|
Demophilus Of Thespiae
Demophilus ( el, Δημόφιλος ''Demophilos''), according to Herodotus, was the commander of a contingent of 700 Thespians at the Battle of Thermopylae (480 BC). His father was Diadromes (). Demophilus and his men fought at the battle and at the end they stood along with the 300 Spartans at the last stand, all were killed. The ancient Greek traveler and geographer Pausanias also wrote about the stay of the Thespians at Thermopylae together with the Spartans. After the Battle of Thermopylae, the Persian army burned down the city of Thespiae. The citizens had fled to the Peloponnese. Later, the Thespians fought against the Persian army at the Battle of Plataea (479 BC). Demophilos is immortalised in many books and movies. In the 1962 movie ''The 300 Spartans'', Demophilus was portrayed by the Greek actor Yorgos (George) Moutsios. In Thermopylae there is a monument, next to the monument of Leonidas, in memory of him and his men. There is also a monument to Demophilus in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thespiae
Thespiae ( ; grc, Θεσπιαί, Thespiaí) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city (''polis'') in Boeotia. It stood on level ground commanded by the low range of hills which run eastward from the foot of Mount Helicon to Thebes, Greece, Thebes, near modern Thespies. History In the ancient Greece#History, history of ancient Greece, Thespiae was one of the cities of the federal league known as Boeotia, the Boeotian League. Several traditions agree that the Boeotians were a people expelled from Ancient Thessaly, Thessaly some time after the mythical Trojan War, and who colonised the Boeotian plain over a series of generations, of which the occupation of Thespiae formed a later stage. Other traditions suggest that they were of Mycenaeans, Mycenean origin. Archaic period In the Archaic period the Thespian nobility was heavily dependent on Thebes. This possibly reflected that land ownership was concentrated in the hands of a small number of nobles, and therefore there was difficul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
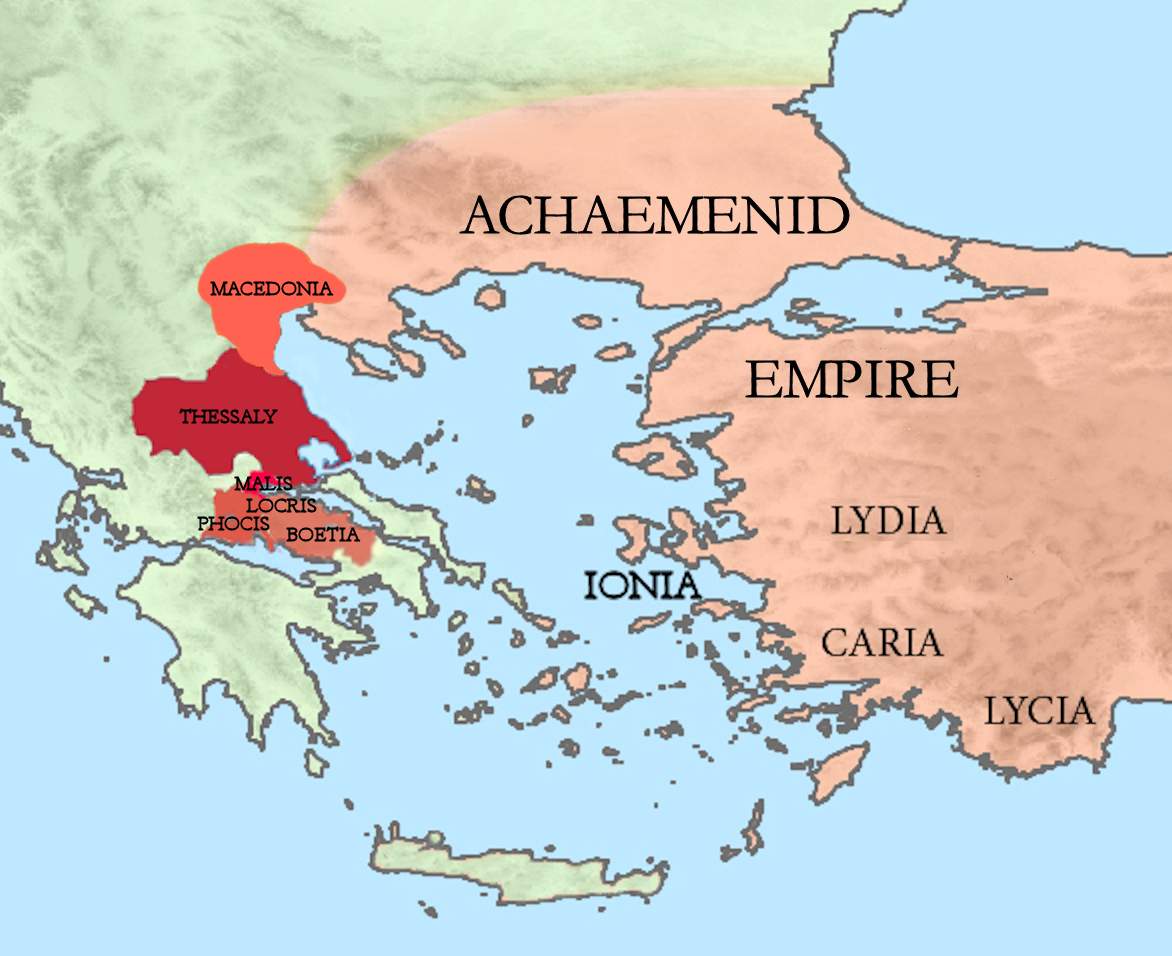
Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur springs."Thermopylae" in: S. Hornblower & A. Spawforth (eds.) ''The Oxford Classical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. (Oxford, 1996). In Greek mythology the Hot Gates is one of the entrances to Hades. Thermopylae is the site of a battle between the Greek forces (including Spartans, Thebans and Thespians) and the invading Persian forces, commemorated by Simonides of Ceos in the epitaph, "Go tell the Spartans, stranger passing by, That here obedient to their laws we lie." Thermopylae is the only land route large enough to bear any significant traffic between Lokris and Thessaly. To go from north to south along the east coast of the Balkans requires use of the pass. In ancient times it was called Malis, named after the Malians ( grc, Μαλιεῖς), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Religion
Religious practices in ancient Greece encompassed a collection of beliefs, rituals, and mythology, in the form of both popular public religion and cult practices. The application of the modern concept of "religion" to ancient cultures has been questioned as anachronistic. The ancient Greeks did not have a word for 'religion' in the modern sense. Likewise, no Greek writer known to us classifies either the gods or the cult practices into separate 'religions'. Instead, for example, Herodotus speaks of the Hellenes as having "common shrines of the gods and sacrifices, and the same kinds of customs." Most ancient Greeks recognized the twelve major Olympian gods and goddesses—Zeus, Hera, Poseidon, Demeter, Athena, Ares, Aphrodite, Apollo, Artemis, Hephaestus, Hermes, and either Hestia or Dionysus—although philosophies such as Stoicism and some forms of Platonism used language that seems to assume a single transcendent deity. The worship of these deities, and several others, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label=Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Greco-Persian Wars. The engagement at Thermopylae occurred simultaneously with the Battle of Artemisium: between July and September 480 BC. The second Persian invasion under Xerxes I was a delayed response to the failure of the first Persian invasion, which had been initiated by Darius I and ended in 490 BC by an Athenian-led Greek victory at the Battle of Marathon. By 480 BC, a decade after the Persian defeat at Marathon, Xerxes had amassed a massive land and naval force, and subsequently set out to conquer all of Greece. In response, the Athenian politician and general Themistocles proposed that the allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the '' Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( /pɔːˈseɪniəs/; grc-gre, Παυσανίας; c. 110 – c. 180) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his ''Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology. Biography Not much is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is mostly certain that he was born c. 110 AD into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From c. 150 until his death in 180, Pausanias travelled through the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing ''Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together a lasting written account of "all things Greek", or ''panta ta hellenika''. Living in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which separates the Gulf of Corinth from the Saronic Gulf. From the late Middle Ages until the 19th century the peninsula was known as the Morea ( grc-x-byzant, Μωρέας), (Morèas) a name still in colloquial use in its demotic Greek, demotic form ( el, Μωριάς, links=no), (Moriàs). The peninsula is divided among three administrative regions of Greece, administrative regions: most belongs to the Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese region, with smaller parts belonging to the West Greece and Attica (region), Attica regions. Geography The Peloponnese is a peninsula located at the southern tip of the mainland, in area, and constitutes the southernmost part of mainland Greece. It is connected to the mainlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states (including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and Megara), and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I (allied with Greece's Boeotians, Thessalians, and Macedonians). The previous year the Persian invasion force, led by the Persian king in person, had scored victories at the battles of Thermopylae and Artemisium and conquered Thessaly, Phocis, Boeotia, Euboea and Attica. However, at the ensuing Battle of Salamis, the allied Greek navy had won an unlikely but decisive victory, preventing the conquest of the Peloponnesus. Xerxes then retreated with much of his army, leaving his general Mardonius to finish off the Greeks the following year. In the summer of 479 BC the Greeks assembled a huge (by ancient standards) army and marched out of the Peloponnesus. The Persians retreated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The 300 Spartans
''The 300 Spartans'' is a 1962 CinemaScope epic film depicting the Battle of Thermopylae. Made with the cooperation of the Greek government, it was shot in the village of Perachora in the Peloponnese. The working title was ''Lion of Sparta''. It stars Richard Egan as the Spartan king Leonidas, Ralph Richardson as Themistocles of Athens and David Farrar as Persian king Xerxes, with Diane Baker as Ellas and Barry Coe as Phylon providing the love interest in the film. Greek warriors, led by 300 Spartans, fight against a Persian army of almost limitless size. Despite the odds, the Spartans will not flee or surrender, even if it means their deaths. When it was released in 1962, critics saw the movie as a commentary on the Cold War, referring to the independent Greek states as "the only stronghold of freedom remaining in the then known world", holding out against the Persian "slave empire". Plot King Xerxes of Persia leads a vast army of soldiers into Europe to defeat the small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonidas I
Leonidas I (; grc-gre, Λεωνίδας; died 19 September 480 BC) was a king of the Greek city-state of Sparta, and the 17th of the Agiad line, a dynasty which claimed descent from the mythological demigod Heracles. Leonidas I was son of King Anaxandridas II. He succeeded his half-brother King Cleomenes I to the throne in c. 489 BC. His co-ruler was King Leotychidas. He was succeeded by his son, King Pleistarchus. Leonidas had a notable participation in the Second Greco-Persian War, where he led the allied Greek forces to a last stand at the Battle of Thermopylae (480 BC) while attempting to defend the pass from the invading Persian army; he died at the battle and entered myth as the leader of the 300 Spartans. While the Greeks lost this battle, they were able to expel the Persian invaders in the following year. Life According to Herodotus, Leonidas' mother was not only his father's wife but also his father's niece and had been barren for so long that the ephors, the five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thespies
Thespies ( el, Θεσπιές; before 1934: ''Erimókastro'') is a village in Boeotia, Greece. A former municipality, which included the village, shared the same name. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Aliartos, of which it is a municipal unit. Population 4,793 (2011). The municipal unit has an area of 108.152 km2, the community 12.725 km2. Thespies is named after the ancient city of Thespiae. Thespies or then Erimokastro used to be an Arvanite Arvanites (; Arvanitika: , or , ; Greek: , ) are a bilingual population group in Greece of Albanian origin. They traditionally speak Arvanitika, an Albanian language variety, along with Greek. Their ancestors were first recorded as settler ... settlement of 1.095 people in 1907. References Populated places in Boeotia {{CentralGreece-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century BC Greek People
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but this campaign was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |