|
Deep Decarbonization Pathways Initiative
The Deep Decarbonization Pathways initiative (DDPi) is a global consortium formed in 2013 which researches methods to limit the rise of global temperature due to global warming to 2°C or less. The focus of the DDPP is on decarbonization pathways for sustainable energy systems, other sectors of the economy, such as agriculture and land-use, are not directly considered. Methods Analyses of possible scenarios assume no major changes in culture and rely on existing technology. They assume no major changes in the lifestyles of people in developed countries and do not include possible future technologies such as nuclear fusion. Population growth of 1% per year and economic growth of 3% is assumed. Analyses show a need for continued research on energy technologies. The DDPi rejects an incrementalist approach to climate protection. Instead, meeting the climate change mitigation challenge (as set out in the 2015 Paris Agreement) will require backcasting to a suitable attractor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffrey Sachs
Jeffrey David Sachs ( ; born November 5, 1954) is an American economist and public policy analyst who is a professor at Columbia University, where he was formerly director of The Earth Institute. He worked on the topics of sustainable development and economic development. Sachs is director of the Center for Sustainable Development at Columbia University and president of the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network. He is an SDG Advocate for United Nations (UN) Secretary-General António Guterres on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a set of 17 global goals adopted at a UN summit meeting in September 2015. From 2001 to 2018, Sachs was special advisor to the UN Secretary General, and held the same position under the previous UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon and prior to 2016 a similar advisory position related to the earlier Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stranded Asset
Stranded assets are "assets that have suffered from unanticipated or premature write-downs, devaluations or conversion to liabilities". Stranded assets can be caused by a variety of factors and are a phenomenon inherent in the 'creative destruction' of economic growth, transformation and innovation; as such they pose risks to individuals and firms and may have systemic implications. Climate change is expected to cause a significant increase in stranded assets for carbon-intensive industries and investors, with a potential ripple effect throughout the world economy. The term is important to financial risk management in order to avoid economic loss after an asset has been converted to a liability. Accountants have measures to deal with the impairment of assets (e.g. IAS 16) which seek to ensure that an entity's assets are not carried at more than their recoverable amount. In this context, stranded assets are also defined as an asset that has become obsolete or non-performing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Energy Modelling Initiative
The Open Energy Modelling Initiative (openmod) is a grassroots community of energy system modellers from universities and research institutes across Europe and elsewhere. The initiative promotes the use of open-source software and open data in energy system modelling for research and policy advice. The Open Energy Modelling Initiative documents a variety of open-source energy models and addresses practical and conceptual issues regarding their development and application. The initiative runs an email list, an internet forum, and a wiki and hosts occasional academic workshops. A statement of aims is available. Context The application of open-source development to energy modelling dates back to around 2003. This section provides some background for the growing interest in open methods. Growth in open energy modelling Just two active open energy modelling projects were cited in a 2011 paper: OSeMOSYS and TEMOA. Balmorel was also public at that time, having been m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Modeling Forum
The Energy Modeling Forum (EMF) is a structured forum for discussing important issues related to energy and the environment. The EMF was established in 1976 at Stanford University. The EMF works through a series of ad hoc working groups, each focusing on specific corporate or policy decisions. The EMF provides a non-partisan platform that ensures objective consideration of opposing views. Participation is by invitation only. Since the late 1990s, the EMF has made contributions to the economics of climate change, as reflected in the reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and in the field of integrated assessment modeling more generally. John Weyant is the current director of the EMF. Other members of the EMF include Hillard Huntington, James Sweeney, and Frank Wolak. Ethos The EMF was convened in 1976 over concerns that the insights that large-scale energy models could provide policymakers were being overshadowed by the "plethora of detailed quant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Modeling
Energy modeling or energy system modeling is the process of building computer models of energy systems in order to analyze them. Such models often employ scenario analysis to investigate different assumptions about the technical and economic conditions at play. Outputs may include the system feasibility, greenhouse gas emissions, cumulative financial costs, natural resource use, and energy efficiency of the system under investigation. A wide range of techniques are employed, ranging from broadly economic to broadly engineering. Mathematical optimization is often used to determine the least-cost in some sense. Models can be international, regional, national, municipal, or stand-alone in scope. Governments maintain national energy models for energy policy development. Energy models are usually intended to contribute variously to system operations, engineering design, or energy policy development. This page concentrates on policy models. Individual building energy simula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Mitigation Scenarios
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme is the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change Mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, replacing fossil fuels with sustainable energy, clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and carbon sequestration, removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100, significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C. Solar energy and wind power can replace fossil fuels at the lowest cost compared to other renewable energy options.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Domestic Product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance of a country or region. Several national and international economic organizations maintain definitions of GDP, such as the OECD and the International Monetary Fund. GDP is often used as a metric for international comparisons as well as a broad measure of economic progress. It is often considered to be the world's most powerful statistical indicator of national development and progress. The GDP can be divided by the total population to obtain the average GDP per capita. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. Nominal GDP is useful when comparing national economies on the international market according to the exchange rate. To compare economies over time inflation can be adjus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land-use Change
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: forest land, cropland (agricultural land), grassland, wetlands, settlements and other lands. The way humans use land, and how land use is changing, has many impacts on the environment. Effects of land use choices and changes by humans include, for example, urban sprawl, soil erosion, soil degradation, land degradation and desertification. Land use and land management practices have a major impact on natural resources including water, soil, nutrients, plants and animals. ''Land use change'' is "the change from one land-use category to another". Land-use change, together with use of fossil fuels, are the major anthropogenic sources of carbon dioxide, a dominant greenhouse gas. Human activity is the most significant cause of land cover change, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
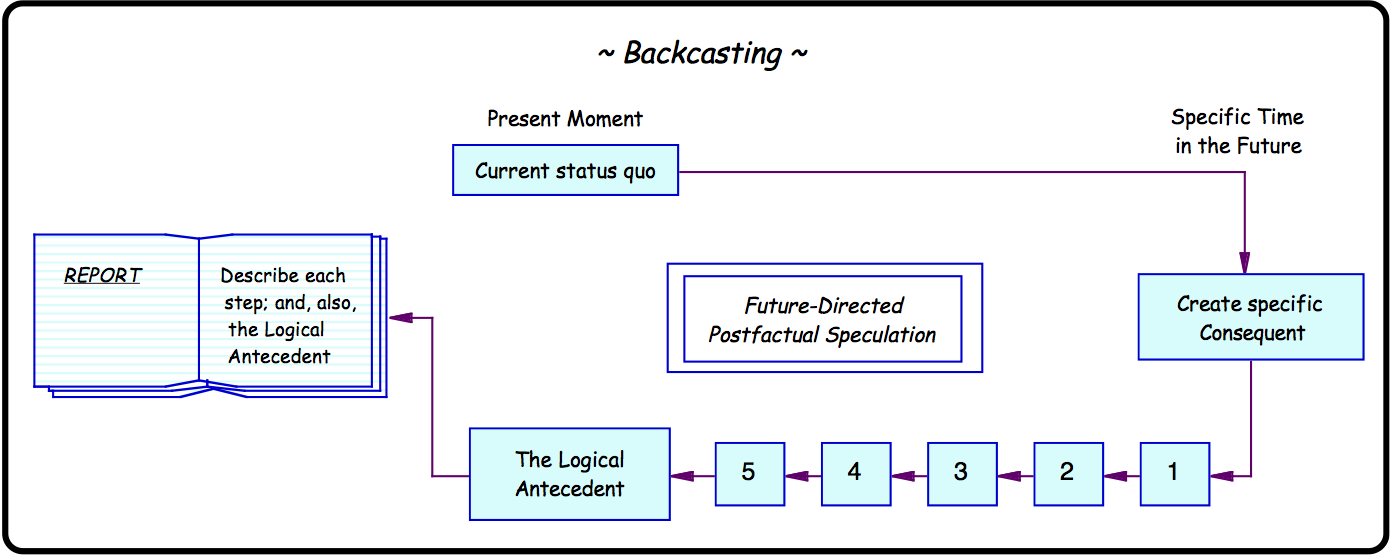
Backcasting
Backcasting is a planning method that starts with defining a desirable future and then works backwards to identify policies and programs that will connect that specified future to the present. The fundamentals of the method were outlined by John B. Robinson from the University of Waterloo in 1990.Robinson, John B. 1990. Futures under glass: a recipe for people who hate to predict ''Futures'', vol. 22, issue 8, pp. 820–842. The fundamental question of backcasting asks: "if we want to attain a certain goal, what actions must be taken to get there?" While forecasting involves predicting the future based on current trend analysis, backcasting approaches the challenge of discussing the future from the opposite direction; it is "a method in which the future desired conditions are envisioned and steps are then defined to attain those conditions, rather than taking steps that are merely a continuation of present methods extrapolated into the future". In statistics and data analysis, bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was negotiated by 196 parties at the 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference near Paris, France. As of February 2023, 195 members of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are parties to the agreement. Of the three UNFCCC member states which have not ratified the agreement, the only major emitter is Iran. The United States, the second largest emitter, withdrew from the agreement in 2020, rejoined in 2021, and announced its withdrawal again in 2025. The Paris Agreement has a long-term temperature goal which is to keep the rise in global surface temperature to well below above pre-industrial levels. The treaty also states that preferably the limit of the increase should only be . These limits are defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |