|
Deiotarus
Deiotarus of Galatia (in Galatian and Greek Deiotaros, surnamed Philoromaios ("Friend of the Romans"); 42 BC, 41 BC or 40 BC) was a Chief Tetrarch of the Tolistobogii in western Galatia, Asia Minor, and a King of Galatia ("Gallo-Graecia"). He was considered one of the most adept of Celtic kings, ruling the three tribes of Celtic Galatia from his fortress in Blucium. The name Deiotarus is generally translated as Galatian Celtic "Divine-bull" (*''deiuo-tauros''; cf. Old Irish ''dia'', Welsh ''duw'', Old Welsh ''duiu'', "God" and Old Irish ''tarb'', Welsh ''tarw'' "bull", with Western Celtic metathesis of the cluster ''-uro''- to ''-ruo-''). Biography Deiotarus was a faithful ally of the Romans and became involved in the struggles between the Roman generals that led to the fall of the Republic from 44 BC. He changed sides and supported the triumvirs, keeping his kingdom until his death. He is first heard of at the beginning of the Third Mithridatic War, when he drove the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharnaces II Of Pontus
Pharnaces II of Pontus ( grc-gre, Φαρνάκης; about 97–47 BC) was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithridates VI of Pontus from his first wife, his sister Queen Laodice. He was born and raised in the Kingdom of Pontus and was the namesake of his late double great grandfather Pharnaces I of Pontus. After his father was defeated by the Romans in the Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC) and died in 63 BC, the Romans annexed the western part of Pontus, merged it with the former Kingdom of Bithynia and formed the Roman province of Bithynia and Pontus. The eastern part of Pontus remained under the rule of Pharnaces as a client kingdom until his death. Rebellion against his father Pharnaces II was raised as his father's successor and treated with distinction. However, we know little of his youth from ancient writers and find him first mentioned afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio XXII Deiotariana
Legio XXII Deiotariana ("Deiotarus' Twenty-Second Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army, founded ca. 48 BC and disbanded during the Bar Kokhba revolt of 132–136. Its cognomen comes from Deiotarus, a Celtic king of Galatia. Its emblem is unknown. Legion history Origin of the legion The legion was levied by Deiotarus, king of the Celtic tribe of the Tolistobogii, who lived in Galatia, modern Turkey. Deiotarus became an ally of the Roman Republic's general Pompey in 63 BC, who named him king of all the Celtic tribes of Asia minor, which were collectively known as ''Galatians'' (hence the name Galatia for the region). Deiotarus levied an army and trained it with Roman help; the army, in 48 BC, was composed of 12,000 infantrymen and 2,000 horsemen. Cicero writes that the army was divided into thirty cohortes, which were roughly equivalent to three Roman legions of the time. This army supported the Romans in their wars against king Mithridates VI of Pontus, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
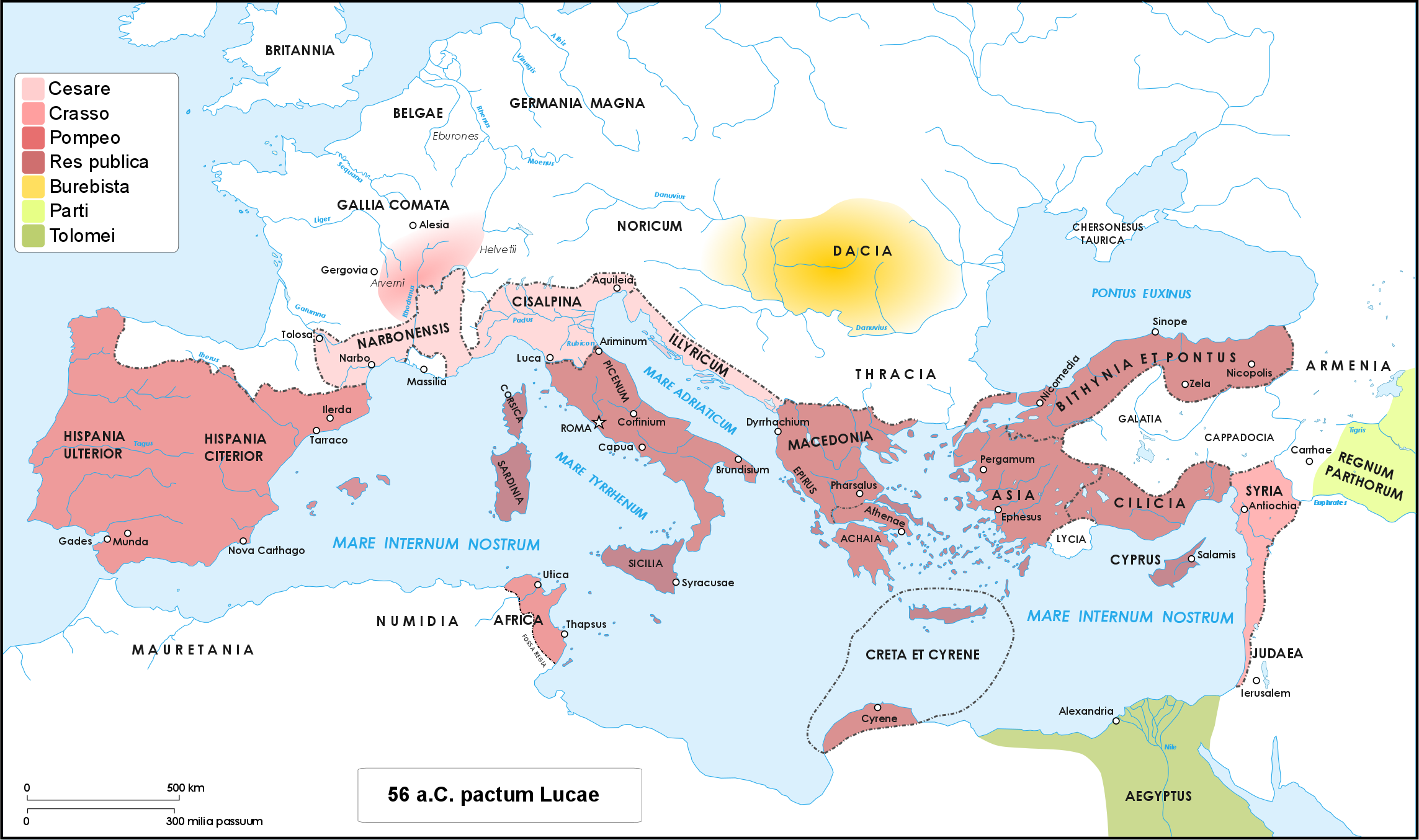
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of Rome from republic to empire. He was (for a time) a student of Roman general Sulla as well as the political ally, and later enemy, of Julius Caesar. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving the dictator Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–82 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first Roman consulship without following the traditional '' cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as Roman consul on three occasions. He celebrated three Roman triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, the Third Servile War, the Third Mithridatic War, and in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autocratic Roman Empire. Antony was a relative and supporter of Julius Caesar, and served as one of his generals during the conquest of Gaul and the Civil War. Antony was appointed administrator of Italy while Caesar eliminated political opponents in Greece, North Africa, and Spain. After Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, Antony joined forces with Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, another of Caesar's generals, and Octavian, Caesar's great-nephew and adopted son, forming a three-man dictatorship known to historians as the Second Triumvirate. The Triumvirs defeated Caesar's killers, the ''Liberatores'', at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BC, and divided the government of the Republic between themselves. Antony was assigned Rome's eastern provinces, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blucium
Blucium or Bloukion ( grc, Βλούκιον) was a fortress of the Tolistoboii in ancient Galatia. It was the residence of Deiotarus, in defence of whom Cicero Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the est ... made an oration, addressed to the Dictator Caesar. In the text of Cicero, the name is read Luceium, and, accordingly, some translators amend Strabo by writing Λούκειον. Its site is located near Karalar, Asiatic Turkey. References Populated places in ancient Galatia Former populated places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey History of Ankara Province {{Ankara-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nicopolis (48 BC)
{{Campaignbox Caesar's Civil War The Battle of Nicopolis was fought in December 48 BC between the army of Pharnaces II of Pontus, the son of Mithdridates VI Eupator, and a Roman army led by Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus. Prelude After defeating Pompey and the optimates at Pharsalus, Julius Caesar pursued his opponents to Asia Minor and then to Egypt. In the Roman province of Asia he left Calvinus in command with an army including the 36th Legion, mainly made up of veterans from Pompey's disbanded legions. With Caesar preoccupied in Egypt and the Roman Republic in the midst of a civil war, Pharnaces saw an opportunity to expand his Kingdom of the Bosphorus into his father's old Pontic empire. In 48 BC he invaded Cappadocia, Bithynia, and Armenia Parva. Calvinus concentrated his forces at Comana. These forces consisted of the veteran 36th legion, one recently levied legion of raw recruits (recruited from locals, not Romans), two legions of Galatians (armed, trained, and organized i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Zela
The Battle of Zela was a battle fought in 47 BC between Julius Caesar and Pharnaces II of the Kingdom of Pontus. The battle took place near Zela (modern Zile), which is now a small hilltop town in the Tokat province of northern Turkey. The battle ended the ambitions of king Pharnaces who wanted to expand his rule over Asia-Minor. Prelude After the defeat of the Ptolemaic forces at the Battle of the Nile, Caesar left Egypt and travelled through Syria, Cilicia and Cappadocia to fight Pharnaces, son of Mithridates VI. Pharnaces had defeated Caesar's Legate Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus, and his small Roman and allied army at the Battle of Nicopolis. He then committed atrocities against the Roman prisoners and against any Roman civilians he found in the region. When Pharnaces received word of Caesar's approach, he sent envoys to seek peace, which Caesar refused outright. Pharnaces had made camp near the town of Zela on the site of a great victory ( the Battle of Zela of 67 BC) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here and became a small transient foreign tribe in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of the East. Geography Galatia was bounded on the north by Bithynia and Paphlagonia, on the east by Pontus and Cappadocia, on the south by Cilicia and Lycaonia, and on the west by Phrygia. Its capital was Ancyra (i.e. Ankara, today the capital of modern Turkey). Celtic Galatia The terms "Galatians" came to be used by the Greeks for the three Celtic peoples of Anatolia: the Tectosages, the Trocmii, and the Tolistobogii. By the 1st century BC, the Celts had become so Hellenized that some Greek writers called them ''Hellenogalatai'' (Ἑλληνογαλάτ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mithridates I Of The Bosporus
Mithridates II of the Bosporus, also known as Mithridates of Pergamon (flourished 1st century BC), was a nobleman from Anatolia. Mithridates was one of the sons born to King Mithridates VI of Pontus from his mistress, the Galatian Princess Adobogiona the Elder. He also had a full-blooded sister called Adobogiona the Younger. The Pontic prince was of Persian, Macedonian and Galatian ancestry. Early life His father sent Mithridates to Pergamon to be educated, where he became a leading citizen of that city. Mithridates was a tetrarch over the Trocmi tribe. Roman Civil War In the winter of 48/47 BC, Julius Caesar was under siege in Alexandria by the armies of Achillas, guardian and general for King Ptolemy XIII Theos Philopator. Mithridates raised an army and came to Caesar's relief. In the aftermath of the Battle of Zela, Caesar made him king of the Bosporan Kingdom. Mithridates's niece Dynamis and her husband Asander were the ruling monarchs at the time, and were defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trocmi
The Trocmii or Trocmi were one of the three ancient tribes of Galatia in central Asia Minor, together with the Tolistobogii and Tectosages,Livy, xxxviii. 16 part of the possible Gallic group who moved from Macedonia into Asia Minor Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ... in the early third century BCE. All three tribes were beaten in 189 BCE by the Roman consul Gnaeus Manlius Vulso at the battles of Mt. Olympus and Mt. Magaba. References * *John King, Celt Kingdoms Ancient Galatia Historical Celtic peoples Gauls {{ethno-group-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |