|
Demonax (mythology)
Demonax ( el, Δημώναξ, ''Dēmōnax'', ''gen''.: Δημώνακτος; c. AD 70 – c. 170) was a Greek Cynic philosopher. Born in Cyprus, he moved to Athens, where his wisdom, and his skill in solving disputes, earned him the admiration of the citizens. He taught Lucian, who wrote a ''Life of Demonax'' in praise of his teacher. When he died he received a magnificent public funeral. Life The only source known for the life of Demonax is Lucian, who describes Demonax in glowing terms, in contrast to the disreputable Cynics whom Lucian reviled. He is not mentioned by any other contemporary writer. He is mentioned in the 5th century by Eunapius, but only because he knows of him from Lucian's work. It is possible, therefore, that Demonax is a character invented by Lucian. There are, however, some sayings attributed to Demonax found in anthologies compiled by later writers which are not found in Lucian's work. Demonax was born c. 70 AD, in Cyprus, where he belonged to an influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitive Case
In grammar, the genitive case (abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can also serve purposes indicating other relationships. For example, some verbs may feature arguments in the genitive case; and the genitive case may also have adverbial uses (see adverbial genitive). Genitive construction includes the genitive case, but is a broader category. Placing a modifying noun in the genitive case is one way of indicating that it is related to a head noun, in a genitive construction. However, there are other ways to indicate a genitive construction. For example, many Afroasiatic languages place the head noun (rather than the modifying noun) in the construct state. Possessive grammatical constructions, including the possessive case, may be regarded as a subset of genitive construction. For example, the genitive constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no texts and is known mainly through the posthumous accounts of classical writers, particularly his students Plato and Xenophon. These accounts are written as dialogues, in which Socrates and his interlocutors examine a subject in the style of question and answer; they gave rise to the Socratic dialogue literary genre. Contradictory accounts of Socrates make a reconstruction of his philosophy nearly impossible, a situation known as the Socratic problem. Socrates was a polarizing figure in Athenian society. In 399 BC, he was accused of impiety and corrupting the youth. After a trial that lasted a day, he was sentenced to death. He spent his last day in prison, refusing offers to help him escape. Plato's dialogues are among the most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, movies/videos, moving images, and millions of books. In addition to its archiving function, the Archive is an activist organization, advocating a free and open Internet. , the Internet Archive holds over 35 million books and texts, 8.5 million movies, videos and TV shows, 894 thousand software programs, 14 million audio files, 4.4 million images, 2.4 million TV clips, 241 thousand concerts, and over 734 billion web pages in the Wayback Machine. The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chreia
The ''chreia'' or ''chria'' ( el, χρεία) was, in antiquity and the Byzantine Empire, both a genre of literature and one of the progymnasmata. Definition A chreia was a brief, useful (χρεία means "use") anecdote about a particular character. That is, a chreia was shorter than a narration—often as short as a single sentence—but unlike a maxim, it was attributed to a character. Usually it conformed to one of a few patterns, the most common being "On seeing..." (ιδών or ''cum vidisset''), "On being asked..." (ἐρωτηθείς or ''interrogatus''), and "He said..." (ἔφη or ''dixit''). This is similar to the use of koans by zen buddhists. Examples The following chreia, the most common in ancient sources,E.g. it is found in the ''Progymnasmata'' attributed to Hermogenes, in Libanius, and in Aphthonius, whose ''progymnasmata'' were extensively commented by John of Sardis in the 9th century. It is also quoted in Olympiodorus' commentary on Plato's ''Gorgias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anecdotes
An anecdote is "a story with a point", such as to communicate an abstract idea about a person, place, or thing through the concrete details of a short narrative or to characterize by delineating a specific quirk or trait. Occasionally humorous, anecdotes differ from jokes because their primary purpose is not simply to provoke laughter but to reveal a truth more general than the brief tale itself. Anecdotes may be real or fictional; the anecdotal digression is a common feature of literary works and even oral anecdotes typically involve subtle exaggeration and dramatic shape designed to entertain the listener. An anecdote is always presented as the recounting of a real incident involving actual people and usually in an identifiable place. In the words of Jürgen Hein, they exhibit "a special realism" and "a claimed historical dimension" . Etymology and usage The word ''anecdote'' (in Greek: ἀνέκδοτον "unpublished", literally "not given out") comes from Procopius of Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerambycidae
The longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae), also known as long-horned or longicorns, are a large family of beetles, with over 35,000 species described. Most species are characterized by extremely long antennae, which are often as long as or longer than the beetle's body. In various members of the family, however, the antennae are quite short (e.g., '' Neandra brunnea'') and such species can be difficult to distinguish from related beetle families such as the Chrysomelidae. The scientific name of this beetle family goes back to a figure from Greek mythology: after an argument with nymphs, the shepherd Cerambus was transformed into a large beetle with horns. Description Other than the typical long antennal length, the most consistently distinctive feature of the family is that the antennal sockets are located on low tubercles on the face; other beetles with long antennae lack these tubercles, and cerambycids with short antennae still possess them. They otherwise vary greatly in size, shap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonax (beetle)
''Demonax'' is a genus of the family of the longhorn beetle The longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae), also known as long-horned or longicorns, are a large family of beetles, with over 35,000 species described. Most species are characterized by extremely long antennae, which are often as long as or longer than ...s (Cerambycidae), containing the following species groups and species: Retrieved on 16 September 2018. Species groups *species group ''semiluctuosus'' *species group ''albicinctus'' *species group ''vethi'' *species group ''polyzonus'' *species group ''algebraicus'' *species group ''maximus'' *species group ''mulio'' *species group ''protogenes'' *species group ''lineatus'' *species group ''laticollis'' *species group ''notabilis'' *species group ''mustel ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synodic period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonax (crater)
Demonax is a lunar impact crater near the southern limb of the Moon. This location makes the crater difficult to observe due to foreshortening. The crater is also illuminated at a very low angle, when it is in the sunlit side. Demonax lies just to the north of the crater Scott, one of the south polar formations. To the north-northwest is Boguslawsky. This crater has a worn and eroded rim, with several small craters lying along the edge and the inner walls. The southeast rim in particular has a notable collection of impacts, including the satellite crater Demonax A which intrudes into the interior floor. The crater bottom has been resurfaced, leaving a flat, level floor. However, there is a group of central peaks near the midpoint, and the northern part of the floor is rough and hummocky. The remains of some terrace Terrace may refer to: Landforms and construction * Fluvial terrace, a natural, flat surface that borders and lies above the floodplain of a stream or river * Terra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
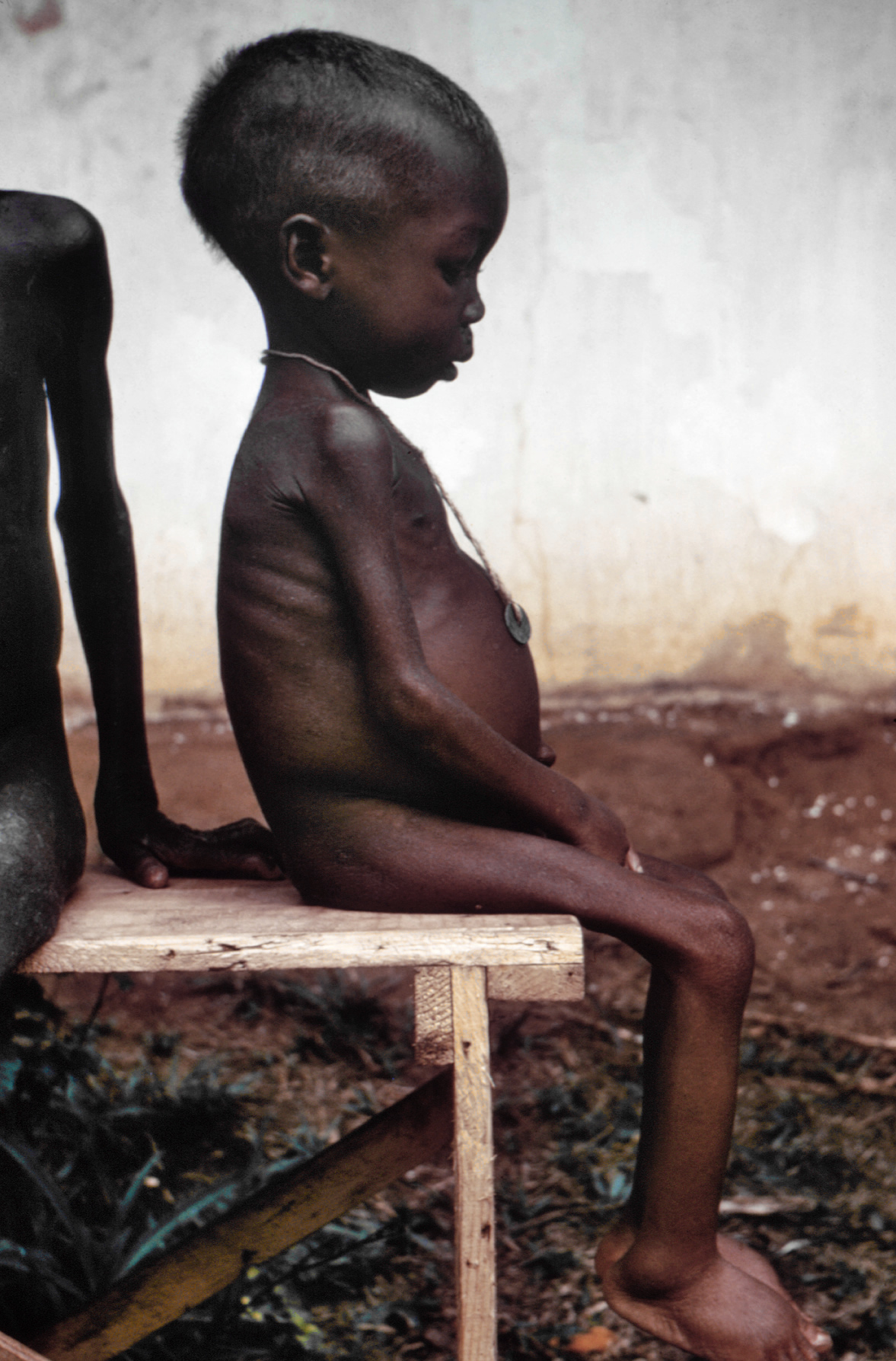
Starving
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death. The term ''inanition'' refers to the symptoms and effects of starvation. Starvation may also be used as a means of torture or execution. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hunger is the single gravest threat to the world's public health.Malnutrition The Starvelings The WHO also states that is by far the biggest contributor to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleusinian Mysteries
The Eleusinian Mysteries ( el, Ἐλευσίνια Μυστήρια, Eleusínia Mystḗria) were initiations held every year for the cult of Demeter and Persephone based at the Panhellenic Sanctuary of Elefsina in ancient Greece. They are the "most famous of the secret religious rites of ancient Greece". Their basis was an old agrarian cult, and there is some evidence that they were derived from the religious practices of the Mycenean period.Dietrich (1975) ''The origins of Greek Religion''. Bristol Phoenix Press pp. 166, 167Walter Burkert. (1985)''Greek Religion''. Harvard University Press. p. 285 The Mysteries represented the myth of the abduction of Persephone from her mother Demeter by the king of the underworld Hades, in a cycle with three phases: the ''descent'' (loss), the ''search'', and the ''ascent'', with the main theme being the ''ascent'' () of Persephone and the reunion with her mother. It was a major festival during the Hellenic era, and later spread to Rome. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)