|
External Debt
A country's gross external debt (or foreign debt) is the liabilities that are owed to nonresidents by residents. The debtors can be governments, corporations or citizens. External debt may be denominated in domestic or foreign currency. It includes amounts owed to private commercial banks, foreign governments, or international financial institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank. External debt measures an economy's obligations to make future payments and, therefore, is an indicator of a country's vulnerability to solvency and liquidity problems. Another useful indicator is the ''net'' external debt position, which equals gross external debt less external assets in the form of debt instruments. A related concept is the net international investment position (net IIP). Provided that debt securities are measured at market value, the net external debt position equals the net IIP excluding equity and investment fund shares, financial derivatives, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Countries By External Debt
This is a list of countries by external debt, it is the total public and private debt owed to nonresidents repayable in internationally accepted currencies, goods or services, where the public debt is the money or credit owed by any level of government, from central to local, and the private debt the money or credit owed by private households or private corporations based on the country under consideration. For informational purposes, several non-sovereign entities are also included in this list. Note that while a country may have a relatively large external debt (either in absolute or per capita terms) it could actually be a "net international creditor" if its external debt is less than the total of external debt of other countries held by it. List See also * Balance of trade * Domestic liability dollarization * List of countries by corporate debt * List of countries by household debt * List of countries by public debt * List of sovereign states by financial assets * Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Debt To Gdp
External may refer to: * External (mathematics), a concept in abstract algebra * Externality In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either co ..., in economics, the cost or benefit that affects a party who did not choose to incur that cost or benefit * Externals, a fictional group of X-Men antagonists See also * * Internal (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odious Debt
In international law, odious debt, also known as illegitimate debt, is a legal theory that says that the national debt incurred by a despotic regime should not be enforceable. Such debts are, thus, considered by this doctrine to be personal debts of the regime that incurred them and not debts of the state. In some respects, the concept is analogous to the invalidity of contracts signed under coercion. Despite antecedents dating back to the 1800s and support from diverse fields such as economics, philosophy, political science, history, and law, odious debt is not part of international law; in fact, " national or international tribunal has ever cited Odious Debt as grounds for invalidating a sovereign obligation."Mitu Gulati, Duke University School of Law; Ugo Panizza, The Graduate Institute Geneva and CEPR. The Hausmann-Gorky Effect. Working Paper No. HEIDWP02-2018. Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies, International Economics Department. Instead, interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
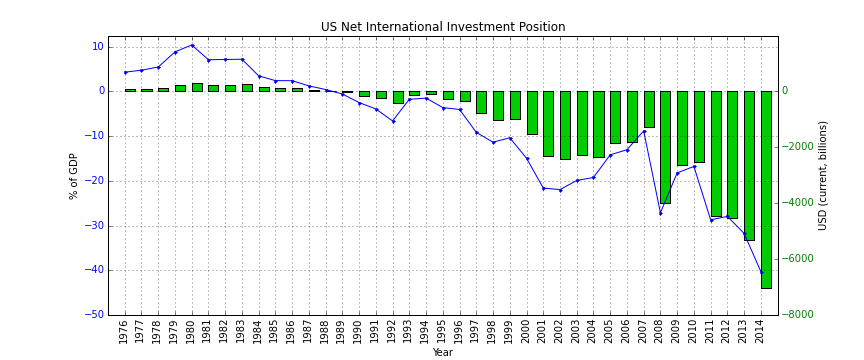
Net International Investment Position
__FORCETOC__ The net international investment position (NIIP) is the difference in the external financial assets and liabilities of a country. External debt of a country includes government debt and private debt. External assets publicly and privately held by a country's legal residents are also taken into account when calculating NIIP.Ministry of Economic and Finance of ArgentinInternational Investment Position Methodologypage.1 Commodities and currencies tend to follow a cyclical pattern of significant valuation changes, which is also reflected in NIIP. The International investment position (IIP) of a country is a financial statement of the value and composition of its external financial assets and liabilities. A positive NIIP value indicates that a nation is a creditor nation, while a negative value indicates that it is a ''debtor nation''. History The US was the world's largest creditor until the 1960s. However, over the last few decades, the US has become the world's larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jubilee Debt Campaign
Debt Justice (formerly Jubilee Debt Campaign, Jubilee Debt Coalition and Drop The Debt) is a UK-based campaigning organisation that exists to end unjust developing countries' debt and the poverty and inequality it perpetuates. The organisation’s activities include campaigning, advocacy, community organising and activism and aims to build collective power with people most affected by debt to demand a fair economy for all. History The Coalition was formed as a successor organisation to the Jubilee 2000 Coalition. Many campaigners felt that it was necessary to continue working together to monitor the G8's promise to deliver $100 billion of debt relief at Cologne in 1999, and make further progress on the cancellation of the poorest countries' debts. The name was chosen in 1995/1996, as preparations were gathering pace for the celebration of the millennium. The concept was that justice and poverty alleviation through the cancellation of debts would be a fitting celebration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurodad
Eurodad (European Network on Debt and Development) is a network of 53 non-governmental organisations and seven statutory allies from 29 European countries. Eurodad and its members make up a network, this network researches and works on issues that are related to debt, development finance and poverty reduction. Recently this network has focussed on issues such as tracking the aid spent by European countries, multilateral debt cancellation, debt sustainability, aid quality, conditionality and harmonisation, illegitimate debt, and export credit debts. Eurodad's main targets are organisations such as the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, however it also targets European governments themselves. Eurodad’s stated aims are to: * push for development policies that support pro-poor and democratically defined sustainable development strategies. * support the empowerment of Southern people to chart their own path ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966, which is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. The bank also maintains 31 field offices around the world to promote social and economic development in Asia. The bank admits the members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP, formerly the Economic Commission for Asia and the Far East or ECAFE) and non-regional developed countries. From 31 members at its establishment, ADB now has 68 members. The ADB was modeled closely on the World Bank, and has a similar weighted voting system where votes are distributed in proportion with members' capital subscriptions. ADB releases an annual report that summarizes its operations, budget and other materials for review by the public. The ADB-Japan Scholarship Program (ADB-JSP) enrolls about 300 students annually in academic institutions loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt-to-GDP Ratio
In economics, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio between a country's government debt (measured in units of currency) and its gross domestic product (GDP) (measured in units of currency per year). While it is a "ratio", it is technically measured in units of year, and can be interpreted as the number of years a country needs to pay off its entire debt, if all its GDP is devoted towards it. A low debt-to-GDP ratio indicates that an economy produces goods and services sufficient to pay back debts without incurring further debt. Geopolitical and economic considerations – including interest rates, war, recessions, and other variables – influence the borrowing practices of a nation and the choice to incur further debt. It should not be confused with a deficit-to-GDP ratio, which, for countries running budget deficits, measures a country's annual net fiscal loss in a given year ( total expenditures minus total revenue, or the net change in debt per annum) as a percentage share of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Present Value
The net present value (NPV) or net present worth (NPW) applies to a series of cash flows occurring at different times. The present value of a cash flow depends on the interval of time between now and the cash flow. It also depends on the discount rate. NPV accounts for the time value of money. It provides a method for evaluating and comparing capital projects or financial products with cash flows spread over time, as in loans, investments, payouts from insurance contracts plus many other applications. Time value of money dictates that time affects the value of cash flows. For example, a lender may offer 99 cents for the promise of receiving $1.00 a month from now, but the promise to receive that same dollar 20 years in the future would be worth much less today to that same person (lender), even if the payback in both cases was equally certain. This decrease in the current value of future cash flows is based on a chosen rate of return (or discount rate). If for example there exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt Rescheduling
Debt rescheduling is the lengthening of the time of debt repayment by restructuring the terms of an existing loan. Types of resecheduling In retail banking, the debt rescheduling can be applied for personal loans given to individuals as education loan, consumer credit, mortgage loan and loans given for making investment in financial assets such as equity shares, debenture, and bond (finance). In North America North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ... and Europe, there are the portals which offers loan rescheduling/restructuring/consolidation via peer-to-peer lending marketplace such as Prosper Marketplace and LendingClub. Approaches; * Reduce payment amounts by extending the payment period and increasing the number of payments. * Pause payments by adding deb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt Relief
Debt relief or debt cancellation is the partial or total forgiveness of debt, or the slowing or stopping of debt growth, owed by individuals, corporations, or nations. From antiquity through the 19th century, it refers to domestic debts, in particular agricultural debts and freeing of debt slaves. In World War I the United States Treasury made large loans to the allies that were postponed, reduced and finally paid off in 1953. In the late 20th century, it came to refer primarily to Third World debt, which started exploding with the Latin American debt crisis (Mexico 1983, etc.). In the early 21st century, it is of increased applicability to individuals in developed countries, due to credit bubbles and housing bubbles. International debt relief First World War reparations War debt payments by World War I Allies to the U.S. had been suspended in 1931—only Finland paid in full—and American public opinion demanded repayments resume as a condition of U.S. postwar aid. Germany ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |