|
Denis Hensley Fulton Barnett
Air Chief Marshal Sir Denis Hensley Fulton Barnett, (11 February 1906 – 31 December 1992) was a squadron commander and senior officer in the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. In the post war years he held high command, serving as the British air commander during the Suez War and subsequently the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief Transport Command and the Commander of British Forces Cyprus. Barnett was born in Dunedin, New Zealand, his parents being Sir Louis Barnett and Mabel Violet Barnett née Fulton (daughter of Catherine Fulton and James Fulton). He had three elder brothers, including Miles Barnett, and an older sister. He married Pamela Grant (21 December 1918 - 30 August 2010) on 22 April 1939, and they went on to have three daughters and one son. RAF career The New Zealander Barnett was commissioned into the Royal Air Force in 1929. He was appointed Officer Commanding No. 84 Squadron in 1938 and then served in the Second World War taking charge o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". The R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
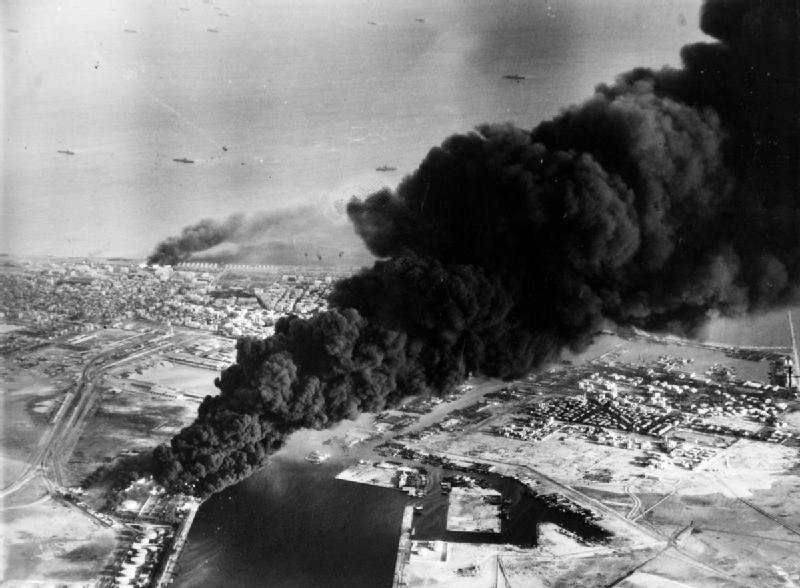
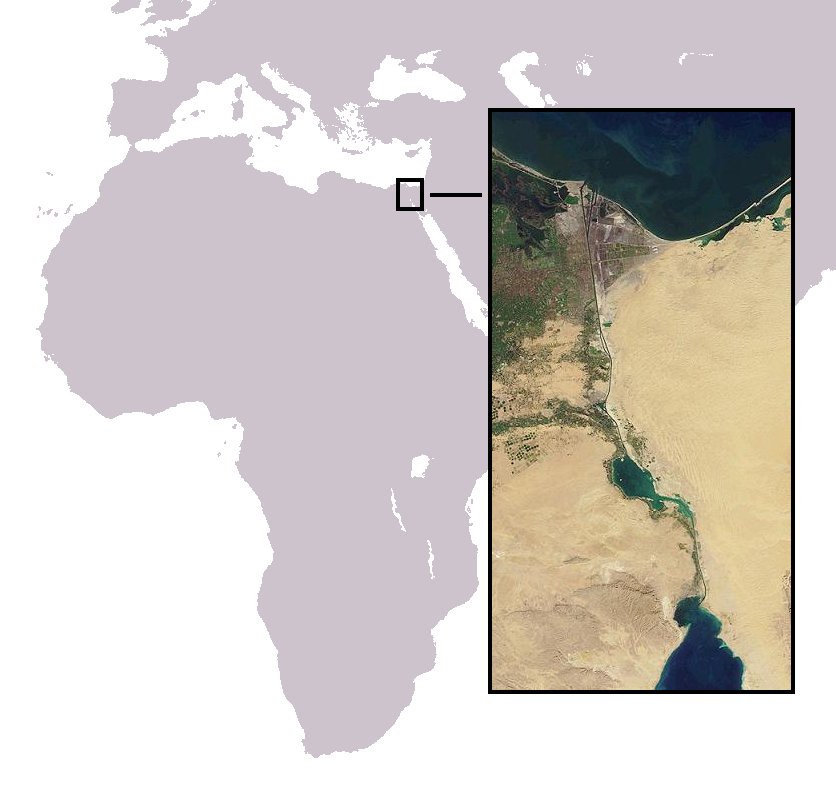
Suez War
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 War; other names include the ''Sinai war'', ''Suez–Sinai war'', ''1956 Arab–Israeli war'', the Second Arab–Israeli war, ''Suez Campaign'', ''Sinai Campaign'', ''Kadesh Operation'' and ''Operation Musketeer'' was an invasion of Egypt in late 1956 by Israel, followed by the United Kingdom and France. The aims were to regain control of the Suez Canal for the Western powers and to remove Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had just swiftly nationalised the foreign-owned Suez Canal Company, which administered the canal. Israel's primary objective was to re-open the blocked Straits of Tiran. After the fighting had started, political pressure from the United States, the Soviet Union and the United Nations led to a withdrawal by the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Superiority
Aerial supremacy (also air superiority) is the degree to which a side in a conflict holds control of air power over opposing forces. There are levels of control of the air in aerial warfare. Control of the air is the aerial equivalent of command of the sea. Air power has increasingly become a powerful element of military campaigns; military planners view having an environment of at least air superiority as a necessity. Air supremacy allows increased bombing efforts, tactical air support for ground forces, paratroop assaults, airdrops and simple cargo plane transfers, which can move ground forces and supplies. Air power is a function of the degree of air superiority and numbers or types of aircraft, but it represents a situation that defies black-and-white characterization. The degree of a force's air control is a zero-sum game with its opponent's; increasing control by one corresponds to decreasing control by the other. Air forces unable to contest for air superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Musketeer (1956)
Operation Musketeer (french: Opération Mousquetaire) was the Anglo-French plan for the invasion of the Suez canal zone to capture the Suez Canal during the Suez Crisis in 1956. The operation had initially been given the codename Operation Hamilcar, but this name was quickly dropped when it was found that the British were painting an air recognition letter H on their vehicles, while the French, who spelled Hamilcar differently, were painting an A. Musketeer was chosen as a replacement because it started with M in both languages. Israel, which invaded the Sinai peninsula, had the additional objectives of opening the Straits of Tiran and halting fedayeen incursions into Israel. The Anglo-French military operation was originally planned for early September, but the necessity of coordination with Israel delayed it until early November. However, on 10 September British and French politicians and Chiefs of the General Staff agreed to adopt General Charles Keightley's alterations to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest and most familiar international organization. The UN is headquarters of the United Nations, headquartered on extraterritoriality, international territory in New York City, and has other main offices in United Nations Office at Geneva, Geneva, United Nations Office at Nairobi, Nairobi, United Nations Office at Vienna, Vienna, and Peace Palace, The Hague (home to the International Court of Justice). The UN was established after World War II with Dumbarton Oaks Conference, the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective. On 25 April 1945, 50 governments met in San Francisco for United Nations Conference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of State for Air. Organisations before the Air Ministry The Air Committee On 13 April 1912, less than two weeks after the creation of the Royal Flying Corps (which initially consisted of both a naval and a military wing), an Air Committee was established to act as an intermediary between the Admiralty and the War Office in matters relating to aviation. The new Air Committee was composed of representatives of the two war ministries, and although it could make recommendations, it lacked executive authority. The recommendations of the Air Committee had to be ratified by the Admiralty Board and the Imperial General Staff and, in consequence, the Committee was not particularly effective. The increasing separation of army and naval aviation from 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the strategic bombing of Germany in World War II. From 1942 onward, the British bombing campaign against Germany became less restrictive and increasingly targeted industrial sites and the civilian manpower base essential for German war production. In total 364,514 operational sorties were flown, 1,030,500 tons of bombs were dropped and 8,325 aircraft lost in action. Bomber Command crews also suffered a high casualty rate: 55,573 were killed out of a total of 125,000 aircrew, a 44.4% death rate. A further 8,403 men were wounded in action, and 9,838 became prisoners of war. Bomber Command stood at the peak of its post-war military power in the 1960s, the V bombers holding the United Kingdom's nuclear deterrent and a supplemental force of Canberra light bombers. In August 2006, a memorial was unveiled at Lincoln Cathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Officer Commanding
The officer commanding (OC), also known as the officer in command or officer in charge (OiC), is the commander of a sub-unit or minor unit (smaller than battalion size), principally used in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth. In other countries, the term commanding officer is applied to commanders of minor as well as major units. Normally an officer commanding is a company, squadron or battery commander (typically a major, although formerly a captain in infantry and cavalry units). However, the commanders of independent units of smaller than company size, detachments and administrative organisations, such as schools or wings, may also be designated officers commanding. The term "officer commanding" is not applied to every officer who is given command of a minor unit. For example, a platoon commander whose platoon is part of a company would not be an officer commanding. The officer commanding with power over that platoon would be the company OC. "Officer commanding" is an appoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Officer (armed Forces)
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service. Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer, or a warrant officer. However, absent contextual qualification, the term typically refers only to a force's ''commissioned officers'', the more senior members who derive their authority from a commission from the head of state. Numbers The proportion of officers varies greatly. Commissioned officers typically make up between an eighth and a fifth of modern armed forces personnel. In 2013, officers were the senior 17% of the British armed forces, and the senior 13.7% of the French armed forces. In 2012, officers made up about 18% of the German armed forces, and about 17.2% of the United States armed forces. Historically, however, armed forces have generally had much lower proportions of officers. During the First World War, fewer than 5% of British soldiers were officers (partly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miles Barnett
Miles Aylmer Fulton Barnett (30 April 1901 – 27 March 1979) was a New Zealand physicist and meteorologist. Born in Dunedin, New Zealand, he studied in that country but obtained his PhD in the United Kingdom at the University of Cambridge. He worked there on the propagation of radio waves and the ionosphere. Later, he returned in New Zealand where he helped to the development of the MetService, Meteorological Office and became its director in 1939, just before the start of World War II. After the war, he participated to the transition between the International Meteorological Organization (IMO) and the new United Nations' World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Biography Miles Barnett is born in Dunedin on 30 April 1901, the son of a surgeon. He attended school in Christchurch before going to the University of Otago, where he gained many scholarships in mathematics. In 1924, he graduated MSc with in mathematics and physics, writing a thesis about the equipment used by Profes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |