|
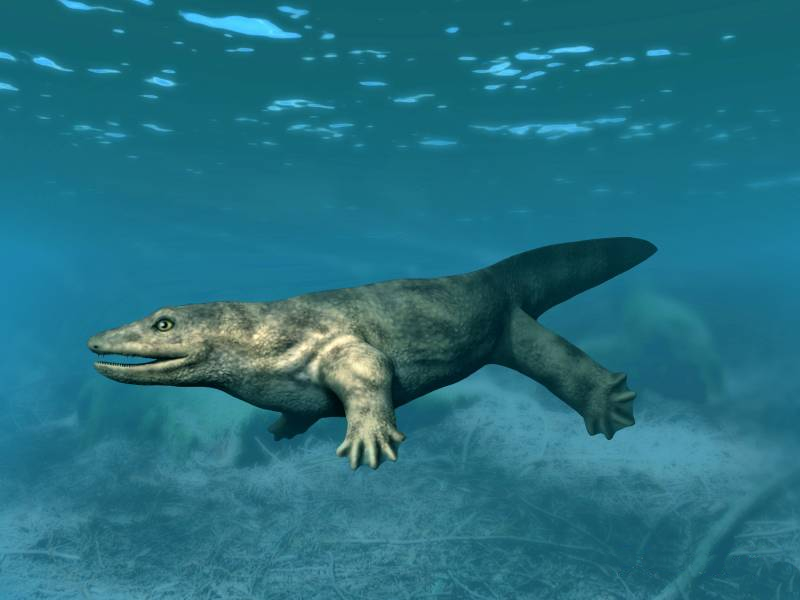
Deltaherpeton
''Deltaherpeton'' is an extinct genus of colosteid from middle Mississippian (late Viséan age) deposits of Delta, Iowa, United States. It was first named by John R. Bolt and R. Eric Lombard in 2010 and the type species is ''Deltaherpeton hiemstrae''. ''Deltaherpeton'' can be differentiated from other colosteids due to possessing several unique bones along the midline of the skull, separating paired skull bones which typically contact each other along the midline. These include an internasal, an oval-shaped bone which lies at the intersection of the paired premaxillae and nasal bones at the top of the snout. Internasals are known from several of the earliest four-limbed vertebrates, such as ''Acanthostega'', '' Ichthyostega'', and baphetids. Further back, what seems to be a pair of lozenge-shape bones lie at the intersection of the nasal bones and frontal bones. These bones may be interfrontonasals, which have been found in some eryopoids and microsaurs. In addition, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whatcheeria
''Whatcheeria'' is an extinct genus of early tetrapod from the Mississippian (Early Carboniferous) of Iowa. Fossils have been found in 340 million year old fissure fill deposits in the town of Delta. The type species, ''Whatcheeria deltae'' was named in 1995. It is classified within the family Whatcheeriidae, along with the closely related ''Pederpes'' and possibly ''Ossinodus.'' ''Whatcheeria'' is named after What Cheer, Iowa, the hometown of Pat McAdams, the geologist who discovered the first skeletons of the animal. The species is named after Delta, Iowa, the location where the fossils were uncovered. Description ''Whatcheeria'' possesses a mixture of both primitive and derived traits. It shares with earlier stem tetrapods a series of lateral lines across the skull, rows of teeth on the palate, and small Meckelian groove, Meckelian foramina across the surface of the lower jaw. It has a cleithrum, a bone in the pectoral girdle that extends from the scapula. The cleithrum o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
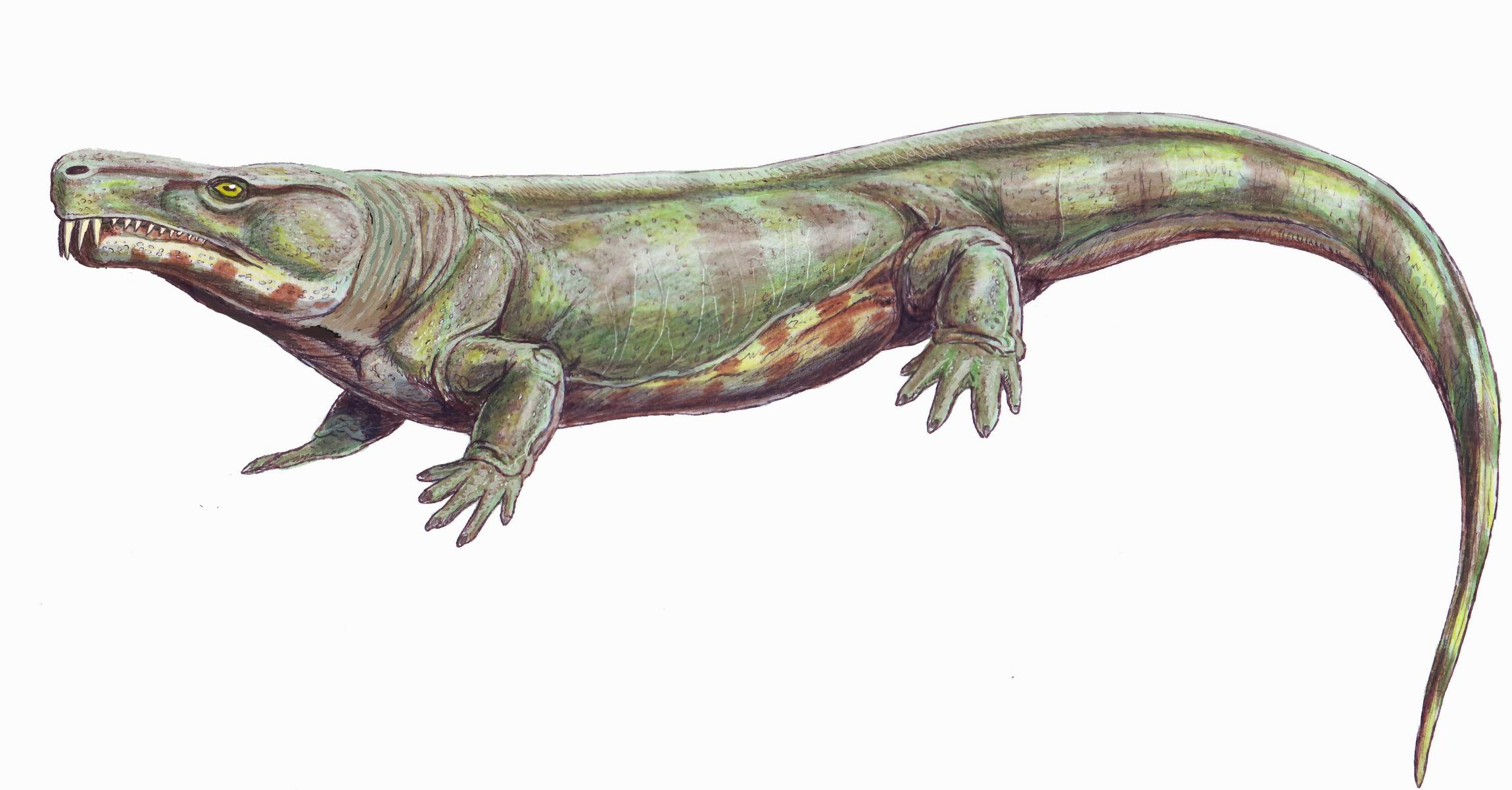
Colosteidae
Colosteidae is a family of stegocephalians (tetrapod-like vertebrates) that lived in the Carboniferous period. They possessed a variety of characteristics from different tetrapod or stem-tetrapod groups, which made them historically difficult to classify. They are now considered to be part of a lineage intermediate between the earliest Devonian terrestrial vertebrates (such as '' Ichthyostega''), and the different groups ancestral to all modern tetrapods, such as temnospondyls (probably ancestral to modern amphibians) and reptiliomorphs (ancestral to amniotes such as mammals, reptiles, and birds). Description Colosteids had elongated bodies, with an estimated 40 vertebrae, not including the tail. The skull is flat and composed of many separate bones, like that of other stegocephalians. Colosteids lacked otic notches at the back of the head, unlike temnospondyls and other "labyrinthodont "Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
