (Columbia University Press) The name Dondra is the an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenavaram Temple
Tenavaram temple ( ta, தென்னாவரம் கோயில்) (historically known as the Tenavaram Kovil, Tevanthurai Kovil or Naga-Risa Nila Kovil) is a historic Hindu temple complex situated in the port town Tenavaram, Tevanthurai (or Dondra Head), Matara) near Galle, Southern Province, Sri Lanka. Its primary deity was a Hindu god ''Tenavarai Nayanar'' (Upulvan) and at its zenith was one of the most celebrated Hindu temple complexes of the island, containing eight major '' kovil'' shrines to a thousand deity statues of stone and bronze and two major shrines to Vishnu and Shiva. Administration and maintenance was conducted by residing Hindu Tamil merchants during Tenavaram's time as a popular pilgrimage destination and famed emporium employing over five hundred devadasis. The complex, bordered by a large quadrangle cloister, was a collection of several historic Hindu Kovil shrines, with its principle shrine designed in the Kerala and Pallava style of Dravidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dravidian Architecture
Dravidian architecture, or the South Indian temple style, is an architectural idiom in Hindu temple architecture that emerged from South India, reaching its final form by the sixteenth century. It is seen in Hindu temples, and the most distinctive difference from north Indian styles is the use of a shorter and more pyramidal tower over the garbhagriha or sanctuary called a vimana, where the north has taller towers, usually bending inwards as they rise, called shikharas. However, for modern visitors to larger temples the dominating feature is the high gopura or gatehouse at the edge of the compound; large temples have several, dwarfing the vimana; these are a much more recent development. There are numerous other distinct features such as the ''dwarapalakas'' – twin guardians at the main entrance and the inner sanctum of the temple and ''goshtams'' – deities carved in niches on the outer side walls of the garbhagriha. Mentioned as one of three styles of temple building in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is the southwestern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain slopes. The term is used to refer to the entire Indian coast from the western coast of Konkan to the tip of India at Kanyakumari. The peak of Anamudi, which is also the point of highest altitude in India outside the Himalayas, and Kuttanad, which is the point of least elevation in India, lie on the Malabar Coast. Kuttanad, also known as ''The Rice Bowl of Kerala'', has the lowest altitude in India, and is also one of the few places in the world where cultivation takes place below sea level. The region parallel to the Malabar Coast gently slopes from the eastern highland of Western Ghats ranges to the western coastal lowland. The moisture-laden winds of the Southwest monsoon, on reaching the southernmost point of the Indian Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marketplace
A marketplace or market place is a location where people regularly gather for the purchase and sale of provisions, livestock, and other goods. In different parts of the world, a marketplace may be described as a '' souk'' (from the Arabic), ''bazaar'' (from the Persian), a fixed '' mercado'' (Spanish), or itinerant ''tianguis'' (Mexico), or ''palengke'' (Philippines). Some markets operate daily and are said to be ''permanent'' markets while others are held once a week or on less frequent specified days such as festival days and are said to be ''periodic markets.'' The form that a market adopts depends on its locality's population, culture, ambient and geographic conditions. The term ''market'' covers many types of trading, as market squares, market halls and food halls, and their different varieties. Thus marketplaces can be both outdoors and indoors, and in the modern world, online marketplaces. Markets have existed for as long as humans have engaged in trade. The earlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dappula I Of Anuradhapura
Dappula I was King of Anuradhapura in the 7th century, whose reign lasted from 661 to 664. He succeeded Kassapa II as King of Anuradhapura and was succeeded by Dathopa Tissa II. See also * List of Sri Lankan monarchs * History of Sri Lanka The history of Sri Lanka is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions, comprising the areas of South Asia, Southeast Asia and Indian Ocean. The early human remains found on the island of Sri La ... References External links Kings & Rulers of Sri LankaCodrington's Short History of Ceylon Monarchs of Anuradhapura D D D {{SriLanka-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upulvan
Upulvan ( si, උපුල්වන් දෙවියෝ, pi, Uppalavanna; Sanskrit: Utpalavarna), also known as Vishnu (''Vishnu deviyo'') is a guardian deity (Pali: Khettapala; Sanskrit: Kshetrapala) of Sri Lanka. Sri Lankan Buddhists believe him also as a protector of the Buddhism in the country. The name Upulvan depicts his body colour which means "blue water lily coloured". The cult of Upulvan started during the medieval period in Sri Lanka. According to the local lore and legend, Upulvan is the god whom the Buddha entrusted with the guardianship of Sri Lanka and Buddha Śāsana of the country. Historical accounts and legends According to the Sri Lankan chronicles Dipavamsa and Mahavamsa, north Indian prince Vijaya and his seven hundred followers were blessed by god Upulvan upon their arrival to Sri Lanka in 543 BC. The second appearance of god Upulvan in literary sources occurs in the 7th and 8th centuries and again after a gap of several centuries his name reappears ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir), Buddhism, Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Islam (whose temples are called mosques), Judaism (whose temples are called synagogues), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baha'i Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baha'i House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are sometimes called Jinja), Confucianism (which are sometimes called the Temple of Confucius), and ancient religions such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. The form and function of temples are thus very variable, though they are often considered by believers to be, in some sense, the "house" of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India. Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages of India.. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). A. K. Ramanujan described it as "the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
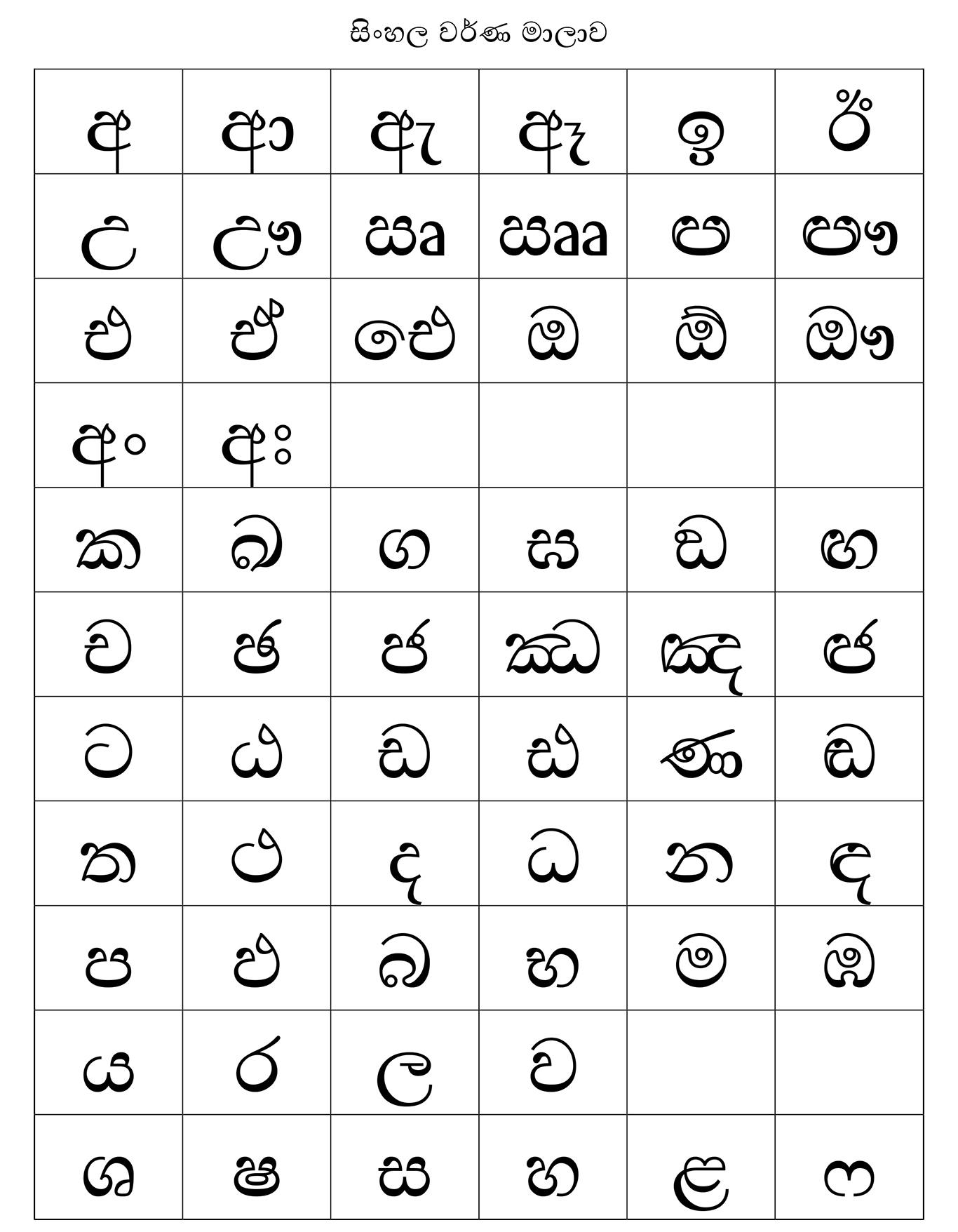
Sinhala Language
Sinhala ( ; , ''siṁhala'', ), sometimes called Sinhalese (), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. Sinhala is also spoken as the first language by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 2 million people as of 2001. It is written using the Sinhala script, which is a Brahmic scripts, Brahmic script closely related to the Grantha script of South India. Sinhala is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka. Along with Pali, it played a major role in the development of Theravada, Theravada Buddhist literature. The early form of the Sinhala language, is attested as early as the 3rd century BCE. The language of these inscriptions with long vowels and aspirated consonants is a Prakrit similar to Magadhi, a regional associate of the Middle Indian Prakrits that has been used during the time of the Buddha. The closest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahāvaṃsa
The ''Mahāvaṃsa'' (, Sinhala: මහාවංශය, Pali: ''මහාවංස (Mahāvaṃsa)'' – written in the 5th century CE) is the meticulously kept historical chronicle of Sri Lanka written in the style of an epic poem written in the Pali language. It relates the history of Sri Lanka from its legendary beginnings up to the reign of Mahasena of Anuradhapura (302 CE) covering the period between the arrival of Prince Vijaya from India in 543 BCE to his reign (277–304 CE) and later updated by different writers. It was composed by a Buddhist monk at the Mahavihara temple in Anuradhapura about the 5th century CE. In 2021, a petition was made to declare the original leaf book a UNESCO heritage. Contents The contents of the ''Mahavamsa'' can be broadly divided into four categories: * The Buddha's Visits to Sri Lanka: This material recounts three legendary visits by the Buddha to the island of Sri Lanka. These stories describe the Buddha subduing or driving away the Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |