|
Density Ratio
The density ratio of a column of seawater is a measure of the relative contributions of temperature and salinity in determining the density gradient. At a density ratio of 1, temperature and salinity are said to be ''compensated'': their density signatures cancel, leaving a density gradient of zero. The formula for the density ratio, R, is: R = αθz/βSz, where * θ is the potential temperature * S is the salinity * z is the vertical coordinate (with subscript denoting differentiation by z) * ρ is the density * α = −ρ−1∂ρ/∂θ is the thermal expansion coefficient * β = ρ−1∂ρ/∂S is the haline contraction coefficient When a water column is "doubly stable"—both temperature and salinity contribute to the stable density gradient—the density ratio is negative (a doubly unstable water column would also have a negative density ratio but does not commonly occur). A statically stable water column with a density ratio between 0 and 1 (cool fresh overlying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts (predominantly sodium () and chloride () ions). The average density at the surface is 1.025 kg/L. Seawater is denser than both fresh water and pure water (density 1.0 kg/L at ) because the dissolved salts increase the mass by a larger proportion than the volume. The freezing point of seawater decreases as salt concentration increases. At typical salinity, it freezes at about . The coldest seawater still in the liquid state ever recorded was found in 2010, in a stream under an Antarctic glacier: the measured temperature was . Seawater pH is typically limited to a range between 7.5 and 8.4. However, there is no universally accepted reference pH-scale for seawater and the difference between measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sodium bicarbonate which dissolve into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
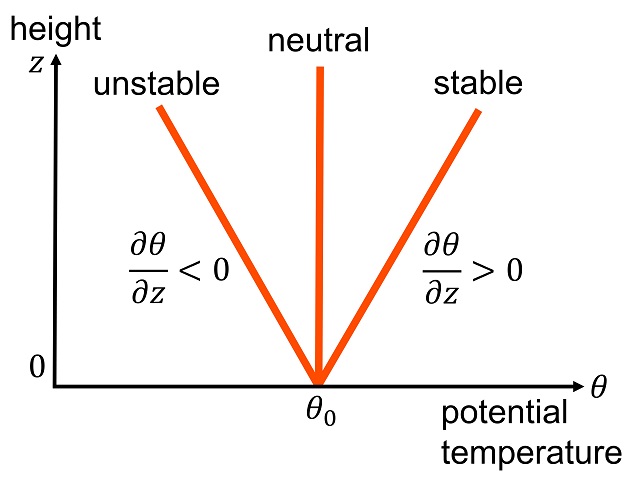
Potential Temperature
The potential temperature of a parcel of fluid at pressure P is the temperature that the parcel would attain if adiabatically brought to a standard reference pressure P_, usually . The potential temperature is denoted \theta and, for a gas well-approximated as ideal, is given by : \theta = T \left(\frac\right)^, where T is the current absolute temperature (in K) of the parcel, R is the gas constant of air, and c_p is the specific heat capacity at a constant pressure. R/c_p = 0.286 for air (meteorology). The reference point for potential temperature in the ocean is usually at the ocean's surface which has a water pressure of 0 dbar. The potential temperature in the ocean doesn't account for the varying heat capacities of seawater, therefore it is not a conservative measure of heat content. Graphical representation of potential temperature will always be less than the actual temperature line in a temperature vs depth graph. Contexts The concept of potential temperature applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiation (mathematics)
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. For example, the derivative of the position of a moving object with respect to time is the object's velocity: this measures how quickly the position of the object changes when time advances. The derivative of a function of a single variable at a chosen input value, when it exists, is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. The tangent line is the best linear approximation of the function near that input value. For this reason, the derivative is often described as the "instantaneous rate of change", the ratio of the instantaneous change in the dependent variable to that of the independent variable. Derivatives can be generalized to functions of several real variables. In this generalization, the derivat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion Coefficient
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. Substances which contract with increasing temperature are unusual, and only occur within limited temperature ranges (see examples below). The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster weakening the intermolecular forces between them, therefore expanding the substance. Overview Predicting expansion If an equation of state is available, it can be used to predict the values of the thermal expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusive Convection
Double diffusive convection is a fluid dynamics phenomenon that describes a form of convection driven by two different density gradients, which have different rates of diffusion. Convection in fluids is driven by density variations within them under the influence of gravity. These density variations may be caused by gradients in the composition of the fluid, or by differences in temperature (through thermal expansion). Thermal and compositional gradients can often diffuse with time, reducing their ability to drive the convection, and requiring that gradients in other regions of the flow exist in order for convection to continue. A common example of double diffusive convection is in oceanography, where heat and salt concentrations exist with different gradients and diffuse at differing rates. An effect that affects both of these variables is the input of cold freshwater from an iceberg. A good discussion of many of these processes is in Stewart Turner's monograph "Buoyancy effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Fingering
Salt fingering is a mixing process, example of double diffusive instability, that occurs when relatively warm, salty water overlies relatively colder, fresher water. It is driven by the fact that heated water diffuses more readily than salty water. A small parcel of warm, salty water sinking downwards into a colder, fresher region will lose its heat before losing its salt, making the parcel of water increasingly denser than the water around it and sinking further. Likewise, a small parcel of colder, fresher water will be displaced upwards and gain heat by diffusion from surrounding water, which will then make it lighter than the surrounding waters, and cause it to rise further. Paradoxically, the fact that salinity diffuses less readily than temperature means that salinity mixes more efficiently than temperature due to the turbulence caused by salt fingers. Salt fingering was first described mathematically by Professor Melvin Stern of Florida State University in 1960 and importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front (oceanography)
In oceanography, a front is a boundary between two distinct water masses. The formation of fronts depends on multiple physical processes and small differences in these lead to a wide range of front types. They can be as narrow as a few hundreds of metres and as wide as several tens of kilometres. While most fronts form and dissipate relatively quickly, some can persist for long periods of time. Definition of fronts Traditionally, ocean fronts have been defined as the boundary between two distinct water masses. However, the current use of satellite data allows a dynamical and higher resolution definition based on the presence of strong currents. Traditional definition The historical definition of fronts using water masses, bodies of water that differ in physical properties such as temperature and salinity, relied on the low-resolution data obtained from research cruises. As it took a long time to combine these data, the obtained front positions gave a time-averaged view show ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity. The atmospheric mixed layer is a zone having nearly constant potential temperature and specific humidity with height. The depth of the atmospheric mixed layer is known as the mixing height. Turbulence typically plays a role in the formation of fluid mixed layers. Oceanic mixed layer Importance of the mixed layer The mixed layer plays an important role in the physical climate. Because the specific heat of ocean water is much larger than that of air, the top 2.5 m of the ocean holds as much heat as the entire atmosphere above it. Thus the heat required to change a mixed layer of 2.5 m by 1 °C would be sufficient to raise the temperature of the atmosphere by 1&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spice (oceanography)
In oceanography, the term spice refers to spatial variations in the temperature and salinity of seawater whose effects on density cancel each other. Such density compensated thermohaline variability is ubiquitous in the upper ocean. Warmer, saltier water is more spicy while cooler, less salty water is more minty. For a density ratio The density ratio of a column of seawater is a measure of the relative contributions of temperature and salinity in determining the density gradient. At a density ratio of 1, temperature and salinity are said to be ''compensated'': their density si ... of 1, all the thermohaline variability is spice, and there are no density fluctuations. References Oceanography {{ocean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)