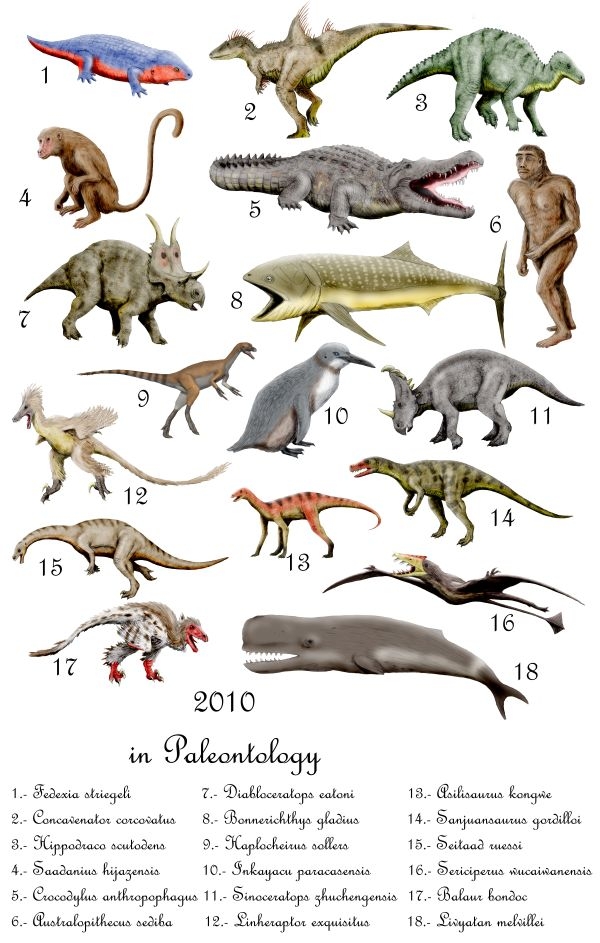
2010 In Paleontology
Plants Angiosperms Molluscs Newly named bivalves Arthropods Fishes Amphibians Newly named amphibians Basal reptiles Newly named basal reptiles Ichthyopterygians Newly named ichthyopterygians Lepidosauromorphs Newly named plesiosaurs Newly named basal lepidosaurs Newly named lizards Newly named snakes Turtles Newly named turtles Archosauromorphs Newly named basal archosauromorphs Archosaurs Synapsids Newly named non-mammalian synapsids Mammals Other animals Footnotes Complete author list As science becomes more collaborative, papers with large numbers of authors are becoming more common. To prevent the deformation of the tables, these footnotes list the contributors to papers that erect new genera and have many authors. References {{Reflist, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lozenge (shape)
A lozenge ( ; symbol: ), often referred to as a diamond, is a form of rhombus. The definition of ''lozenge'' is not strictly fixed, and the word is sometimes used simply as a synonym () for ''rhombus''. Most often, though, lozenge refers to a thin rhombus—a rhombus with two acute and two obtuse angles, especially one with acute angles of 45°. The lozenge shape is often used in parquetry (with acute angles that are 360°/''n'' with ''n'' being an integer higher than 4, because they can be used to form a set of tiles of the same shape and size, reusable to cover the plane in various geometric patterns as the result of a tiling process called tessellation in mathematics) and as decoration on ceramics, silverware and textiles. It also features in heraldry and playing cards. Symbolism The lozenge motif dates from the Neolithic and Paleolithic period in Eastern Europe and represents a sown field and female fertility. The ancient lozenge pattern often shows up in Diamond vault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Animals
Mississippian may refer to: *Mississippian (geology), a subperiod of the Carboniferous period in the geologic timescale, roughly 360 to 325 million years ago *Mississippian culture, a culture of Native American mound-builders from 900 to 1500 AD *Mississippian Railway, a short line railroad *A native of Mississippi Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ... See also * Mississippi (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Tetrapods Of North America
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigournea
''Sigournea'' is a genus of stem tetrapod from the Early Carboniferous. The genus contains only one species, the type species ''Sigournea multidentata'', which was named in 2006 by paleontologists John R. Bolt and R. Eric Lombard on the basis of a single lower jaw from Iowa. The jaw came from a fissure-fill deposit of the St. Louis Limestone that was exposed in a quarry near the town of Sigourney and dates to the Viséan stage, making it approximately 335 million years old. Bolt and Lombard named the genus after Sigourney. The species name ''multidentata'' alludes to the many teeth preserved in the jaw. The jaw, which is housed in the Field Museum and cataloged as FM PR 1820, curves strongly downward but was probably straight to begin with, having been deformed by the process of fossilization after the individual died. Rooted in the dentary bone along the outermost edge of the jaw are 88 small, pointed marginal teeth. An additional row of even smaller teeth runs along the coro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectomorpha
Diadectomorpha is a clade of large tetrapods that lived in Euramerica during the Carboniferous and Early Permian periods and in Asia during Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), They have typically been classified as advanced reptiliomorphs (transitional between "amphibians" ''sensu lato'' and amniotes) positioned close to, but outside of the clade Amniota, though some recent research has recovered them as the sister group to the traditional Synapsida within Amniota, based on inner ear anatomy and cladistic analyses. They include both large (up to 2 meters long) carnivorous and even larger (to 3 meters) herbivorous forms, some semi-aquatic and others fully terrestrial. The diadectomorphs seem to have originated during late Mississippian times, although they only became common after the Carboniferous rainforest collapse and flourished during the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian periods. Anatomy Diadectomorphs possessed both amphibian-like and amniote-like characteristics. Originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabular Bone
The tabular bones are a pair of triangular flat bones along the rear edge of the skull which form pointed structures known as tabular horns in primitive Teleostomi Teleostomi is an obsolete clade of jawed vertebrates that supposedly includes the tetrapods, bony fish, and the wholly extinct acanthodian fish. Key characters of this group include an operculum and a single pair of respiratory openings, featu .... References Fish anatomy Amphibian anatomy {{vertebrate-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supratemporal Bone
The supratemporal bone is a paired cranial bone present in many tetrapods and tetrapodomorph fish. It is part of the temporal region (the portion of the skull roof behind the eyes), usually lying medial (inwards) relative to the squamosal and lateral (outwards) relative to the parietal and/or postparietal. It may also contact the postorbital or intertemporal (which lie forwards), or tabular (which lies backwards), when those bones are present. The supratemporal is a common component of the skull in many extinct amphibians, though it is apparently absent in the lightweight skulls of living lissamphibians (frogs and salamanders). Embryological studies of salamanders suggests that the supratemporal fuses with the squamosal in early development. A separate supratemporal was retained by early synapsids and reptiles, but was strongly reduced in many groups. Squamates (lizards and snakes) still possess a small supratemporal, though archosaurs (crocodilians and birds) and mammals lack i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |