land-use change on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of

 The
The
Annex II: Glossary
öller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.) In
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. AlegrĂa, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029. The same report groups ''land use'' into the following categories: forest land, cropland (
retrieved 14 September 2010 As of the early 1990s, about 13% of the
Summary for Policymakers
In
Climate Change and Land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems
[P.R. Shukla, J. Skea, E. Calvo Buendia, V. Masson-Delmotte, H.- O. Pörtner, D. C. Roberts, P. Zhai, R. Slade, S. Connors, R. van Diemen, M. Ferrat, E. Haughey, S. Luz, S. Neogi, M. Pathak, J. Petzold, J. Portugal Pereira, P. Vyas, E. Huntley, K. Kissick, M. Belkacemi, J. Malley, (eds.)].https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157988.001

 Broadly,
Broadly,
 The rapid decline of the
The rapid decline of the
land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of Earth not submerged by the ocean or another body of water. It makes up 29.2% of Earth's surface and includes all continents and islands. Earth's land sur ...
. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management
Land management is the process of managing the land use, use and development of land resources. Those resources are used for a variety of purposes for example agriculture, forestry, water resource management, Human settlement, human settlements an ...
actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: forest land, cropland (agricultural land
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other organism, forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous ...
), grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominance (ecology), dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other Herbaceo ...
, wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
, settlements and other lands. The way humans use land, and how land use is changing, has many impacts on the environment. Effects of land use choices and changes by humans include, for example, urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city". Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted ...
, soil erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the Topsoil, upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, Atmosphere of Ea ...
, soil degradation
Soil retrogression and degradation are two regressive evolution processes associated with the loss of equilibrium of a soil health, stable soil. Retrogression is primarily due to soil erosion and corresponds to a phenomenon where succession revert ...
, land degradation
Land degradation is a process where land becomes less healthy and productive due to a combination of Human impact on the environment, human activities or natural conditions. The causes for land degradation are numerous and complex. Human activitie ...
and desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
. Land use and land management
Land management is the process of managing the land use, use and development of land resources. Those resources are used for a variety of purposes for example agriculture, forestry, water resource management, Human settlement, human settlements an ...
practices have a major impact on natural resources
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest, and cultural value. ...
including water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
, soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
, nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s, plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s and animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s.
''Land use change'' is "the change from one land-use category to another". Land-use change, together with use of fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
s, are the major anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human impact on the enviro ...
sources of carbon dioxide, a dominant greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
. Human activity is the most significant cause of land cover change, and humans are also directly impacted by the environmental consequences of these changes. For example, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
(the systematic and permanent conversion of previously forested land for other uses) has historically been a primary facilitator of land use and land cover change.
The study of land change relies on the synthesis of a wide range of data and a diverse range of data collection methods. These include land cover monitoring and assessments, modeling risk and vulnerability, and land change modeling
Land change models (LCMs) describe, project, and explain changes in and the dynamics of land use and Land cover, land-cover. LCMs are a means of understanding ways that humans change the Earth's surface in the past, present, and future.
Land chan ...
.
Definition and categories

 The
The IPCC
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations. Its job is to "provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies". The World M ...
defines the term ''land use'' as the "total of arrangements, activities and inputs applied to a parcel of land".IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary
öller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.) In
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. AlegrĂa, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029. The same report groups ''land use'' into the following categories: forest land, cropland (
agricultural land
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other organism, forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous ...
), grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominance (ecology), dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other Herbaceo ...
, wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
, settlements and ''other lands''.
Another definition is that of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
' Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
: "Land use concerns the products and/or benefits obtained from use of the land as well as the land management
Land management is the process of managing the land use, use and development of land resources. Those resources are used for a variety of purposes for example agriculture, forestry, water resource management, Human settlement, human settlements an ...
actions (activities) carried out by humans to produce those products and benefits."FAO Land and Water Divisionretrieved 14 September 2010 As of the early 1990s, about 13% of the
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
was considered arable land, with 26% in pasture, 32% forests and woodland, and 1.5% urban areas.
As of 2015, the total arable land
Arable land (from the , "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for the purposes of a ...
is 10.7% of the land surface, with 1.3% being permanent cropland.
For example, the US Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and producti ...
has identified six major types of land use in the United States. Acreage statistics for each type of land use in the contiguous 48 states in 2017 were as follows:
''Special use'' areas in the table above include national parks (29 M acres) and state parks (15 M), wildlife areas (64.4 M), highways (21 M), railroads (3M), military bases (25 M), airports (3M) and a few others. ''Miscellaneous'' includes cemeteries, golf courses, marshes, deserts, and other areas of "low economic value". The total land area of the United States is 9.1 M km2 but the total used here refers only to the contiguous 48 states, without Alaska etc.
Land use change
''Land use change'' is "the change from one land-use category to another". Land-use change, together with use offossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
s, are the major anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human impact on the enviro ...
sources of carbon dioxide, a dominant greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
.
Human activity is the most significant cause of land cover change, and humans are also directly impacted by the environmental consequences of these changes. Collective land use and land cover changes have fundamentally altered the functioning of key Earth systems. For instance, human changes to land use and land cover have a profound impact on climate at a local and regional level, which in turn contributes to climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
.
Land use by humans has a long history, first emerging more than 10,000 years ago. Human changes to land surfaces have been documented for centuries as having significant impacts on both earth systems and human well-being. Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
is an example of large-scale land use change. The deforestation of temperate regions since 1750 has had a major effect on land cover. The reshaping of landscapes to serve human needs, such as the deforestation for farmland
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with bot ...
, can have long-term effects on earth systems and exacerbate the causes of climate change.
Although the burning of fossil fuels is the primary driver of present-day climate change, prior to the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
and irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
were the largest sources of human-driven greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate chan ...
. Even today, 35% of anthropogenic carbon dioxide contributions can be attributed to land use or land cover changes. Currently, almost 50% of Earth’s non-ice land surface has been transformed by human activities, with approximately 40% of that land used for agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, surpassing natural systems as the principal source of nitrogen emissions.
Increasing land conversion by humans in future is not inevitable: In a discussion on response options to climate change mitigation
Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include energy conservation, conserving energy and Fossil fuel phase-out, repl ...
and adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
an IPCC special report stated that "a number of response options such as increased food productivity, dietary choices and food losses, and waste reduction, can reduce demand for land conversion, thereby potentially freeing land and creating opportunities for enhanced implementation of other response options".IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers
In
Climate Change and Land: an IPCC special report on climate change, desertification, land degradation, sustainable land management, food security, and greenhouse gas fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems
[P.R. Shukla, J. Skea, E. Calvo Buendia, V. Masson-Delmotte, H.- O. Pörtner, D. C. Roberts, P. Zhai, R. Slade, S. Connors, R. van Diemen, M. Ferrat, E. Haughey, S. Luz, S. Neogi, M. Pathak, J. Petzold, J. Portugal Pereira, P. Vyas, E. Huntley, K. Kissick, M. Belkacemi, J. Malley, (eds.)].
Analytical methods
Land change science relies heavily on the synthesis of a wide range of data and a diverse range of data collection methods, some of which are detailed below.Land cover monitoring and assessments
A primary function of land change science is to document and model long-term patterns of landscape change, which may result from both human activity and natural processes. In the course of monitoring and assessing land cover and land use changes, scientists look at several factors, including where land-cover and land-use are changing, the extent and timescale of changes, and how changes vary through time. To this end, scientists use a variety of tools, includingsatellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell im ...
and other sources of remotely sensed data (e.g., aircraft imagery), field observations, historical accounts, and reconstruction modeling. These tools, particularly satellite imagery, allow land change scientists to accurately monitor land-change rates and create a consistent, long-term record to quantify change variability over time. Through observing patterns in land cover changes, scientists can determine the consequences of these changes, predict the impact of future changes, and use this information to inform strategic land management
Land management is the process of managing the land use, use and development of land resources. Those resources are used for a variety of purposes for example agriculture, forestry, water resource management, Human settlement, human settlements an ...
.
Modeling risk and vulnerability
Modelingrisk
In simple terms, risk is the possibility of something bad happening. Risk involves uncertainty about the effects/implications of an activity with respect to something that humans value (such as health, well-being, wealth, property or the environ ...
and vulnerability
Vulnerability refers to "the quality or state of being exposed to the possibility of being attacked or harmed, either physically or emotionally." The understanding of social and environmental vulnerability, as a methodological approach, involves ...
is also one of land change science's practical applications. Accurate predictions of how human activity will influence land cover change over time, as well as the impact that such changes have on the sustainability of ecological and human systems, can inform the creation of policy designed to address these changes.
Studying risk and vulnerability entails the development of quantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis
...
, qualitative, and geospatial
Geographic data and information is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as data and information having an implicit or explicit association with a location relative to Earth (a geographic location or geographic position). It is also call ...
models, methods, and support tools. The purpose of these tools is to communicate the vulnerability of both human communities and natural ecosystems to hazard events or long-term land change. Modeling risk and vulnerability requires analyses of community sensitivity to hazards, an understanding of geographic distributions of people and infrastructure, and accurate calculation of the probability of specific disturbances occurring.
Land change modeling
A key method for studying risk and vulnerability island change modeling
Land change models (LCMs) describe, project, and explain changes in and the dynamics of land use and Land cover, land-cover. LCMs are a means of understanding ways that humans change the Earth's surface in the past, present, and future.
Land chan ...
(LCM), which can be used to simulate changes and land use and land cover. LCMs can be used to predict how land use and land cover may change under alternate circumstances, which is useful for risk assessment, in that it allows for the prediction of potential impacts and can be used to inform policy decisions, albeit with some uncertainty.
Examples of land use change
Deforestation

Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
is the systematic and permanent conversion of previously forested land for other uses. It has historically been a primary facilitator of land use and land cover change. Forests are a vital part of the global ecosystem and are essential to carbon capture, ecological processes, and biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
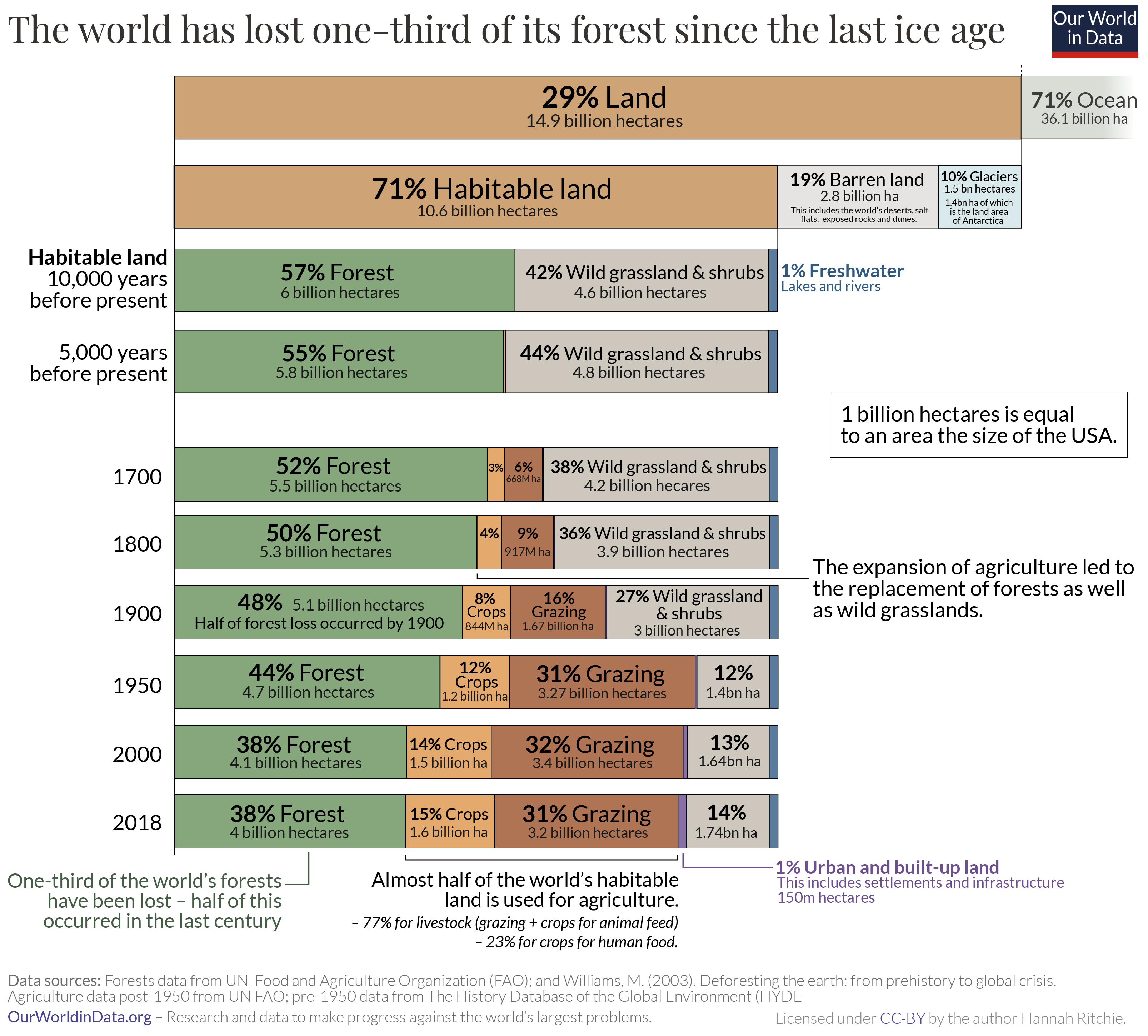
. However, since the invention of agriculture, global forest cover has diminished by 35%.
There is rarely one direct or underlying cause for deforestation. Rather, deforestation is the result of intertwining systemic forces working simultaneously or sequentially to change land cover. Deforestation occurs for many interconnected reasons. For instance, mass deforestation is often viewed as the product of industrial agriculture, yet a considerable portion old-growth forest
An old-growth forest or primary forest is a forest that has developed over a long period of time without disturbance. Due to this, old-growth forests exhibit unique ecological features. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Natio ...
deforestation is the result of small-scale migrant farming. As forest cover is removed, forest resources become exhausted and increasing populations lead to scarcity, which prompts people to move again to previously undisturbed forest, restarting the process of deforestation. There are several reasons behind this continued migration: poverty-driven lack of available farmland and high costs may lead to an increase in farming intensity on existing farmland. This leads to the overexploitation of farmland, and down the line results in desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
, another land cover change, which renders soil unusable and unprofitable, requiring farmers to seek out untouched and unpopulated old-growth forests.
In addition to rural migration and subsistence farming, economic development can also play a substantial role in deforestation. For example, road and railway expansions designed to increase quality of life have resulted in significant deforestation in the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
and Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually ...
. Moreover, the underlying drivers of economic development are often linked to global economic engagement, ranging from increased exports
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an ...
to a foreign debt.
Urbanization
 Broadly,
Broadly, urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
is the increasing number of people who live in urban areas. Urbanization refers to both urban population growth and the physical growth of urban areas. According to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
, the global urban population has increased rapidly since 1950, from 751 million to 4.2 billion in 2018, and current trends predict this number will continue to grow.United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2019). World Urbanization Prospects 2018: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/421). Accompanying this population shift are significant changes in economic flow, culture and lifestyle, and spatial population distribution. Although urbanized areas cover just 3% of the Earth's surface, they nevertheless have a significant impact on land use and land cover change.
Urbanization is important to land use and land cover change for a variety of reasons. In particular, urbanization affects land change elsewhere through the shifting of ''urban-rural linkages,'' or the ecological footprint
The ecological footprint measures human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people and their economies. It tracks human demand on nature through an ecological accounting system. The accounts contrast the biolo ...
of the transfer of goods and services
Goods are items that are usually (but not always) tangible, such as pens or Apple, apples. Services are activities provided by other people, such as teachers or barbers. Taken together, it is the Production (economics), production, distributio ...
between urban and rural areas. Increases in urbanization lead to increases in consumption, which puts increased pressure on surrounding rural lands. The outward spread of urban areas can also take over adjacent land formerly used for crop cultivation.
Urbanization additionally affects land cover through the urban heat island effect. Heat islands occur when, due to high concentrations of structures, such as buildings and roads, that absorb and re-emit solar radiation, and low concentrations of vegetative cover, urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding areas. The high temperatures associated with heat islands can compromise human health, particularly in low-income areas.
Decline of the Aral Sea
 The rapid decline of the
The rapid decline of the Aral Sea
The Aral Sea () was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakhstan to its north and Uzbekistan to its south, which began shrinking in the 1960s and had largely dried up into desert by the 2010s. It was in the Aktobe and Kyzylorda regions of Kazakhst ...
is an example how local-scale land use and land change can have compounded impacts on regional climate systems, particularly when human activities heavily disrupt natural climatic cycles, how land change science can be used to map and study such changes. In 1960, the Aral Sea, located in Central Asia, was the world's fourth largest lake. However, a water diversion project, undertaken by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
to irrigate arid plains in what is now Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
, resulted in the Aral Sea losing 85% of its land cover and 90% of its volume. The loss of the Aral Sea has had a significant effect on human-environment interactions in the region, including the decimation of the sea's fishing industry and the salinization of agricultural lands by the wind-spread of dried sea salt beds.
Additionally, scientists have been able to use technology such as NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) to track changes to the Aral Sea and its surrounding climate over time. This use of modeling and satellite imagery to track human-caused land cover change is characteristic of the scope of land change science.
Regulation
Commonly, politicaljurisdiction
Jurisdiction (from Latin 'law' and 'speech' or 'declaration') is the legal term for the legal authority granted to a legal entity to enact justice. In federations like the United States, the concept of jurisdiction applies at multiple level ...
s will undertake land-use planning
Land use planning or ''Land-use regulation'' is the process of regulating the use of land by a central authority. Usually, this is done to promote more desirable social and environmental outcomes as well as a more efficient use of resources. ...
and regulate the use of land in an attempt to avoid land-use conflicts. Land use plans are implemented through land division and use ordinances and regulations, such as zoning regulations.
The urban growth boundary is one form of land-use regulation. For example, Portland, Oregon
Portland ( ) is the List of cities in Oregon, most populous city in the U.S. state of Oregon, located in the Pacific Northwest region. Situated close to northwest Oregon at the confluence of the Willamette River, Willamette and Columbia River, ...
is required to have an urban growth boundary which contains at least of vacant land. Additionally, Oregon restricts the development of farmland. The regulations are controversial, but an economic analysis concluded that farmland appreciated similarly to the other land.
United States
In colonial America, few regulations were originally put into place regarding the usage of land. As society shifted from rural to urban, public land regulation became important, especially to city governments trying to control industry, commerce, and housing within their boundaries. The first zoning ordinance was passed inNew York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
in 1916, and, by the 1930s, most states had adopted zoning
In urban planning, zoning is a method in which a municipality or other tier of government divides land into land-use "zones", each of which has a set of regulations for new development that differs from other zones. Zones may be defined for ...
laws. In the 1970s, concerns about the environment and historic preservation led to further regulation.
Today, federal, state, and local governments regulate growth and development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
through statutory law
A statute is a law or formal written enactment of a legislature. Statutes typically declare, command or prohibit something. Statutes are distinguished from court law and unwritten law (also known as common law) in that they are the expressed wi ...
. The majority of controls on land, however, stem from the actions of private developers and individuals. Judicial decisions and enforcement of private land-use arrangements can reinforce public regulation, and achieve forms and levels of control that regulatory zoning cannot. There is growing concern that land use regulation is a direct cause of housing segregation in the United States today.
Two major federal laws passed in the 1960s limit the use of land significantly. These are the National Historic Preservation Act of 1966
The National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA, , ) is legislation intended to preserve historic and archaeological sites in the United States of America. The act created the National Register of Historic Places, the list of National Historic Landm ...
(today embodied in 16 U.S.C. 461 et seq.) and the National Environmental Policy Act
The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) is a United States environmental law designed to promote the enhancement of the environment. It created new laws requiring U.S. federal government agencies to evaluate the environmental impacts of ...
of 1969 (42 U.S.C. 4321 et seq.).
See also
* * * * * * *References
{{Portal bar, Agriculture and Agronomy